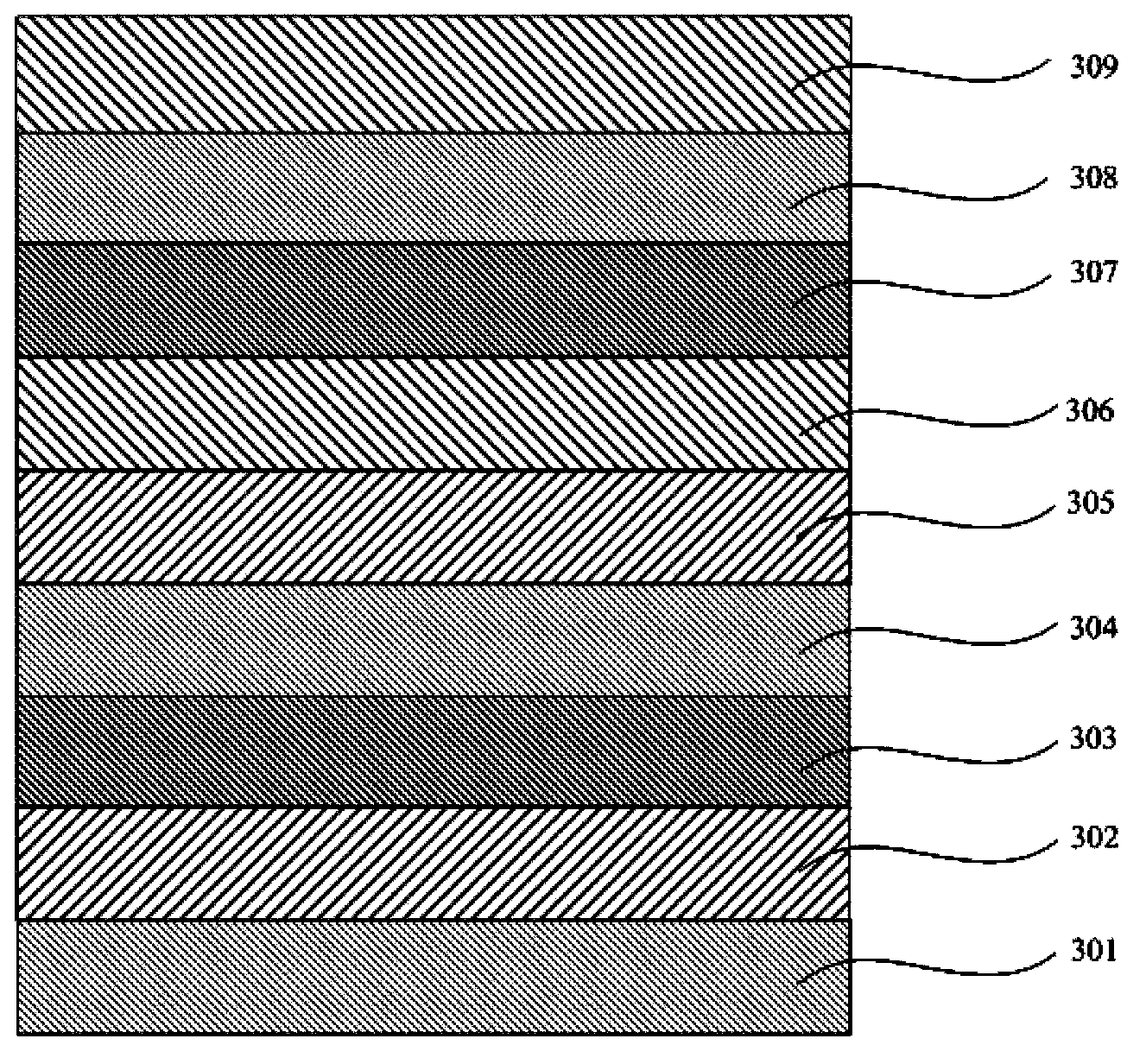
Organic electrophosphorescent materials, preparing method thereof and organic electroluminescence devices
A phosphorescent material, electromechanical technology, used in luminescent materials, electro-solid devices, organic chemistry, etc., to reduce self-quenching, increase solubility, and reduce direct effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0037] The present invention also relates to a method for preparing the above-mentioned organic electrophosphorescent material, which method comprises the following steps in sequence:
[0038] 1. Synthesize compound C through Suzuki coupling reaction between compound E and compound F; wherein, compound F is 2,3,4-trifluorophenylboronic acid, and the structural formulas of compound E and compound C are as follows:
[0039] Compound E is Compound C is
[0040] 2. Reaction of compound C prepared in step 1 with compound D to generate a chlorine-bridged dimer, namely compound A. Wherein, compound D is trihydrate iridium trichloride IrCl 3 ·3H 2 O. The structural formula of compound A is as follows:
[0041]
[0042] 3. Compound A prepared in step 2 is used as the main structure of the ring metal ligand, and 2-pyridinecarboxylic acid (compound B) is used as an auxiliary ligand source to react compound A and compound B to obtain an iridium metal complex, that is, Electrom...
Embodiment 1
[0050] The organic electrophosphorescent material disclosed in this example is the complex bis(2-(4',5',6'-trifluorophenyl)pyrimidine-N,C 2 ') (2-pyridinecarbonyl) iridium, its structural formula is as follows:
[0051]
[0052] It is prepared by the following steps:
[0053] (1) Synthesis of 2-(2',3',4'-trifluorophenyl)pyrimidine
[0054] The synthetic reaction formula is as follows:
[0055]
[0056] The specific steps are: under nitrogen atmosphere, combine 1.59g (10mmol) 2-bromopyrimidine, 2.11g (12mmol) 2,3,4-trifluorophenylboronic acid and 0.58g (0.5mmol) tetrakis(triphenylphosphine) Palladium was dissolved in 40ml of toluene, then 20ml of aqueous solution containing 2.76g (20mmol) of potassium carbonate was added dropwise to the reaction system, heated, stirred and reacted at 100°C for 6h, after the reaction solution was cooled to room temperature, dichloromethane Extraction, liquid separation, washing with water until neutral, drying with anhydrous magnesium s...
Embodiment 2
[0072] The organic electrophosphorescent material disclosed in this example is the complex bis(2-(4',5',6'-trifluorophenyl)-5-methylpyrimidine-N,C2')(2-pyridinemethyl Acyl) iridium, its structural formula is as follows:
[0073]
[0074] It is prepared by the following steps:
[0075] (1) Synthesis of 2-(2',3',4'-trifluorophenyl)-5-methylpyrimidine
[0076] The synthetic reaction formula is as follows:
[0077]
[0078] The specific steps are: under nitrogen atmosphere, mix 1.73g (10mmol) 2-bromo-5-methylpyrimidine, 1.76g (10mmol) 2,3,4-trifluorophenylboronic acid and 0.28g (0.4mmol) dichlorobis (Triphenylphosphine)palladium was dissolved in 50ml of DMF, and then 25ml of an aqueous solution containing 3.18g (30mmol) of sodium carbonate was added dropwise to the reaction system. Heat to 90°C and stir to react for 8 hours. After the reaction solution is cooled to room temperature, extract with dichloromethane, separate liquids, wash with water until neutral, dry with an...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com