Fault-tolerant method aiming at TSV fault grading in 3D NoC
A fault classification and fault technology, applied in the direction of response errors, etc., can solve the problems of reducing system performance degradation, TSV faults, large area and power consumption overhead, so as to reduce delay and power consumption overhead, ensure reliability, The effect of reducing network congestion
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
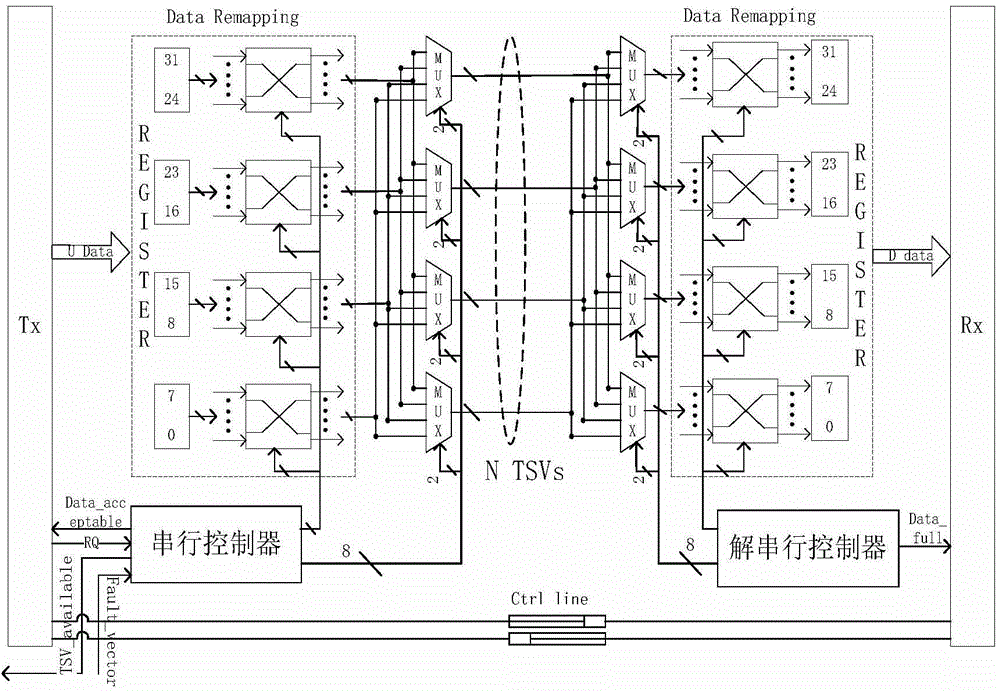
[0027] A fault-tolerant method for TSV fault classification in 3D NoC, the operation steps are as follows:
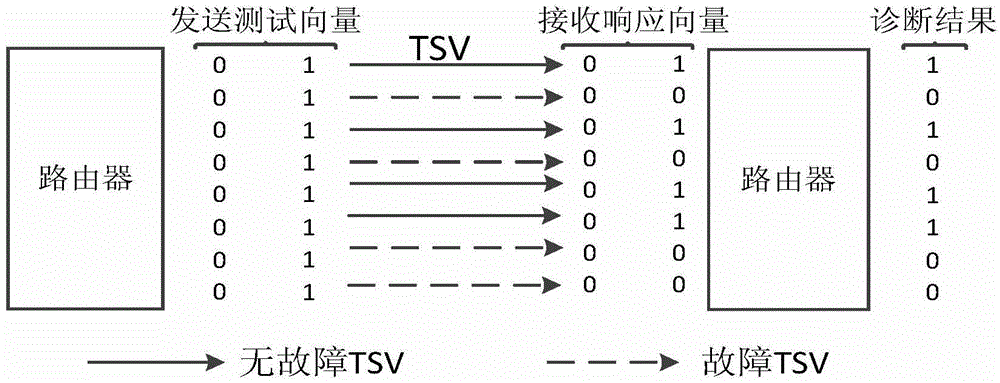
[0028] a. Carry out fault test to TSV link, obtain the fault status of each TSV bit line in the TSV link;
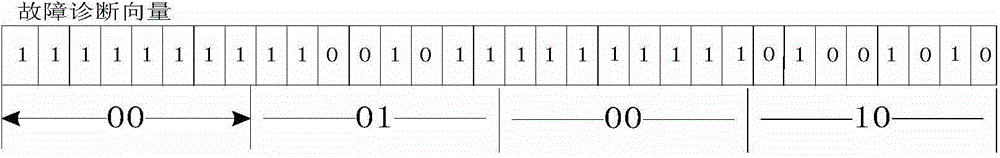
[0029] b. Determine the fault state of each group of TSVs in the TSV link, if there is no TSV fault, mark the fault state of the group as (00) 2 , if the number of faulty TSVs in the group ≤ 1 / 2 the number of TSVs in the group, mark the fault status of the group as (01) 2 , otherwise mark its failure state as (10) 2 ; for (00) 2 The data corresponding to the group is transferred once; for (01) 2 The data corresponding to the group is transmitted twice; (10) 2 The data corresponding to the group is passed by not(10) 2 When the sum of the four TSV status values is greater than 6, the TSV link is unavailable;
[0030] c. When the TSV link is faulty and still available, the data is transmitted serially through TSV;
[0031] d. For unavailable TSV links, the d...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com