Nucleic acid aptamer of affinity viral hepatitis C core protein and application of nucleic acid aptamer
A nucleic acid aptamer and core protein technology, applied in the direction of DNA/RNA fragments, measuring devices, instruments, etc., can solve the problems of high cost of HCV virus, harsh storage conditions, and high price, and achieve high application value, easy preparation, and low cost low effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0038] Embodiment 1, preparation of related proteins and related solutions
[0039] 1. Preparation of HCV core protein (target protein) with histidine tag
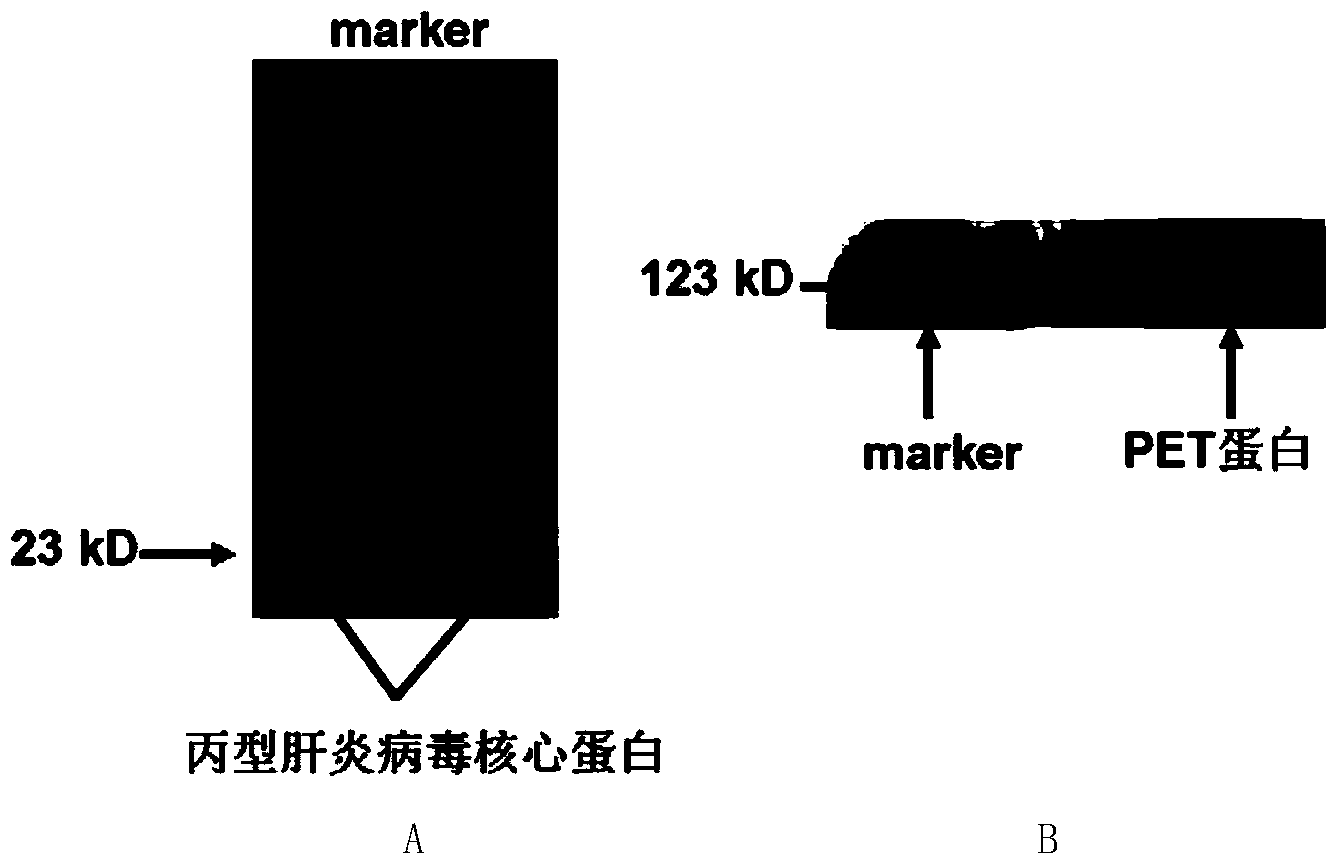
[0040] 1. Amplification of the coding gene of HCV core protein
[0041] Prepare the DNA shown in the sequence 4 of the sequence listing (the coding gene of the hepatitis C virus core protein, GENBANK ACCESSION NO.HM566118.1, the hepatitis C virus core protein shown in the sequence 3 of the coding sequence listing), as PCR amplification The template is used for PCR amplification with a primer pair consisting of primer 1 and primer 2 to obtain a PCR amplification product.
[0042] Primer 1 (upstream primer): 5'-CGCGC GAATTC ATGAGCACGAATCCT-3';
[0043] Primer 2 (downstream primer): 5'-CTGCAG GGATCC AGAGGCCGGGACGGTCA-3';
[0044] EcoRI restriction site and BamHI restriction site were introduced into the 5' ends of the upstream and downstream primers respectively.
[0045] PCR amplification conditions: 95°C for 2min; 3...
