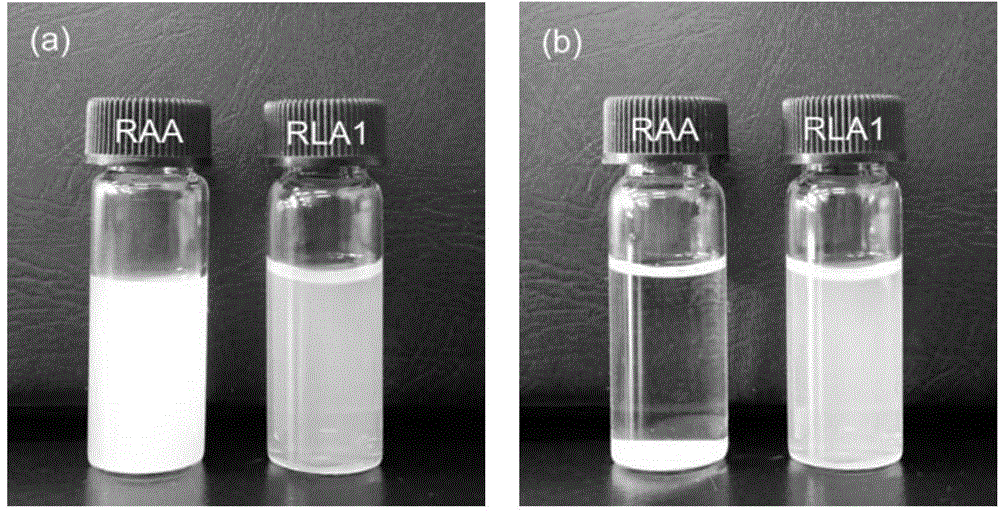
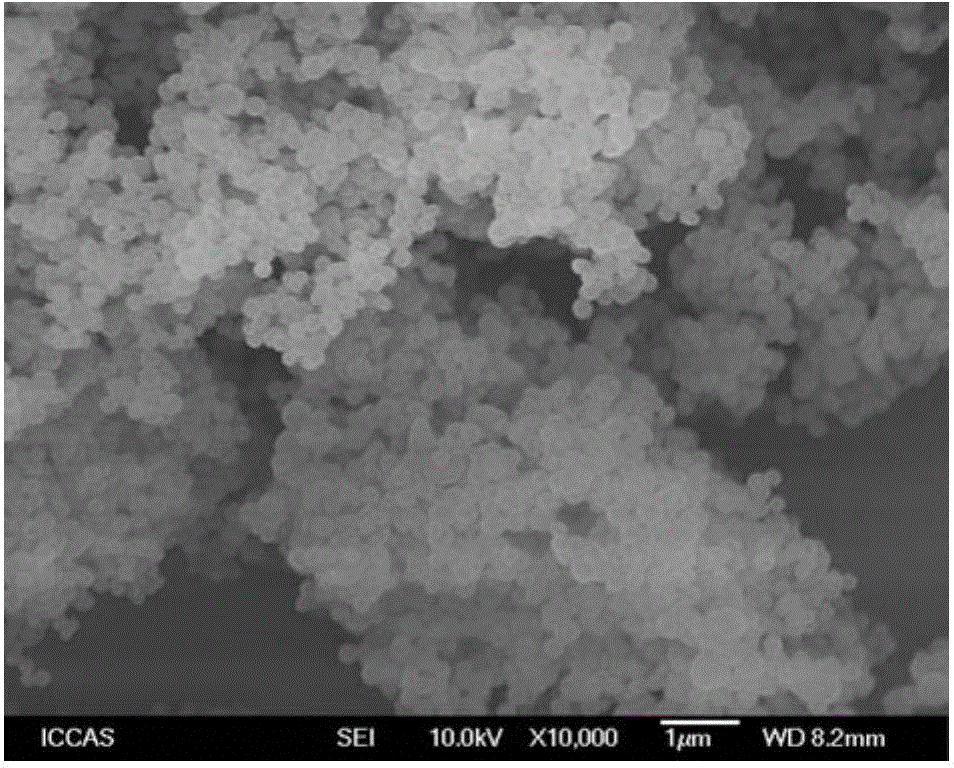
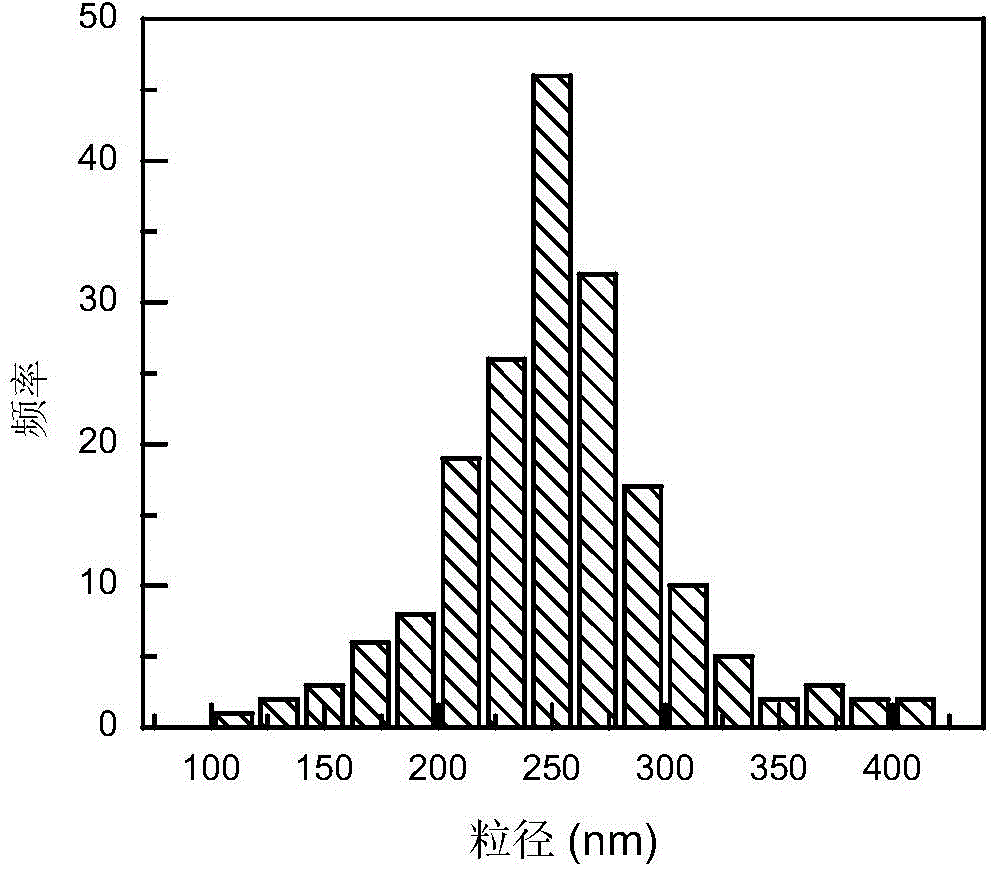
Preparation method for starch nanospheres
A nano-starch and microsphere technology, applied in the preparation of microspheres, microcapsule preparations, etc., can solve the problems of low product yield, uneven particles, long cycle, etc., and achieve easy industrialization promotion, uniform particle size distribution, and easy process control. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0037] The preparation of nano starch microspheres in embodiment 1, LiOH solution
[0038] (1) Add 0.1 g of corn amylose (purchased from Sigma Aldrich, molecular weight 40 to 340K) into a sample bottle containing 10 mL of 0.25 mol / L LiOH solution, and stir at a constant speed of 400 rpm under normal temperature and pressure for 30 min to form a uniform Dispersed starch suspension.
[0039] (2) Put the above-mentioned starch suspension into the freezer of the refrigerator and let it stand for 40 minutes until it freezes completely. The set temperature of the freezer of the refrigerator is -10°C.
[0040] (3) Take the pre-frozen sample obtained in step (2) out of the freezer compartment of the refrigerator, and place it on the test bench at normal temperature and pressure until it completely melts to obtain a transparent and clear starch solution.
[0041] (4) Transfer the starch solution obtained in step (3) into a cellulose acetate dialysis bag with a molecular weight cutoff ...
Embodiment 2
[0044] The preparation of nano starch microspheres in embodiment 2, KOH solution
[0045] (1) Add 0.1 g of rice amylose (purchased from Sigma Aldrich, molecular weight 40 to 340K) into a sample bottle filled with 10 mL of 0.25 mol / L KOH solution, stir magnetically at a constant speed of 400 rpm under normal temperature and pressure for 60 min to form a uniform Dispersed starch suspension.
