Spinning scouring agent
A scouring agent and molecular technology, applied in textiles, papermaking, fiber treatment, etc., can solve the problems of low permeability and wettability, capillary effect and poor whiteness
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
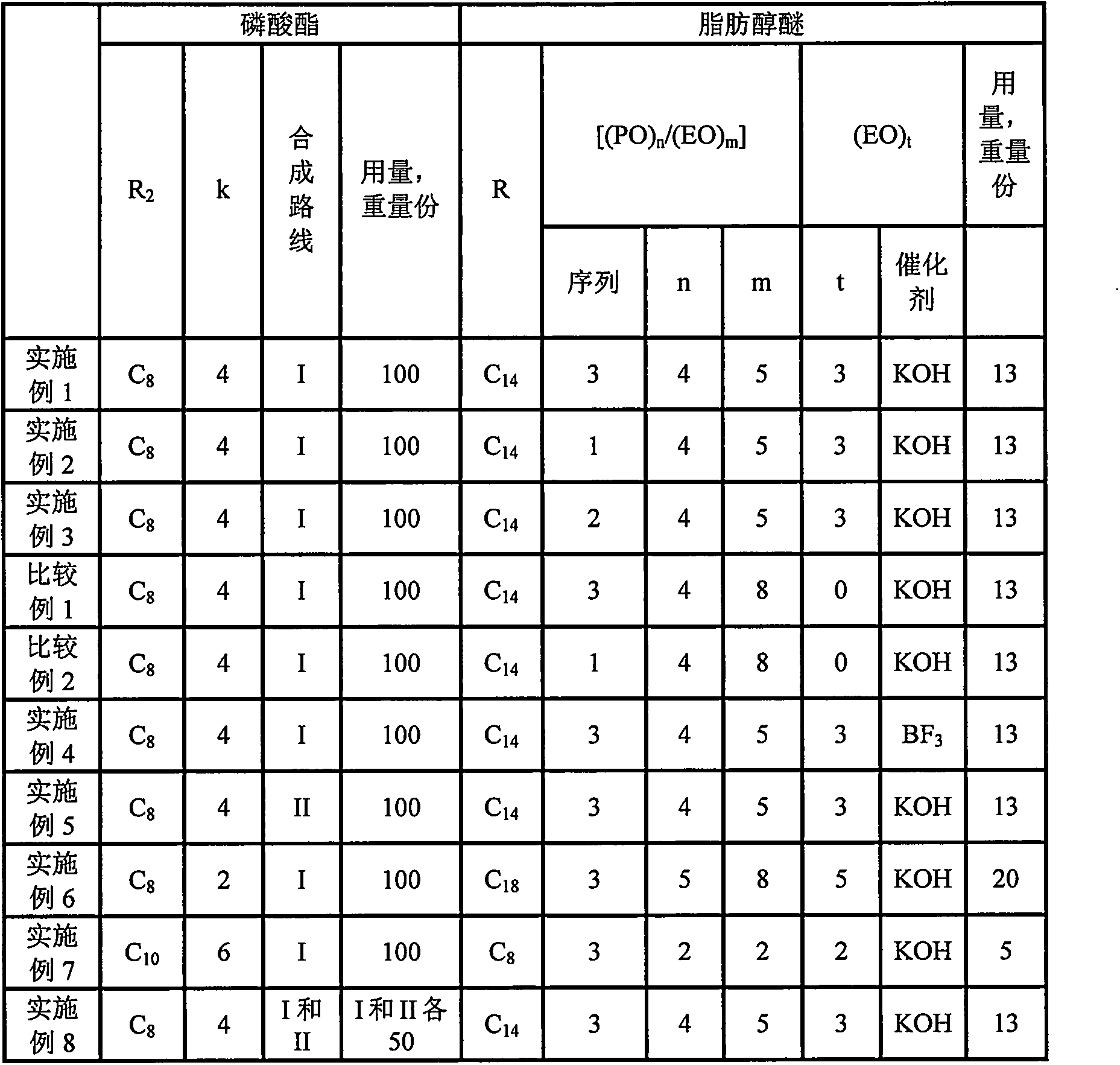
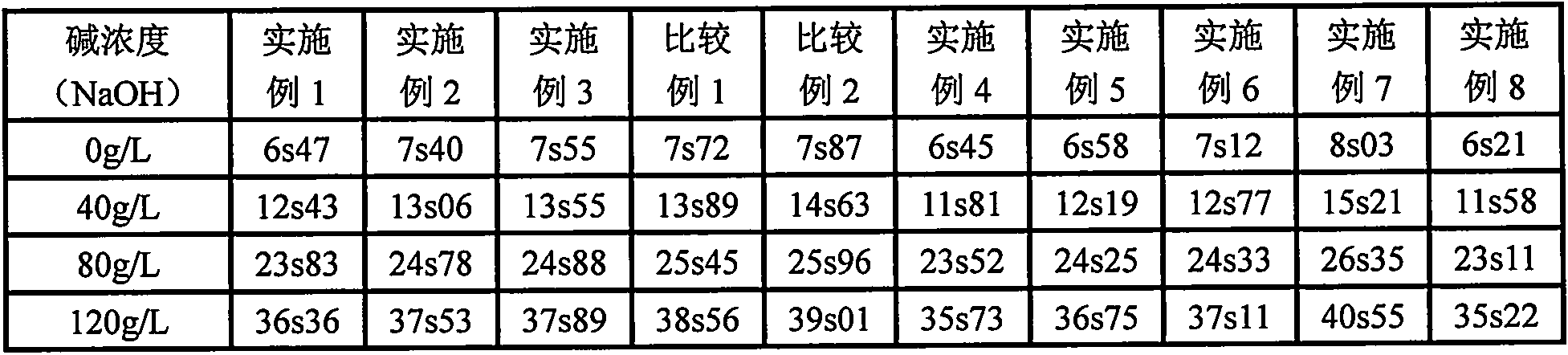
Embodiment 1
[0065] 1. Synthesis of Phosphate Ester
[0066] (1) make isooctyl alcohol and P 2 o 5 React at 48°C for 70 minutes; among them, isooctyl alcohol and P 2 o 5 The molar ratio in is 1:0.50;
[0067] (2) heat preservation at 75°C for 4 hours;
[0068] (3) adding water according to the isooctanol molar ratio of water to step (1) being 1.2, and hydrolyzing at 90° C. for 1 hour;
[0069] (4) Vacuum dehydration at 105° C. for 60 minutes; add EO at 120° C., the molar ratio of EO to isooctyl alcohol in step (1) is 4, and control the gauge pressure to 0.2 MPa during adding EO;
[0070] (5) After adding EO, keep the temperature at 130° C. for 1 hour, and then vacuum at 110° C. for 30 minutes to obtain the phosphoric acid ester.
[0071] 2. Synthesis of Fatty Alcohol Ether
[0072] Into a dry 2 L reaction kettle with stirring, electric heating mantle and internal water cooling coil was charged 2 moles of tetradecyl alcohol and potassium hydroxide. Seal the reaction kettle, replace ...
Embodiment 2
[0079] 1. Synthesis of Phosphate Ester
[0080] (1) make isooctyl alcohol and P 2 o 5 React at 48°C for 70 minutes; among them, isooctyl alcohol and P 2 o 5 The molar ratio in is 1:0.50;
[0081] (2) heat preservation at 75°C for 4 hours;
[0082] (3) adding water according to the isooctanol molar ratio of water to step (1) being 1.2, and hydrolyzing at 90° C. for 1 hour;
