Hydrophobic chitosan-silicon dioxide composite aerogel and preparation method and oil absorption application thereof
A composite aerogel and silica technology, applied in coatings and other directions, can solve the problems of weak mechanical properties, other properties decline, limited application, etc., and achieve the effects of high porosity, simple preparation process, and easy availability of raw materials
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
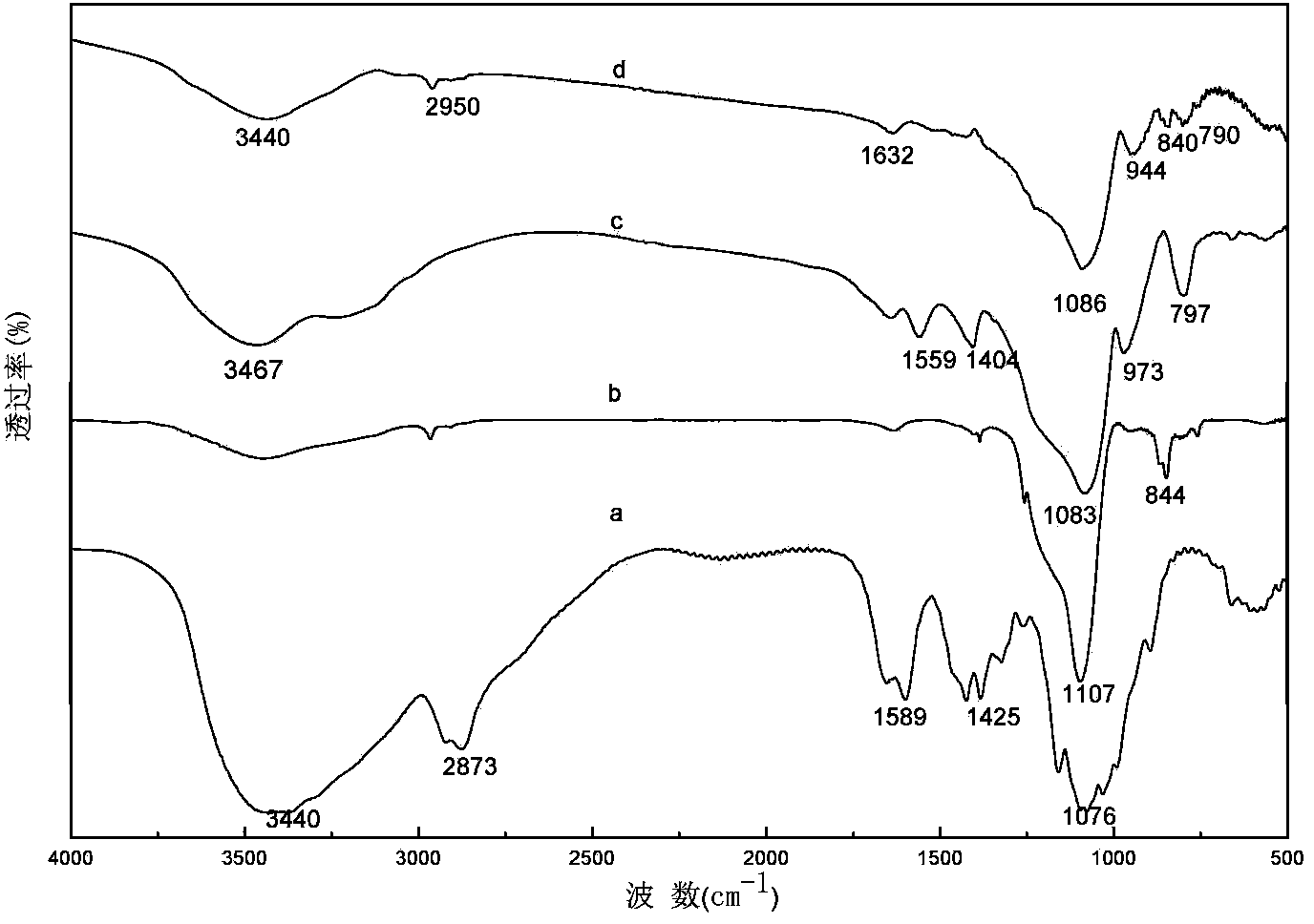
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0032] (a) Dissolve 0.6 g of low-viscosity chitosan (20-200 mPa·s) in 0.5 vol% oxalic acid solution and stir until completely dissolved to form a uniform transparent solution. Add 6mL TEOS and stir for 12h until a completely uniform viscous sol without layering is formed. The sol was placed in a mold and aged for 36 hours to form a stable gel. Rinse and soak with deionized water several times to remove unreacted TEOS remaining in the gel and impurities during the reaction. Vacuum freeze-drying for 12 hours to obtain chitosan-silicon dioxide composite airgel.
[0033] (b) Drop the quantitative hydrophobic modifier HMDZ around the airgel obtained after freeze-drying, and place it at a constant temperature of 60°C. The evaporated modifier will slowly redeposit on the surface of the airgel. After 8 hours, a completely hydrophobic composite airgel was obtained.
[0034] (c) According to the contact angle test, the water contact angle of the prepared hydrophobic composite airgel ...
Embodiment 2
[0036] (a) Dissolve 0.4 g of medium-viscosity chitosan (200-400 mPa·s) in 0.5 vol% acetic acid solution, stir until completely dissolved, and form a uniform transparent solution. Add 5mL of water glass solution and stir for 12h until a completely uniform viscous sol without stratification is formed. The sol was placed in a mold and aged for 24 hours to form a stable gel. Rinse and soak with deionized water several times to remove unreacted raw materials remaining in the gel and impurities during the reaction. Vacuum freeze-drying for 12 hours to obtain chitosan-silicon dioxide composite airgel.
[0037] (b) Drop the quantitative hydrophobic modifier TMCS around the airgel obtained after freeze-drying, and place it at a constant temperature of 60 ° C. The evaporated modifier will slowly redeposit on the surface of the airgel. After 5 hours That is, a completely hydrophobic composite airgel is obtained.
[0038] (c) According to the contact angle test, the water contact angle...
Embodiment 3
[0040] (a) Dissolve 0.3 g of high-viscosity chitosan (400-1000 mPa·s) in 0.5 vol% carbonic acid solution, stir until completely dissolved, and form a uniform transparent solution. Add 5mL TEOS and stir for 15h until a completely uniform viscous sol without stratification is formed. The sol was placed in a mold and aged for 24 hours to form a stable gel. Rinse and soak with deionized water several times to remove unreacted TEOS remaining in the gel and impurities during the reaction. Vacuum freeze-drying for 12 hours to obtain chitosan-silicon dioxide composite airgel.
[0041] (b) Drop the quantitative hydrophobic modifier DMDCS around the airgel obtained after freeze-drying, and place it at a constant temperature of 50°C. The evaporated modifier will slowly redeposit on the surface of the airgel. After 5h That is, a completely hydrophobic composite airgel is obtained.
[0042] (c) According to the contact angle test, the water contact angle of the prepared hydrophobic comp...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com