Embodiment 2
[0074] Example 2, Screening and Preparation of Nucleic Aptamers
[0075] 1. Protein immobilization
[0076] 1. Take Ni-NTA agarose microbeads and place them in a 5ml centrifuge tube, remove the supernatant, and wash with PBS buffer three times;
[0077] 2. Disperse the microbeads in step 1 in the target protein (or control protein), incubate at room temperature for 1 hour, and centrifuge and wash with PBS buffer three times;
[0078] 3. Redisperse the microbeads from step 2 in 1ml of PBS buffer and store at 4°C for later use.
[0079] 2. Design of Random Nucleic Acid Library
[0080] A random nucleic acid library comprising 20 nucleotides at both ends and 40 nucleotides in the middle is designed as follows: 5'-ACGCTCGGATGCCACTACAG(N 40 ) CTCATGGACGTGCTGGTGAC-3'; N 40 Represents 40 random nucleotides.
[0081] 3. Screening of nucleic acid aptamers
[0082] 1. DNA library pretreatment
[0083] The random nucleic acid library is dissolved in binding buffer.
[0084] 2. An...
Embodiment 3
[0092] Example 3, Binding Characterization of Nucleic Aptamer and Hepatitis C Virus Core Protein
[0093] 1. FITC labeling of nucleic acid aptamers and random nucleic acid libraries
[0094] The nucleic acid aptamer HCV-1 prepared in Example 2 was labeled with fluorescein isothiocyanate (FITC).
[0095] The random nucleic acid library prepared in Example 2 was labeled with fluorescein isothiocyanate (FITC).
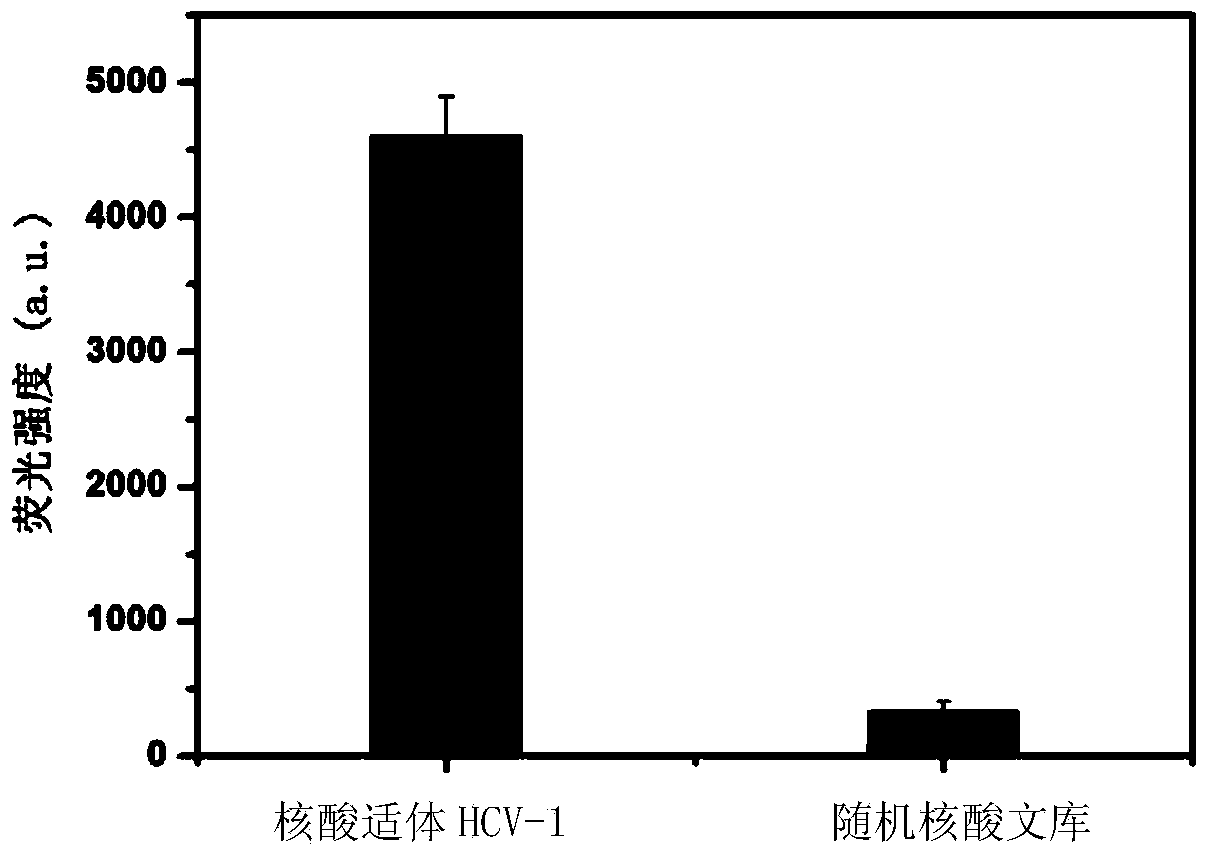
[0096] 2. Binding characterization of nucleic acid aptamer and hepatitis C virus core protein
[0097] 1. Immobilization of target protein
[0098] (1) Take 200 μl Ni-NTA agarose beads and place them in a 5ml centrifuge tube, remove the supernatant, and wash with PBS buffer three times;
[0099] (2) Disperse the microbeads in step (1) in 1 mL of the target protein, incubate at room temperature for 1 h, and centrifuge and wash with PBS buffer three times;
[0100] (3) The microbeads in step (2) were redispersed in 1 ml of PBS buffer, and kept at 4°C for later use.
[...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com