Method for performing distributed channel detection and sequential access
A distributed channel and channel technology, applied in the field of distributed channel detection and sequential access, can solve the problem of detection power affecting applicability and other issues
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
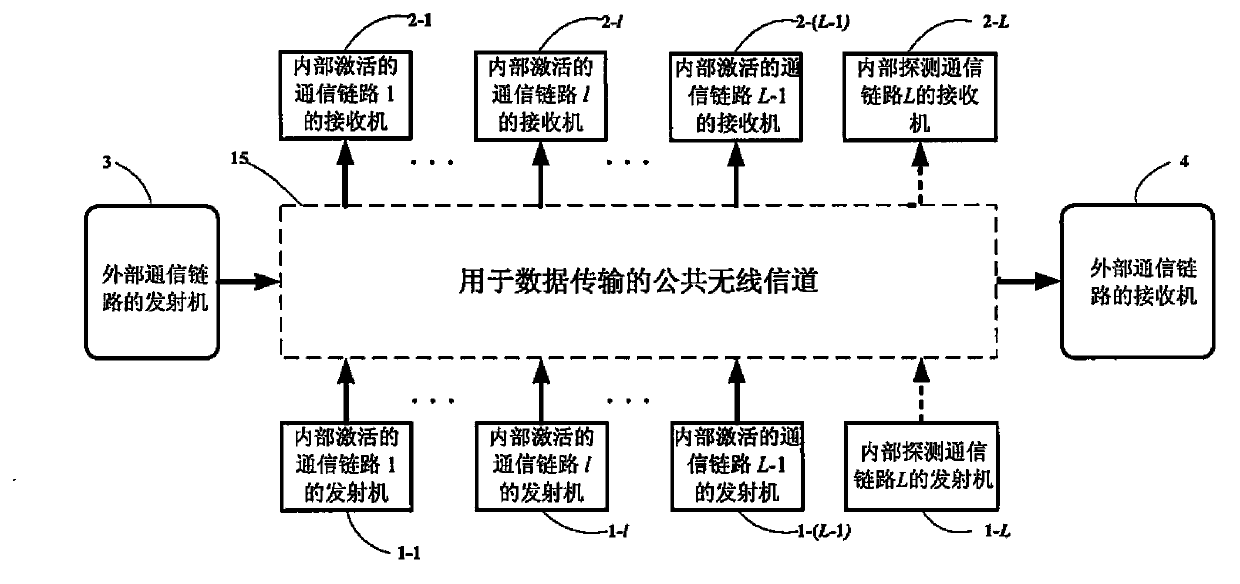
[0066] The present invention proposes a distributed channel detection and sequential access (DSICO-SEA) scheme to expand the network by sequentially superimposing communication links in the same channel automatically to obtain high spatial multiplexing efficiency. The basic idea of the present invention is to propose a distributed algorithm that uses only local measurement values to determine the globally optimal maximum achievable SINR under power constraints. The following will describe in detail the problem of the global-based maximum achievable SINR under power constraints from the perspective of optimization, and how to derive the algorithm mathematically.
[0067] 1. Problem model
[0068] This problem model is suitable for the scenario of sequential access channel. Consider the following scenario: a common wireless channel (eg, a block of time-frequency resources) is shared by active wireless networks and external communication links. The activated wireless networ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com