A rapid method for the identification of auxin-producing endophytic bacteria
A technology of plant endogenous bacteria and endogenous bacteria, which is applied in the field of microbiology, can solve the problems of cumbersome process, time-consuming, slow growth of bacteria, etc., and achieve the effect of simplifying the identification process, reducing the cost of experiments, and effectively identifying
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
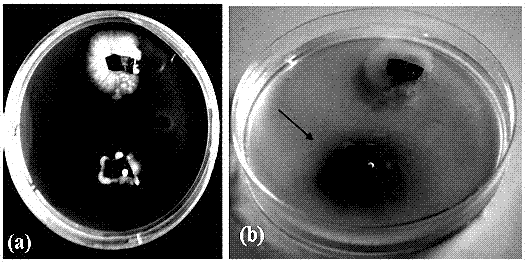
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0023] (1) Preparation of culture medium and chromogenic solution
[0024] Formulate modified R with 0.05% tryptophan 2 A separation and identification medium, the specific formula is as follows: Weigh 0.5 g yeast extract, 0.5 g tryptone, 0.5 g casein acid hydrolyzate, 0.5 g glucose, 0.5 g soluble starch, 0.3 g potassium dihydrogen phosphate, 0.024 g Magnesium sulfate water, 0.3 g sodium pyruvate, 15 g agar powder, 0.5 g tryptophan, dilute to 1 L with double distilled water, and adjust the pH to 7.2 to prepare the improved R 2 A Separation and identification medium, after autoclaving at 115 ℃ for 15 minutes, aliquoted and poured into 9 cm sterile petri dishes, cooled for later use.
[0025] Prepare auxin chromogenic solution: 2 mL of 0.5 M ferric chloride solution and 98 mL of 25% perchloric acid by volume and mix well.
[0026] (2) Pretreatment of plant tissue
[0027] Select well-grown plant tissues and rinse them with distilled water, then place them in an aseptic operat...
Embodiment 2
[0032] (1) Preparation of culture medium and chromogenic solution
[0033] Formulate modified R with 0.1% tryptophan 2A separation and identification medium, the specific formula is as follows: Weigh 0.5 g yeast extract, 0.5 g tryptone, 0.5 g casein acid hydrolyzate, 0.5 g glucose, 0.5 g soluble starch, 0.3 g potassium dihydrogen phosphate, 0.024 g Magnesium sulfate water, 0.3 g sodium pyruvate, 15 g agar powder, 1 g tryptophan, dilute to 1 L with double distilled water, and adjust the pH to 7.2 to prepare the improved R 2 A Separation and identification medium, after autoclaving at 115 ℃ for 15 minutes, aliquoted and poured into 9 cm sterile petri dishes, cooled for later use.
[0034] Prepare auxin chromogenic solution: 2 mL of 0.5 M ferric chloride solution and 98 mL of 30% perchloric acid by volume and mix thoroughly.
[0035] (2) Pretreatment of plant tissue
[0036] Select well-grown plant tissues and rinse them with distilled water, then place them in an aseptic oper...
Embodiment 3
[0041] (1) Preparation of culture medium and chromogenic solution
[0042] Formulate modified R with 0.2% tryptophan 2 A separation and identification medium, the specific formula is as follows: Weigh 0.5 g yeast extract, 0.5 g tryptone, 0.5 g casein acid hydrolyzate, 0.5 g glucose, 0.5 g soluble starch, 0.3 g potassium dihydrogen phosphate, 0.024 g Magnesium sulfate water, 0.3 g sodium pyruvate, 15 g agar powder, 2 g tryptophan, dilute to 1 L with double-distilled water, and adjust the pH to 7.2 to prepare the improved R2A separation and identification medium, after 115 ℃ After autoclaving for 15 min, aliquots were poured into 9 cm sterile Petri dishes, and cooled for later use.
[0043] Prepare auxin chromogenic solution: 2 mL of 0.5 M ferric chloride solution and 98 mL of 35% perchloric acid by volume and mix thoroughly.
[0044] (2) Pretreatment of plant tissue
[0045] Select well-grown plant tissues and rinse them with distilled water, then place them in an aseptic op...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com