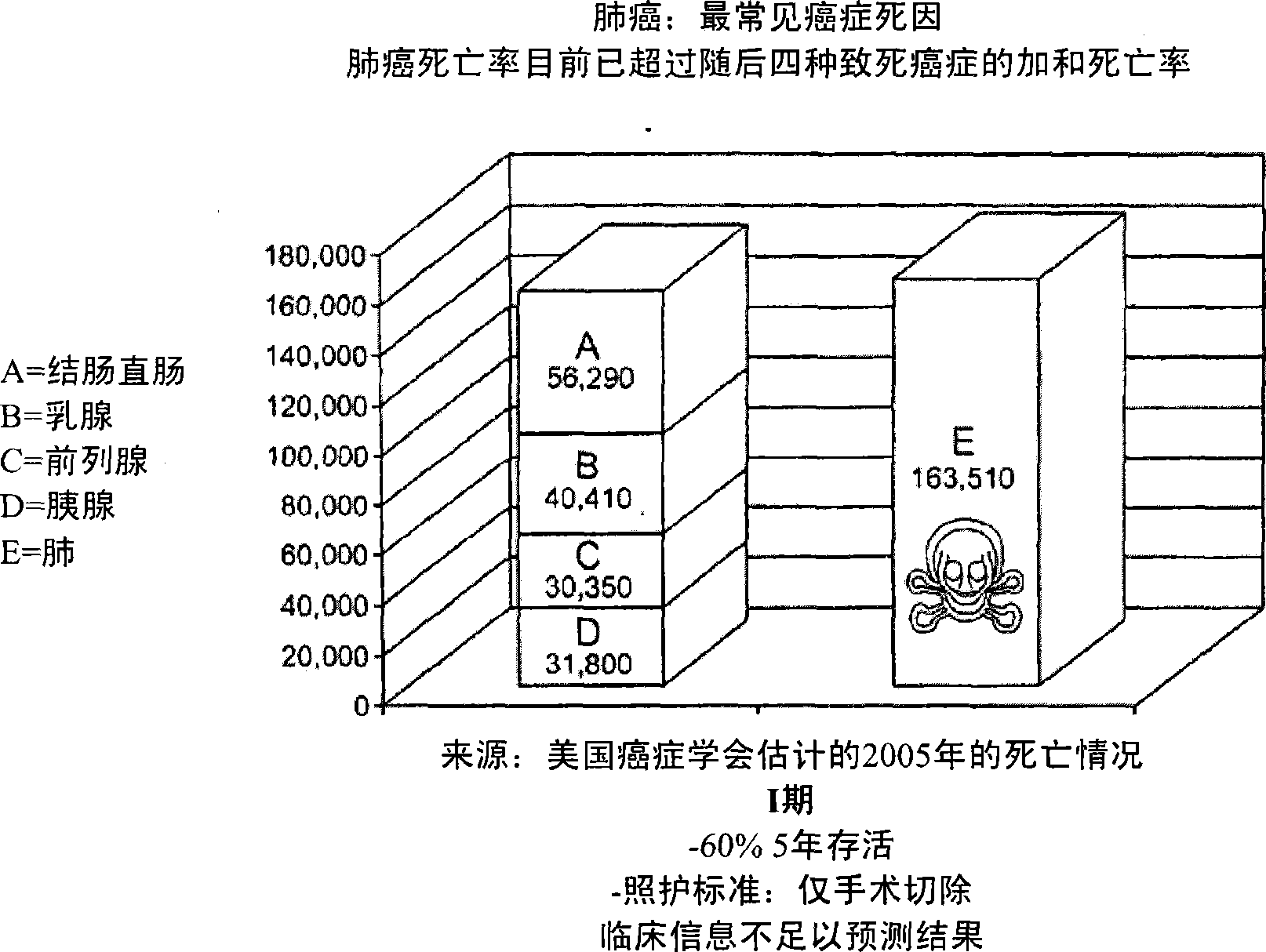
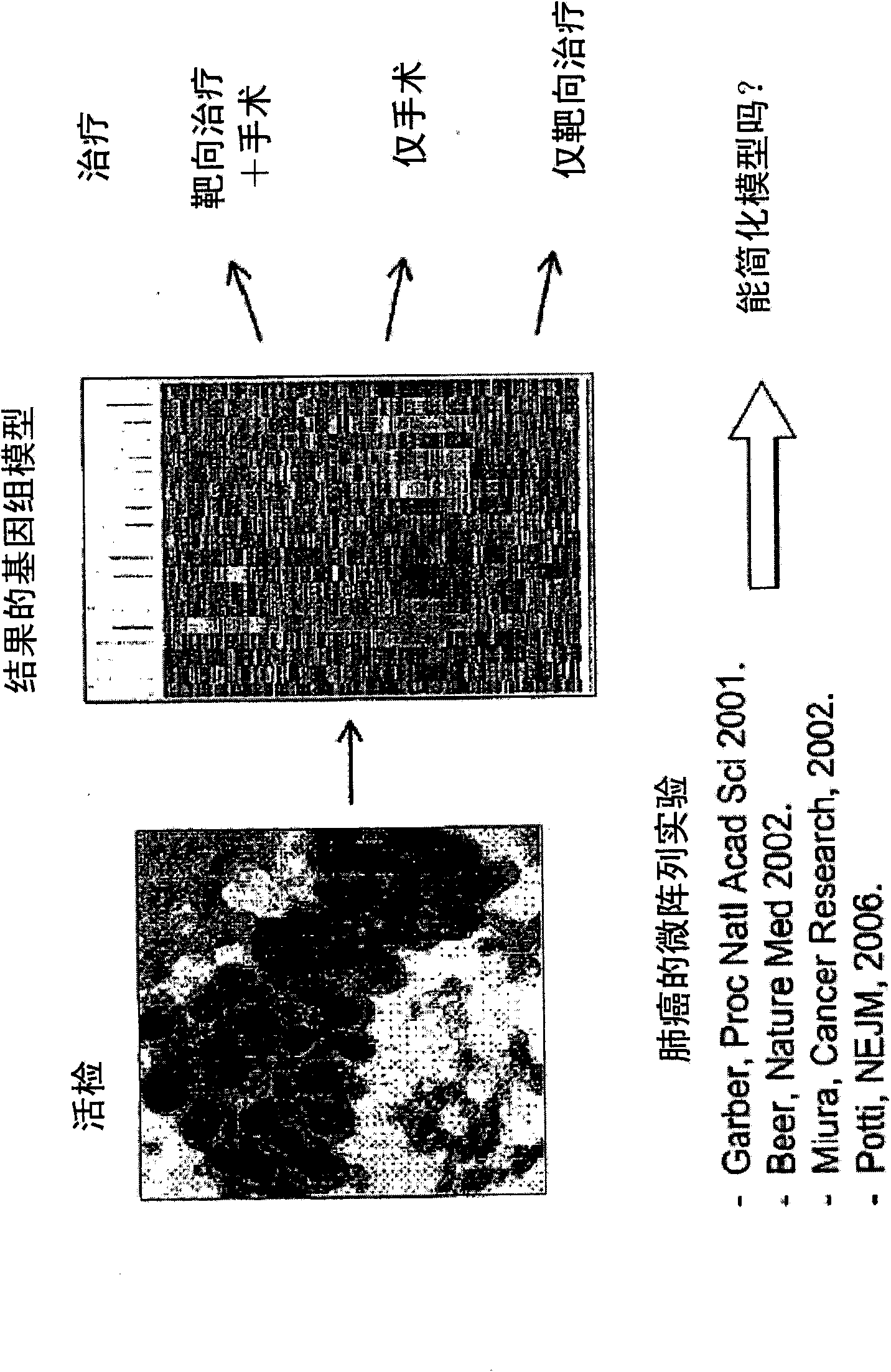
Multigene prognostic assay for lung cancer
A prognostic and lung cancer technology, applied in the field of multi-gene prognostic test of lung cancer, can solve the problems such as poor long-term survival rate of lung cancer patients
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1 example 1
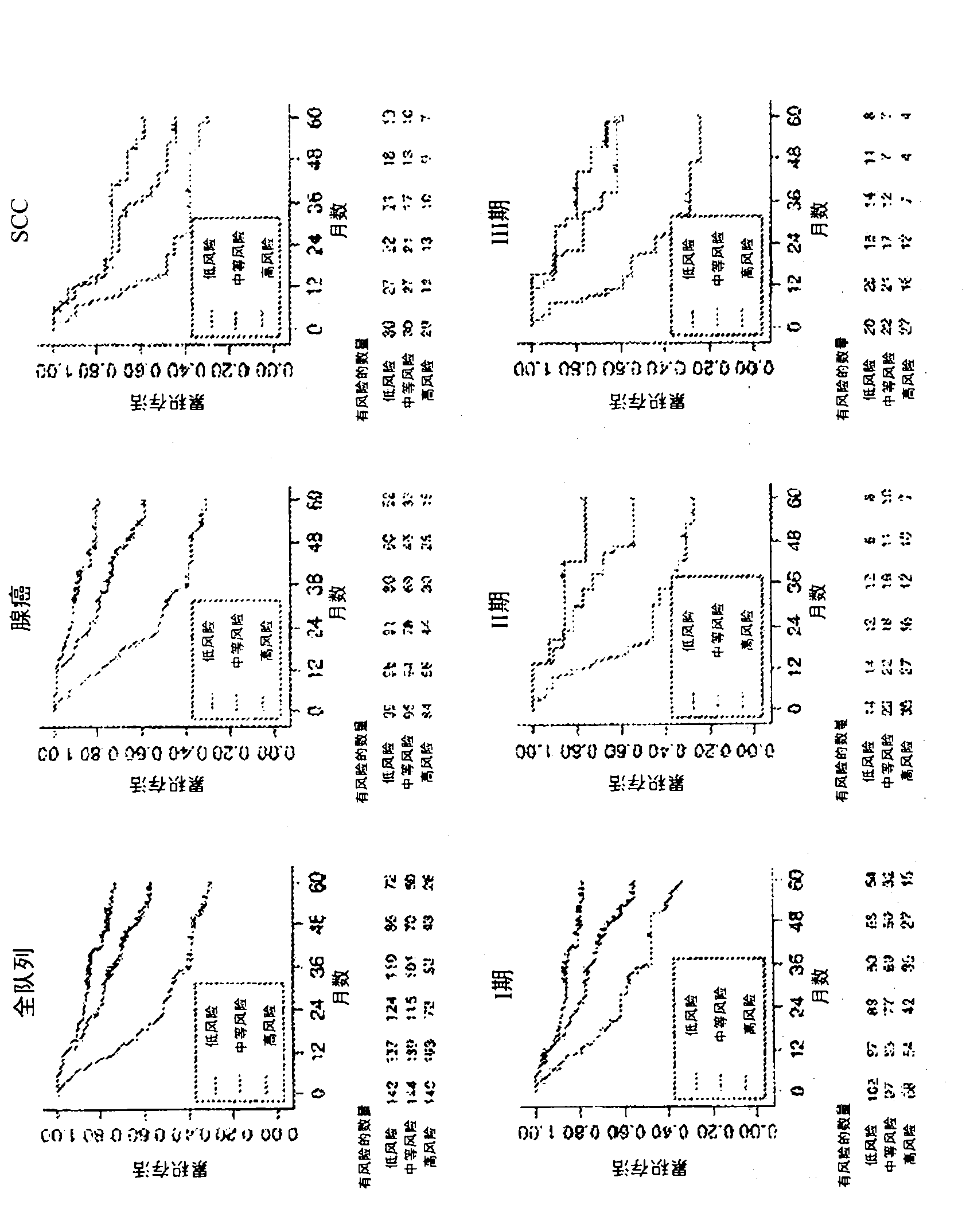
[0120] Example 1. Example 1: Prognostic Trial to Determine Risk Score in Patients with Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC)
[0121] A prognostic test was developed to generate a clinically useful risk score based on the expression patterns of 426 patients undergoing resection of stage I-IV non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) at UCSF. Find a trial that, on average, tends to assign a higher risk score to patients who die from cancer than to those who survive during follow-up. If a patient's sample received a higher risk score, the patient would be considered to have a higher risk of death during the 5-year period following surgery, whereas if a patient's sample received a lower score, the patient would be considered to have a higher risk of death during the 5-year period following his surgery. Time survival is more likely.
