Beamforming weight training method and base station and terminal
A beamforming and training method technology, applied in the field of terminal, beamforming weight training method and base station, can solve problems such as unreasonable number of iterations, and achieve the effect of improving training efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
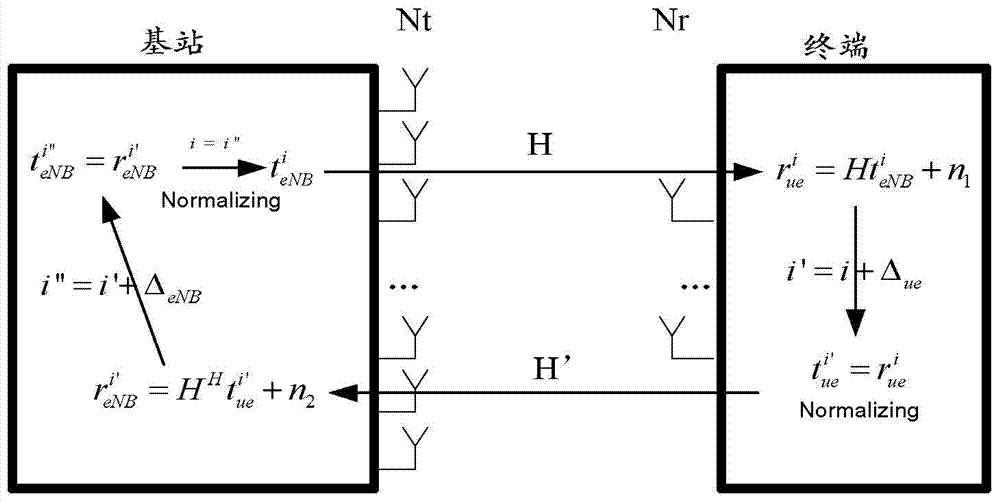
[0088] This embodiment provides a beamforming weight training method, including the following operations: the base station sends N types of beam pilot signals to the terminal, where N is a positive integer, and the UE selects one or more types of received beam pilot signals Beam pilot, and feed back the corresponding beam information to the base station. The base station sends training information to the terminal according to the beam information fed back by the UE.
[0089] Specifically, the terminal feeds back beam position information or indexes corresponding to one or more types of beam pilot signals received to the base station, and the base station determines a training transmission signal according to the beam information fed back by the UE, and sends the training signal to the terminal.
[0090] The base station sends different beam information to the terminal on the subcarriers, and the terminal feeds back the received subcarrier information or indexes of one or more ...
example 1-1
[0104] The base station and the terminal complete the beam selection before training through the following steps.
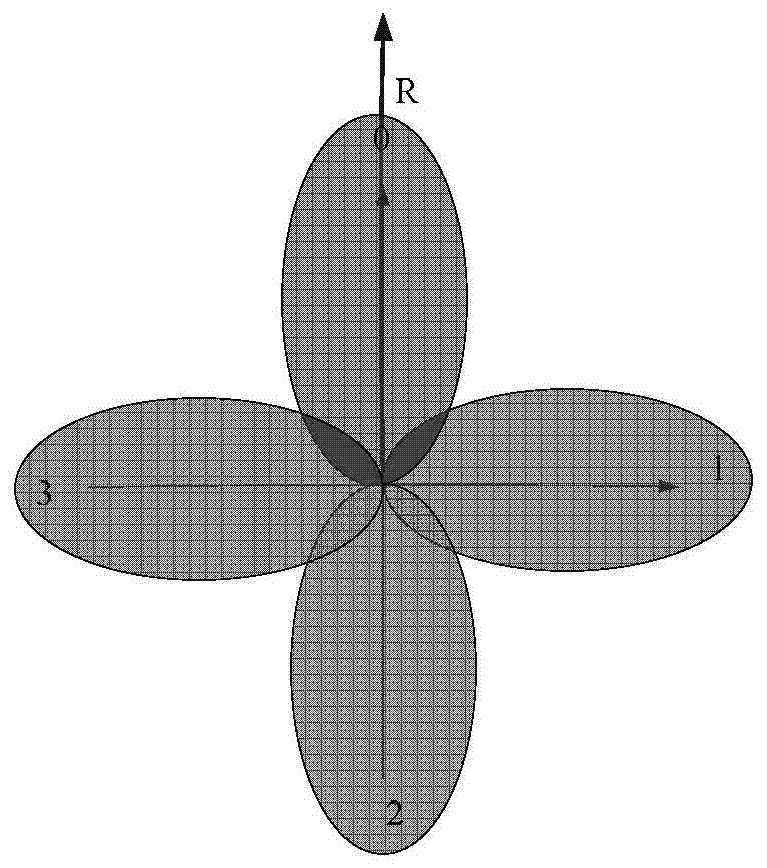
[0105](1) The base station selects a precoding vector in sequence within M agreed time-frequency resources, where M is a positive integer, and sends signals to the terminal, and each symbol is bound to a precoding vector index.
