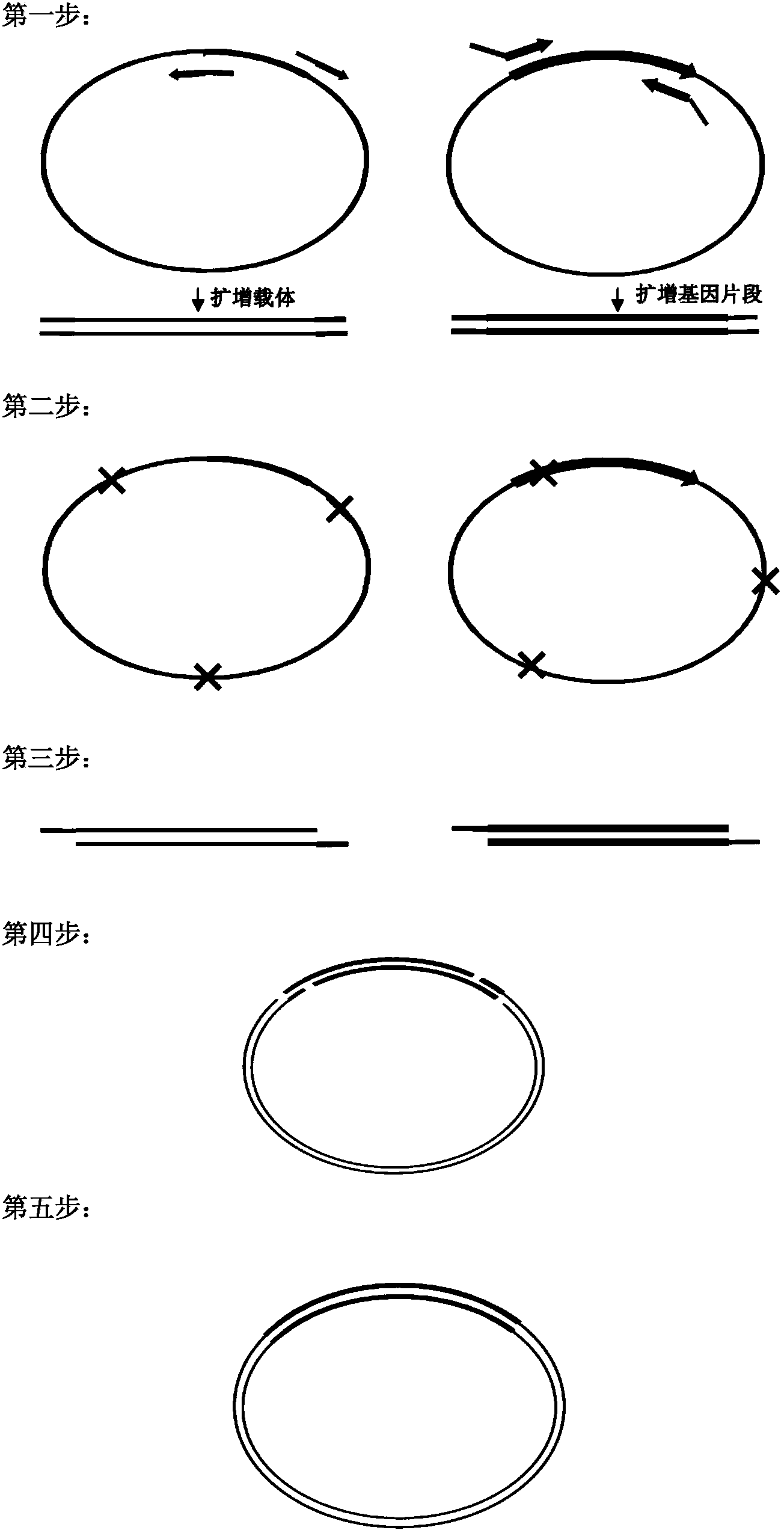
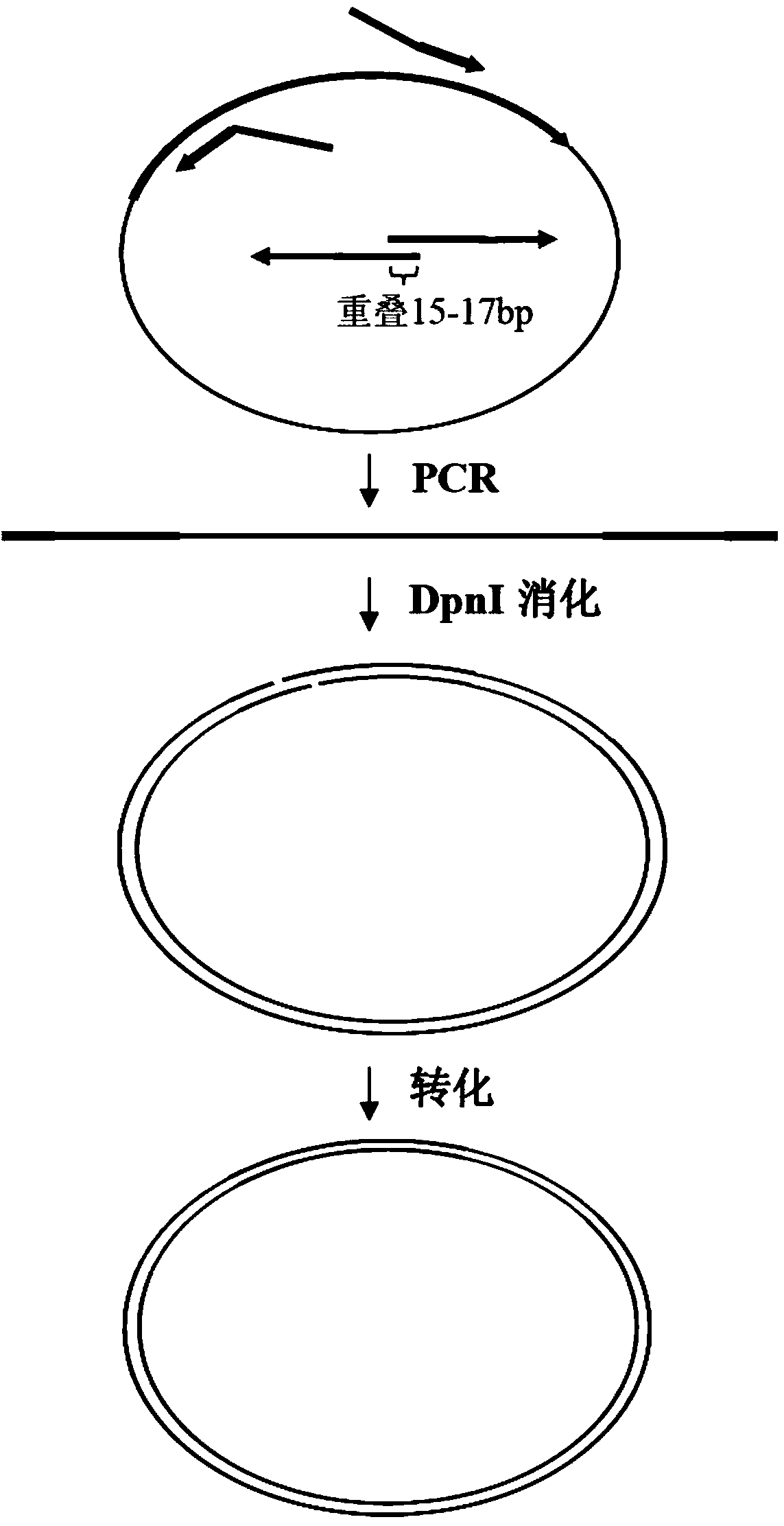
Biomedical molecule cloning method
A technology of molecular cloning and forward primer, applied in the field of genetic engineering, can solve the problems of time-consuming, labor-intensive and expensive
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0082] Example 1. Using the molecular cloning method of the present invention to clone the Parkinson's disease-related gene α-synuclein (α-syn) into the vector pGEX-4T-1
[0083] In this example, the molecular cloning method provided by the present invention is used to replace the partial fragment of the multiple cloning site (position 939-974 in sequence 10) in the pGEX-4T-1 plasmid (sequence 10) with Parkinson's as shown in sequence 8 Disease-related gene α-synuclein (α-syn), thus obtaining the recombinant vector pGEX-4T-α-syn.
[0084] Starting plasmid: methylated pGEX-4T-1 vector.
[0085] Target gene: Parkinson's disease-related gene α-synuclein (α-syn) shown in Sequence 8, present on the methylated pET-α-syn carrier. The pET-α-syn vector is a recombination obtained by inserting the DNA fragment shown in sequence 8 in the sequence table into the multiple cloning site BamH I and Hind III of the pET-28a(+) vector (Novagen, 69864-3) plasmid.
[0086] 1. Primer design
[00...
Embodiment 2
[0113] Example 2. Using the molecular cloning method of the present invention to delete the 3' end of the Parkinson's disease-related gene α-synuclein (α-syn) and then clone it into the vector pGEX-4T-1 to construct a mutant with a fragment deletion
