Method for performing alkoxylation reaction in microreactor
A micro-reactor and alkoxylation technology, applied in chemical instruments and methods, preparation of organic compounds, preparation of aminohydroxy compounds, etc., can solve the problems of reducing the production efficiency of the reaction device, affecting the appearance of products, and prolonging the production cycle, etc. Achieve the effect of low epoxy compound content, saving washing water and reducing energy consumption
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
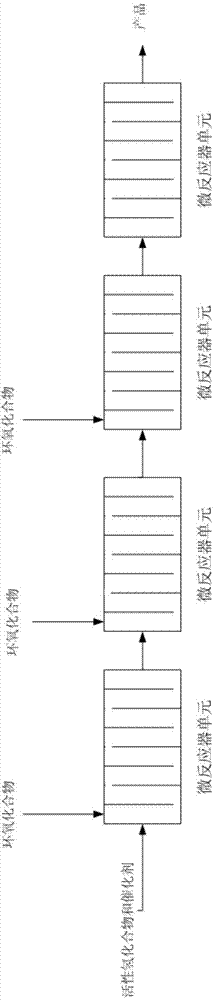
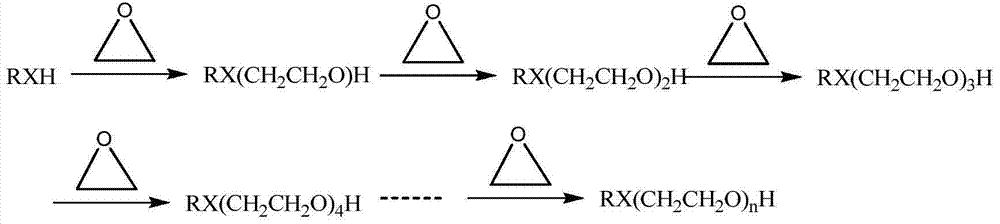
[0087] In the microreactor (including two inlets) in series of four microreactor units, the active hydrogen compound and the catalyst mixture are used as fluid A, and the epoxy compound is used as fluid B, so that the two are mixed in the microreactor reaction. The microreactor is placed in a bath at a certain temperature, and the temperature is regulated through the outer wall of the microreactor unit. The microreactors of Examples 1.1 to 1.11 include a reaction zone of 20 ml, and the minimum equivalent diameter of the cross section is 0.05 mm. The flow rate adopted by fluid A is 15 g / min, and fluid B is put into the first microreactor unit in a certain molar ratio. Table 1 shows the selectivity of mono-addition products collected after the reaction of different active hydrogen compounds and epoxy compounds in Examples 1.1 to 1.11 and the residual amount of epoxy compounds.
[0088] Table 1
[0089]
[0090]
Embodiment 2
[0096] In the microreactor (including 4 inlets) in series of six microreactor units, the active hydrogen compound and the catalyst mixture are used as fluid A, and the epoxy compound is used as fluid B, so that the two are mixed in the microreactor reaction. The microreactor is placed in a bath at a certain temperature, and the temperature is regulated through the outer wall of the microreactor unit. The microreactors of Examples 2.1 to 2.10 comprise a reaction zone of 30 ml, and the minimum equivalent diameter of the cross section is 0.1 mm. The flow rate adopted by fluid A is 3g / min, and fluid B is put into the microreactor from three inlets (each 1 / 3) in a certain molar ratio. Table 3 shows the molecular weights, distribution coefficients and residual amount of epoxy compounds collected after the reaction of different active hydrogen compounds and epoxy compounds in Examples 2.1 to 2.10.
[0097] table 3
[0098]
Embodiment 3
[0104] In the microreactor (containing 5 inlets) that eight microreactor units are connected in series, reclaim the product that obtains in embodiment 2 as fluid A, and with epoxy compound as fluid B, make both carry out in microreactor Mixed reactions. The microreactor is placed in a bath at a certain temperature, and the temperature is regulated through the outer wall of the microreactor unit. The microreactors of Examples 3.1 to 3.6 comprise a reaction zone of 40 ml, and the minimum equivalent diameter of the cross section is 0.5 mm. The flow rate adopted by fluid A is 6g / min, and fluid B is put into the microreactor from four inlets (each 1 / 4) in a certain molar ratio. Table 5 shows the molecular weights, distribution coefficients and residual amounts of epoxy compounds collected after the reactions of different active hydrogen compounds and epoxy compounds in Examples 3.1 to 3.6.
[0105] table 5
[0106]
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com