Biological information processing method, biological information processing apparatus, computer system, and wearable apparatus
An information processing method and biological information technology, applied in medical science, sensors, diagnostic recording/measurement, etc., can solve problems such as reduced measurement accuracy and changes in measured values
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 approach
[0047] The first embodiment is an embodiment in which a so-called "blood sugar level" is measured as biological information of a subject, and the measurement is performed by the "blood vessel method" as a first measurement method. The "blood vessel method" is to obtain a blood sugar level by measuring the glucose concentration in blood, which is extracellular fluid, by using blood vessels as measurement target sites.
[0048] (the whole frame)
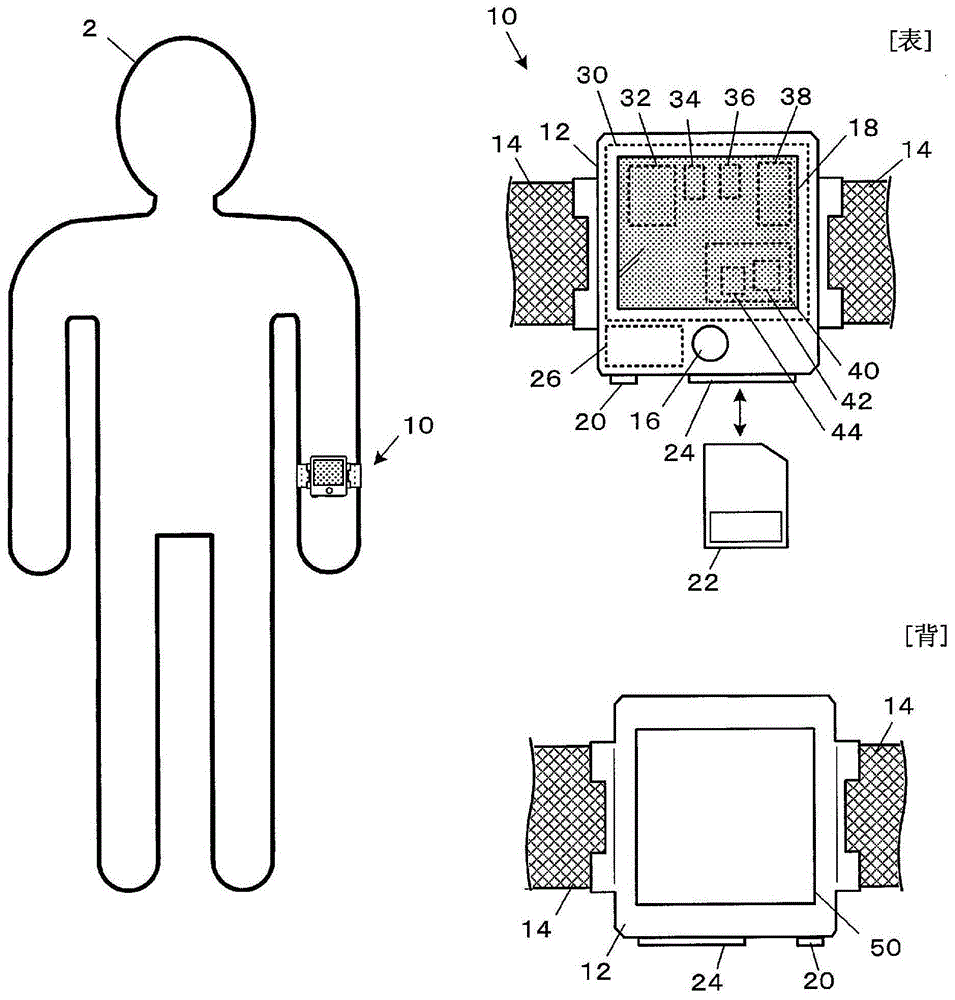
[0049] figure 1It is an external view showing an example of the overall configuration of the noninvasive living body information processing device 10 according to the first embodiment. This biological information processing device 10 functions as a measuring instrument for measuring the components of extracellular fluid such as blood and interstitial fluid of the subject 2, and functions as a data recorder for storing measurement data. is a computer. Such as figure 1 As shown, the biological information processing device 10 is conf...
no. 2 approach
[0120] The second embodiment can basically be implemented in the same manner as the first embodiment, and differs from the first embodiment in that the blood glucose level is repeatedly measured at predetermined measurement timings such as every minute during a predetermined period (for example, one day). This is an embodiment in which the living body information processing device 10 is assumed to be used while being attached to the subject 2 for a long period of time.
[0121] Figure 13 It is a flowchart showing the processing flow (second measurement blow) of the processing unit 150 in the second embodiment. In the second embodiment, Figure 9 The living body information processing device 10 of the first embodiment shown can be realized by storing a second measurement processing program for realizing the second measurement processing in the storage unit 170 instead of the first measurement processing program 171 . Also, in the second embodiment, Figure 14 The display of...
no. 3 approach
[0130] In the third embodiment, the measurement by the "vascular method" described in the first embodiment is switched to the measurement by the "non-vascular method" which is the second measurement method. The "non-vascular method" is to obtain a blood sugar level by measuring the concentration of glucose in interstitial fluid, which is extracellular fluid, using a non-vascular part as a measurement target site. In addition, the same code|symbol is used for the same part as 1st Embodiment or 2nd Embodiment.