[0114] In this example, the molecular cloning method provided by the present invention is used to replace the pGEX-4T-1 plasmid (the partial fragment of the multi-cloning site in sequence 10 (939-974 of sequence 10) with the 1-285 of sequence 8 The indicated Parkinson's disease-related gene α-synuclein (α-syn) deleted the sequence behind the 3' end, thereby obtaining the recombinant vector pGEX-4T-α-syn△C.
[0115] Starting plasmid: methylated pGEX-4T-1 vector.
[0116] Target gene: the sequence after the deletion of the 3' end of the Parkinson's disease-related gene α-synuclein (α-syn) shown in the 1-285th position of Sequence 8, which exists on the methylated pET-α-syn carrier. The pET-α-syn vector is a recombination obtained ...
Embodiment 3
[0144] Example 3. Using the molecular cloning method of the present invention to replace the hydrophobic region at the middle end of the Parkinson's disease-related gene α-synuclein (α-syn) with the corresponding part of β-synuclein (β-syn), constructing a gene fragment replacement mutation body
[0145] In this example, the molecular cloning method provided by the present invention is used to extract the hydrophobic region of the middle end of the Parkinson's disease-related gene α-synuclein (α-syn) in the pGEX-4T-α-syn plasmid (position 181-285 of sequence 8 ) is replaced by the hydrophobic region (SEQ ID NO: 9) at the middle end of the Parkinson's disease-related gene β-synuclein (β-syn), thereby obtaining a recombinant vector.
[0146] Starting plasmid: methylated pGEX-4T-α-syn vector, derived from the pGEX-4T-α-syn plasmid extracted and purified from Escherichia coli DH5α in Example 1. The sequence of the pGEX-4T-α-syn plasmid is the sequence obtained by replacing the 93...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com