[0083] (4) Vacuum dehydration at 105° C. for 60 minutes; add EO at 120° C., the molar ratio of EO to isooctyl alcohol in step (1) is 4, and control the gauge pressure to 0.2 MPa during adding EO;
[0084] (5) After adding EO, keep the temperature at 130° C. for 1 hour, and then vacuum at 110° C. for 30 minutes to obtain the phosphoric acid ester.
[0085] 2. Synthesis of Fatty Alcohol Ether
[0086] Into a dry 2 L reaction kettle with stirring, electric heating mantle and internal water cooling coil was charged 2 moles of tetradecyl alcohol and potassium hydroxide. Seal the reaction kettle, replace ...
Embodiment 3
[0093] 1. Synthesis of Phosphate Ester
[0094] (1) make isooctyl alcohol and P 2 o 5 React at 48°C for 70 minutes; among them, isooctyl alcohol and P 2 o 5 The molar ratio in is 1:0.50;
[0095] (2) heat preservation at 75°C for 4 hours;
[0096] (3) adding water according to the isooctanol molar ratio of water to step (1) being 1.2, and hydrolyzing at 90° C. for 1 hour;
[0097] (4) Vacuum dehydration at 105° C. for 60 minutes; add EO at 120° C., the molar ratio of EO to isooctyl alcohol in step (1) is 4, and control the gauge pressure to 0.2 MPa during adding EO;
[0098] (5) After adding EO, keep the temperature at 130° C. for 1 hour, and then vacuum at 110° C. for 30 minutes to obtain the phosphoric acid ester.
[0099] 2. Synthesis of Fatty Alcohol Ether
[0100]Into a dry 2 L reaction kettle with stirring, electric heating mantle and internal water cooling coil was charged 2 moles of tetradecyl alcohol and potassium hydroxide. Seal the reaction kettle, replace t...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com