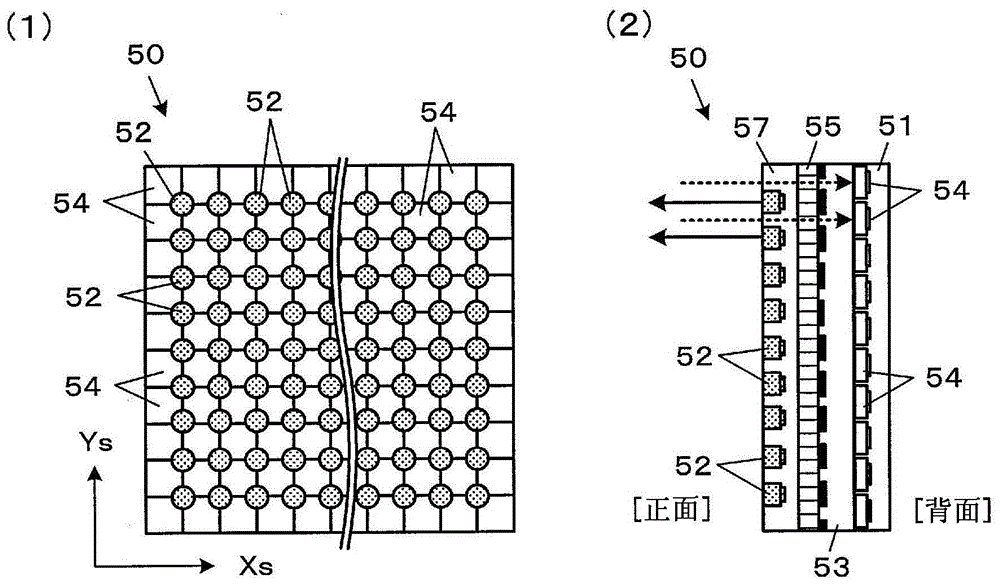
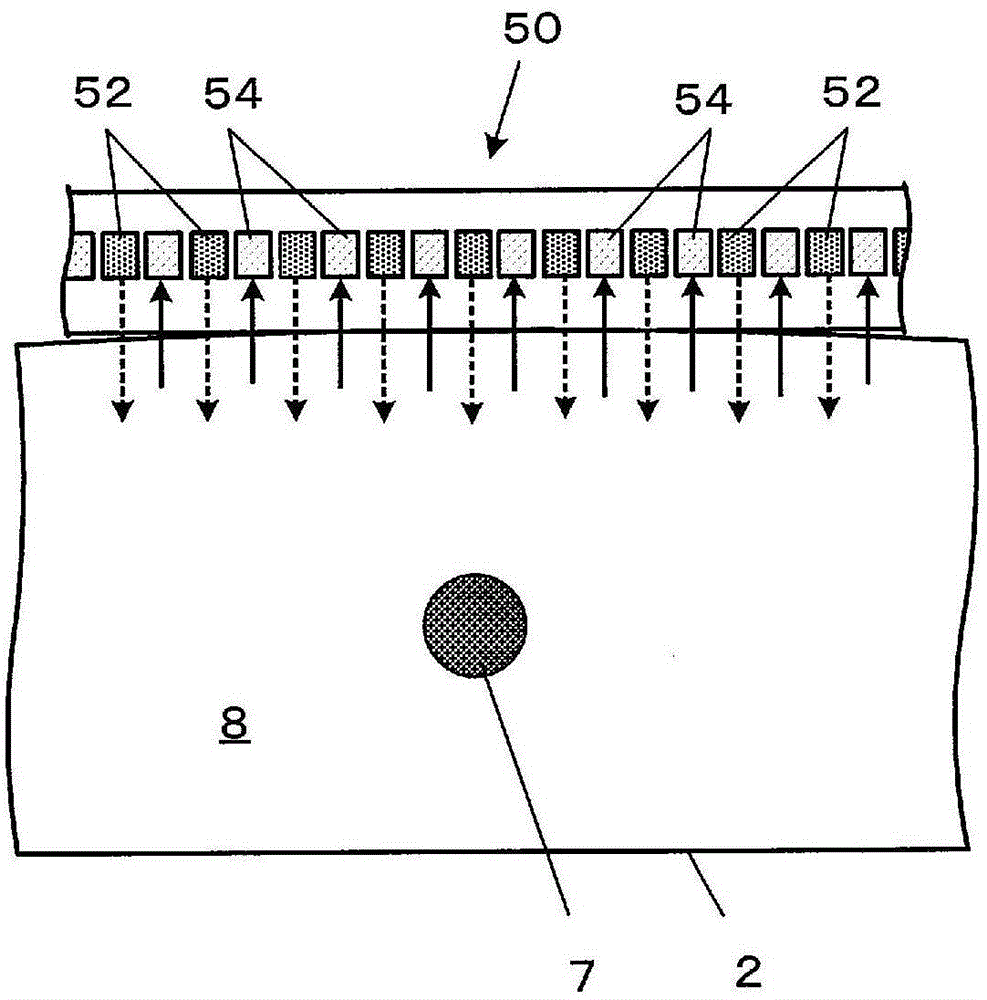
[0131] Here, blood sugar levels can be measured with high precision by using the "blood vessel method" in which blood vessels are the measurement target. On the other hand, since the blood vessel area is narrow, the position of the blood vessel obtained by taking the biological image in advance may not coincide with the actual blood vessel position. As the main factor, for example, the case where the mounting position of the sensor module 50 deviates due to the body mov...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com