[0122]RNA was extracted from FFPE tissue samples and the expression levels of target genes associated with patient prognosis were assessed. Then, the expres...
Embodiment 2
[0164] Example 2: 11-Gene Test to Predict Survival Rate of Resected Non-Squamous Cell Lung Cancer, Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer
[0165] A 14-gene assay using quantitative PCR to analyze formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded (FFPE) tissue was developed with a cohort of 361 patients with resected non-squamous NSCLC at the University of California, San Francisco (UCSF). The assay included 11 biomarkers (BAG1, BRCA1, CDC6, CDK2AP1, ERBB3, FUT3, IL11, LCK, RND3, SH3BGR, and WNT3A) and three housekeeping genes (ESD, TBP, YAP1).
[0166] The test, developed and run by an independent laboratory certified under the Clinical Laboratory Improvement Amendments (CLIA), was later approved by the Kaiser Medical Research Division (KPDOR) at the Kaiser Permanente Northern California System (California, USA). State) in a blinded study design in a cohort of 433 patients with resected stage I non-squamous NSCLC. Trial results were independently compared with actual patient outcomes via KPDOR. Intern...
Embodiment 3
[0239]Example 3: AUROC comparison of the 11-gene assay versus other assays using different gene combinations
[0240] This example predicts the success of the 11-gene assay compared to other gene combinations in assigning patients into high-risk or low-risk categories using the area under the curve of the receiver operating characteristic (AUROC) analysis.
[0241] AUROC analysis was performed on RNA samples extracted from 337 patients with stage I-IV lung cancer. As shown in Table 19 below, it was observed that the 11-gene assay outperformed the other gene combinations tested in this example, as reflected by the higher AUROC c-statistic.
[0242] Table 19: AUROC values
[0243]
[0244]
[0245]
[0246] Selection of the nature of genetic risk
[0247] The 11-gene assay was analyzed using a Cox proportional hazards model to determine which genes confer risk and which genes confer protection. These determinations are listed in Table 20 for each gene.
[0248] Tabl...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com