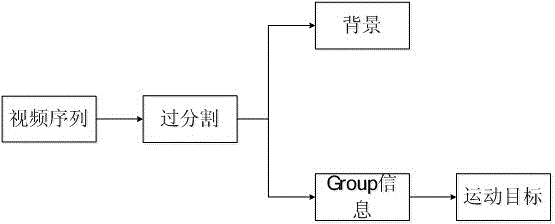
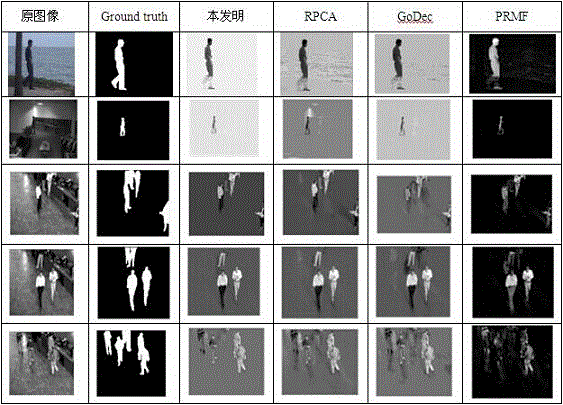
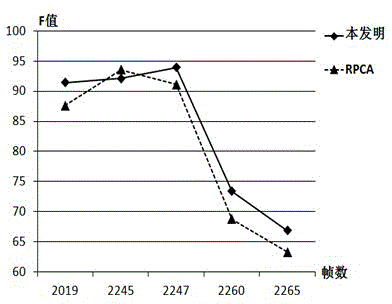
Group sparsity robust PCA-based moving object detecting method
A technology of moving targets and detection methods, applied in image data processing, instruments, calculations, etc., can solve problems such as inability to effectively measure spatial-temporal context correlation, unfavorable elimination of unstructured sparse components, robustness, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0031] Embodiments of the present invention are described in detail below, examples of which are shown in the drawings, wherein the same or similar reference numerals denote the same or similar elements or elements having the same or similar functions throughout. The embodiments described below by referring to the figures are exemplary only for explaining the present invention and should not be construed as limiting the present invention.
[0032] The classic robust PCA detection method uses l 1 The norm independently judges whether each pixel is a moving target, and there are problems such as inaccurate and incomplete boundary positioning, and it is also not conducive to eliminating unstructured sparse components caused by noise and background random disturbances. Due to the continuity of the spatial distribution of moving objects, the sparse part of separated moving objects should also have this structured correlation feature. In order to effectively solve the above-mention...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com