Preparation method of RGD polypeptide grafted poly(maleic anhydride-hexamethylendiamine-DL-lactic acid)/modified hydroxyapatite porous composite material
A technology of porous composite materials and hydroxyapatite, which is applied in the fields of medical science and prostheses, can solve the problems of lack of cell identification signal, tissue aseptic necrosis, poor cell affinity, etc., and achieve simple manufacturing process and prevent sterile Bacterial necrosis, the effect of controlling the accumulation of acid
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0025] 1) First, dissolve 50ml of 5g polylactic acid (PDLLA), 0.5g maleic anhydride (MA), and 0.02g dibenzoyl peroxide (BPO) in dichloromethane, stir to make it evenly mixed, and vacuum-dry until constant Heavy, under the protection of nitrogen, high temperature melting reaction at 90 ℃ for 10h, THF-ethanol co-precipitation method to prepare maleic anhydride grafted polylactic acid MPLA;
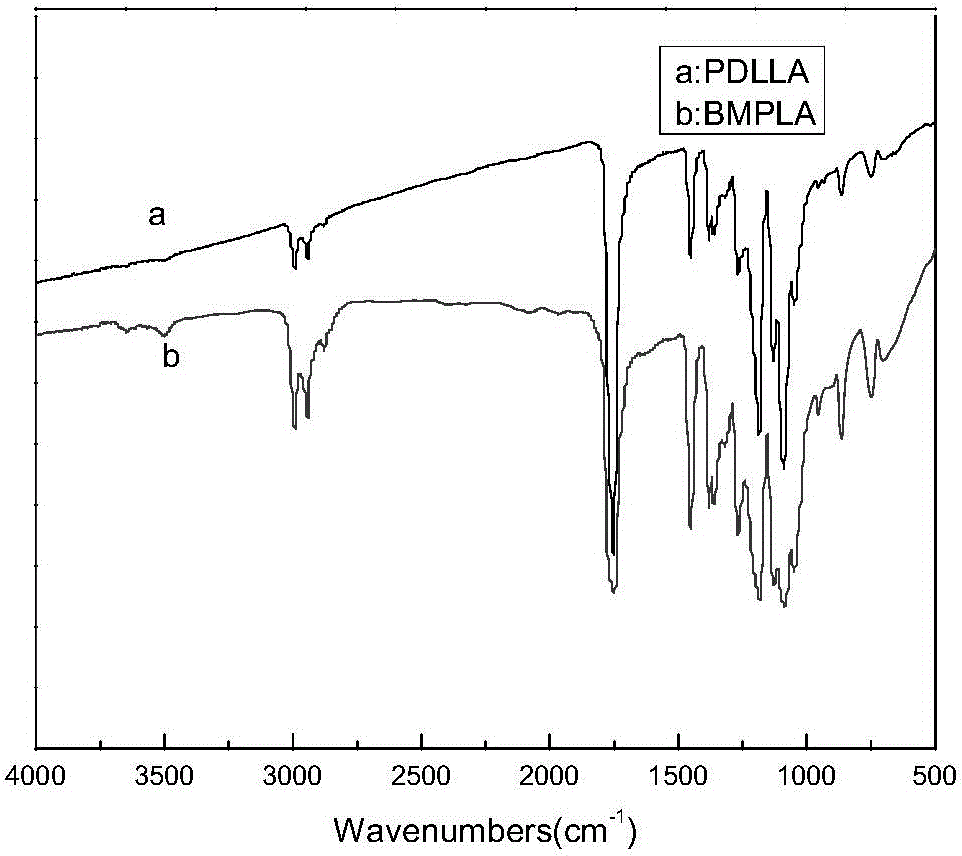
[0026] 2) Dissolve 1g of the product MPLA and 0.0192g of hexamethylenediamine in 50ml and 5ml of tetrahydrofuran (THF) respectively, stir at a low temperature of 8°C, add the product MPLA dropwise in the tetrahydrofuran (THF) solution of hexamethylenediamine and react for 10min Rising to 28°C for 30 minutes, the mixed solution was dropped into excess distilled water to collect the surface film, and the product BMPLA modified by hexamethylenediamine was obtained. The infrared spectrum showed that it was at 1647cm -1 The characteristic absorption peak of the amide bond and the 1558cm -1 The -...
Embodiment 2
[0030] 1) First, dissolve 50ml of 5g polylactic acid (PDLLA), 0.5g maleic anhydride (MA), and 0.02g dibenzoyl peroxide (BPO) in dichloromethane, stir to make it evenly mixed, and vacuum-dry until constant Heavy, under the protection of nitrogen, high temperature melting reaction at 90 ℃ for 10h, THF-ethanol co-precipitation method to prepare maleic anhydride grafted polylactic acid MPLA;
[0031] 2) Dissolve 1g of the product MPLA and 0.0128g of hexamethylenediamine in 50ml and 5ml of tetrahydrofuran (THF) respectively, stir at a low temperature of 20°C, add the product MPLA dropwise in the tetrahydrofuran (THF) solution of hexamethylenediamine and react for 10min Rising to 28°C for 30 minutes, the mixed solution was dropped into excess distilled water to collect the surface film, and the hexamethylenediamine-modified product BMPLA was obtained;
[0032]3) Dissolve 1 g of product BMPLA in 50 ml of THF, adjust the pH, add 0.15 g of 1-ethyl-(3-dimethylaminopropyl) carbodiimide h...
Embodiment 3
[0035] 1) First, dissolve 50ml of 5g polylactic acid (PDLLA), 0.5g maleic anhydride (MA), and 0.02g dibenzoyl peroxide (BPO) in dichloromethane, stir to make it evenly mixed, and vacuum-dry until constant Heavy, under the protection of nitrogen, high temperature melting reaction at 90 ℃ for 10h, THF-ethanol co-precipitation method to prepare maleic anhydride grafted polylactic acid MPLA;
[0036] 2) Dissolve 1g of the product MPLA and 0.0159g of hexamethylenediamine in 50ml and 5ml of tetrahydrofuran (THF) respectively, stir at a low temperature of 8°C, add the product MPLA dropwise in the tetrahydrofuran (THF) solution of hexamethylenediamine and react for 30min Rising to 28°C for 1 hour, the mixed solution was dropped into excess distilled water to collect the surface film, and the hexamethylenediamine-modified product BMPLA was obtained;
[0037] 3) Dissolve 1g of the product BMPLA in 50ml of THF, adjust the pH, add 0.15g of 1-ethyl-(3-dimethylaminopropyl)carbodiimide hydro...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| pore size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com