[0106] (2) The terminal chooses to receive the signal sent by the base station in the M agreed time-frequency resources, and calculates the channel quality information of the corresponding received signal, such as received power, which can also be the received signal-to-noise ratio, received signal-to-interference-noise ratio, and received signal-to-noise ratio. load-to-interference-to-noise ratio, etc. Among them, the channel quality information corresponding to the i-th time slot is CQI i , i=1,...,M.
[0107] (3) The terminal feeds back m CQIs i The corresponding beam index is fed back to the base station, and m is a positive integ...
example 1-2
[0126] The base station and the terminal can also complete beam selection before training through the following steps.
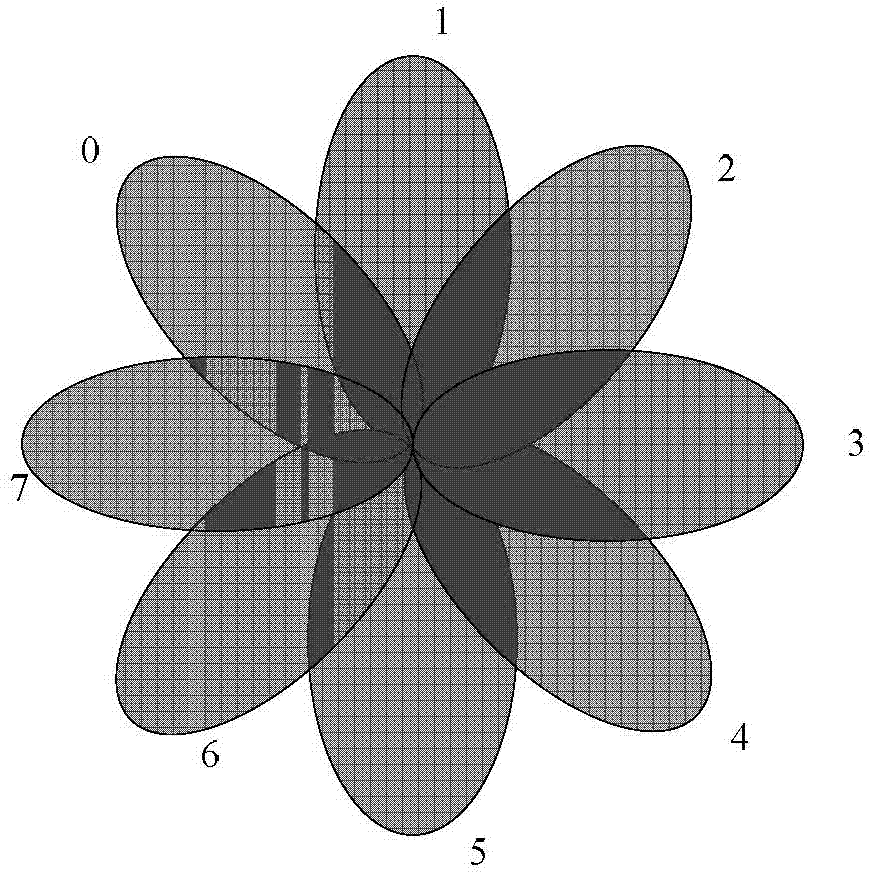
[0127] (1) The base station selects a precoding vector in sequence within M subcarriers, where M is a positive integer, and sends signals to the terminal, and each symbol is bound to a precoding vector index.
[0128] (2) The terminal chooses to receive the signal sent by the base station in M subcarriers, and calculates the channel quality information of the corresponding received signal, such as received power, or received signal-to-noise ratio, received signal-to-interference-to-noise ratio, and received carrier-to-interference-to-noise ratio Wait. Among them, the channel quality information corresponding to the i-th time slot is CQI i , i=1,...,M.
[0129] The M subcarriers may also be M ODFM symbols, or pilot positions, etc.;
[0130] (3) The terminal feeds back m CQIs i The corresponding beam index is fed back to the base station, and m is a posi...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com