[0046] (2) Put the above-mentioned starch suspension into the freezer of the refrigerator and let it stand for 60 minutes until it freezes completely. The set temperature of the freezer of the refrigerator is -10°C.
[0047] (3) Take the pre-frozen sample obtained in step (2) out of the freezer compartment of the refrigerator, and place it on the test bench at normal temperature and pressure until it completely melts to obtain a transparent and clear starch solution.
[0048] (4) Transfer the starch solution obtained in step (3) to a cellulose acetate dialysis bag with a molecular weight c...
Embodiment 3
[0051] The preparation of nano starch microspheres in the NaOH solution of embodiment 3,0.25mol / L
[0052] (1) Add 0.1 g of potato amylose (purchased from Sigma Aldrich, molecular weight 40 to 340K) into a sample bottle filled with 10 mL of 0.25 mol / L NaOH solution, stir at a constant speed of 400 rpm under normal temperature and pressure for 30 min to form a uniform Dispersed starch suspension.
[0053] (2) Put the above suspension in the freezer of the refrigerator and let it stand for 40mim until it freezes completely. The set temperature of the freezer of the refrigerator is -10°C.
[0054] (3) Take out the pre-frozen sample obtained in step (2) from the freezer compartment of the refrigerator, and place it on the test bench under normal temperature and pressure until it completely melts to obtain a transparent and clear starch solution.
[0055] (4) transfer the starch solution obtained in step (3) to a dialysis bag with a molecular weight cutoff of 3500, change the wate...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com