Quenching and readout circuits for single photon avalanche diodes
A single-photon avalanche and readout circuit technology, which is applied in the direction of instruments, can solve the problems of high power consumption, increase the size of the unit layout, and affect the detection accuracy, so as to reduce the probability of post-pulse, facilitate system integration, and have a simple circuit structure Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0041] Embodiments of the present invention are described in detail below, examples of which are shown in the drawings, wherein the same or similar reference numerals designate the same or similar elements or elements having the same or similar functions throughout. The embodiments described below by referring to the figures are exemplary and are intended to explain the present invention and should not be construed as limiting the present invention.
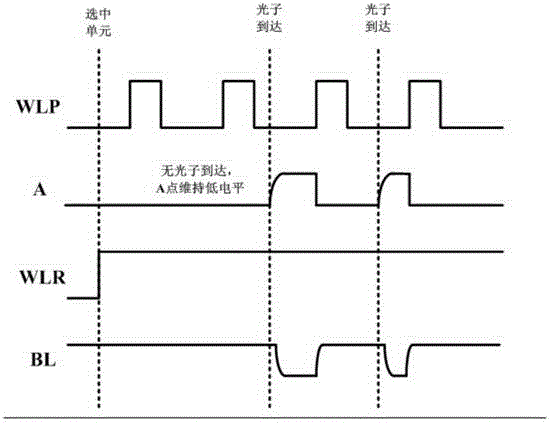
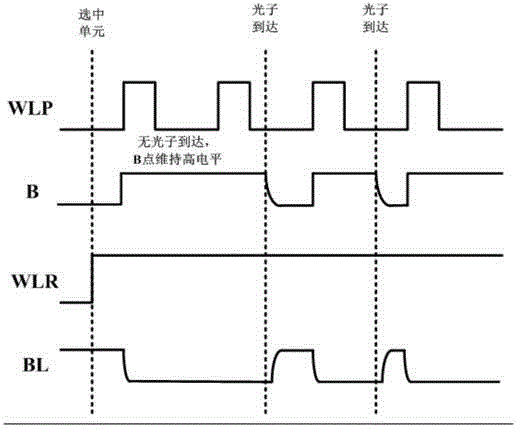
[0042] The working principle and working process of the present invention will be further described below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings and embodiments. It is worth mentioning that the time in the following timing diagrams is not given strictly in proportion, but is only used to illustrate the timing between the various signals relation.
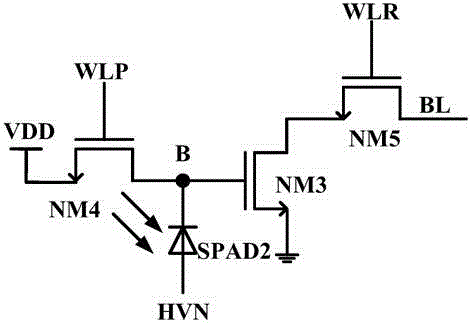
[0043] Figure 4 It is a schematic diagram of the SPAD quenching and readout circuit of the first embodiment of the present invention. Such as Figure 4 As shown, the single ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com