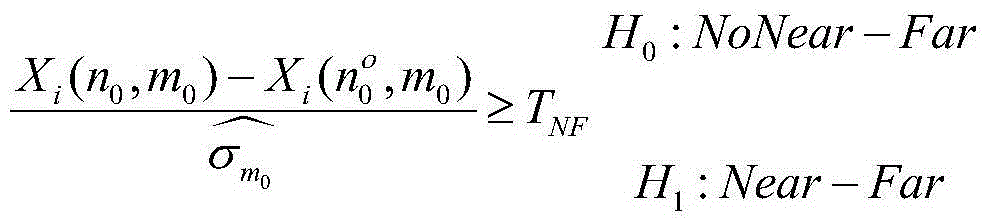Self-adaptive mutual interference restraining method based on GNSS (global navigation satellite system) related peak value detector
A correlation peak and detector technology, which is applied in the field of mutual interference signal suppression of satellite navigation systems, can solve problems such as signal detection, and achieve the effect of reducing the impact of interference performance and reducing the amount of calculation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
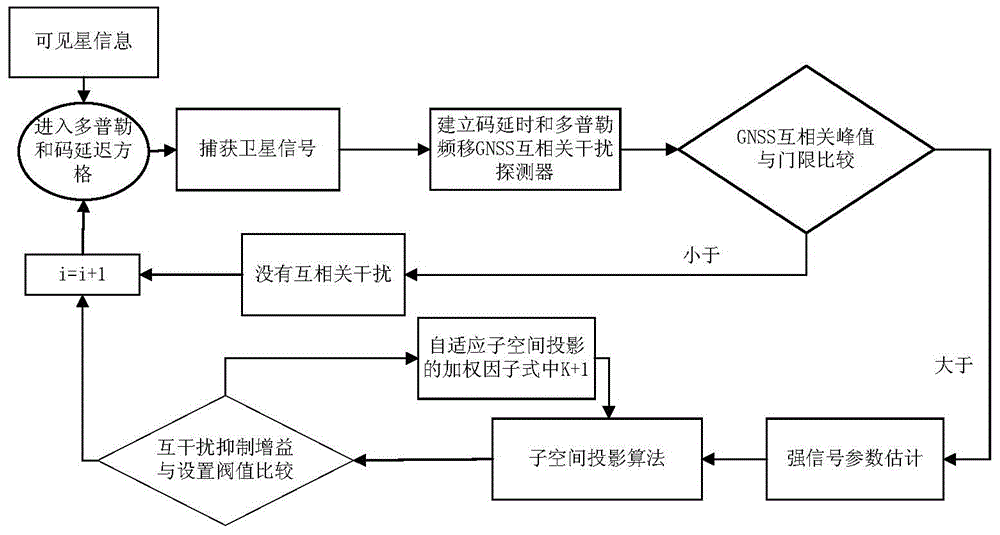
[0028] Such as figure 1 Shown, be the flow chart of the inventive method, comprise the following several steps:
[0029] Step 1: Use the navigation receiver to simultaneously receive the navigation signals of navigation satellite A and other navigation satellites (assuming that the signal of navigation satellite A is the desired signal, and the signal of navigation satellite B or navigation satellite C is the interference signal), and obtain navigation satellite A The cross-correlation interference between the desired signal of the navigation satellite and the interference signal of other navigation satellites, thus obtaining the influence relationship of the interference signal on the acquisition of the desired signal.
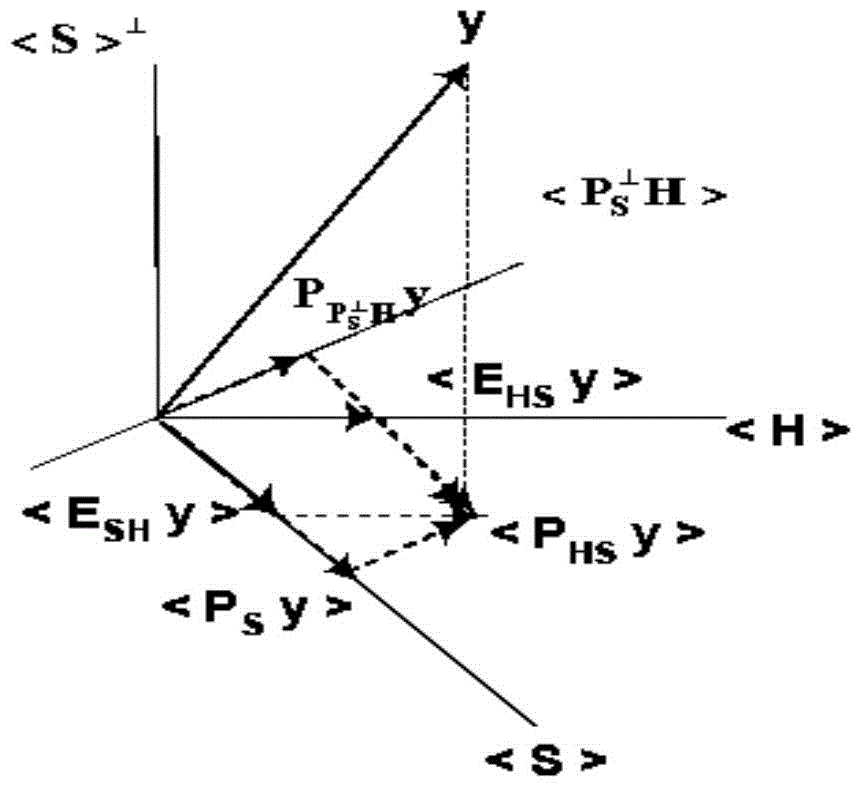
[0030] GNSS satellite navigation system is a kind of information system based on CDMA, because the spreading codes it uses are not completely orthogonal, so its performance faces the influence of cross-correlation interference. The cross-correlation interfer...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com