Dynamic upstream and downstream flow unloading method and system based on heterogeneous network convergence
A heterogeneous network, traffic offloading technology, applied in network traffic/resource management, electrical components, wireless communication, etc., can solve problems such as complex processes and inability to optimize, improve service experience, and avoid network overload problems.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0099] In the scenario where LTE and WLAN RATs coexist, it is assumed that the LTE and WLAN loads respectively reach 50% of their maximum loads at this time, and the network does not face the risk of overloading. When a user initiates a service request, (only discussing user terminal packet-level traffic offloading under dual connections), the specific process of uplink traffic offloading is as follows:
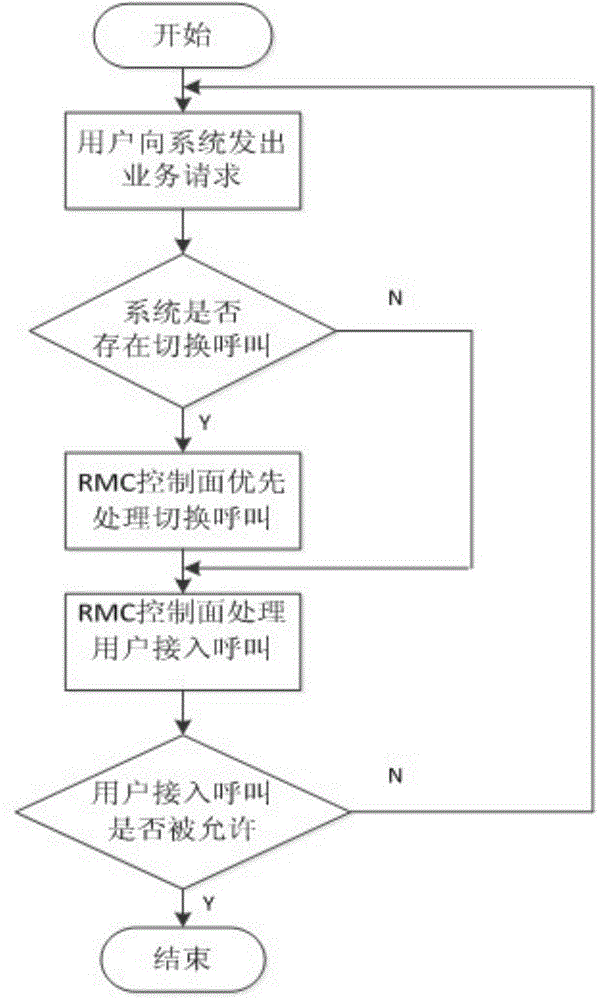
[0100] Step 1: The access control module of the RMC layer determines the network status of the user terminal without affecting the existing user network status by comprehensively considering the network status such as signal quality, call blocking rate, call drop rate, data packet delay and packet loss rate, etc. Simultaneously connect to both LTE and WLAN RATs for service transmission.
[0101] Step 2: The multi-mode base station side performs periodic or timing measurement on the network status (channel quality, RAT load), and determines that the user terminal occupies 25% ...
Embodiment 2
[0106] In a scenario where two RATs of LTE and WLAN coexist, it is assumed that the WLAN load reaches 90% of its maximum load at this time. When user 1 initiates a service request, the specific process of uplink traffic offloading is as follows:
[0107] Step 1: The access control module of the RMC layer determines the network status of the user terminal without affecting the existing user network status by comprehensively considering the network status such as signal quality, call blocking rate, call drop rate, data packet delay and packet loss rate, etc. Simultaneously connect to both LTE and WLAN RATs for service transmission.
[0108] Step 2: The multi-mode base station measures the network status (channel quality, RAT load) periodically, determines that the user terminal occupies 25% of the LTE resources and 75% of the WLAN resources for the service transmission according to the uplink traffic offloading control algorithm, and The user terminal is notified through contro...
Embodiment 3
[0114] In the scenario where LTE and WLAN RATs coexist, assuming that user 1 and user 2 respectively initiate file transfer requests and voice requests in the case of dual links, the specific process of downlink traffic offloading is as follows:
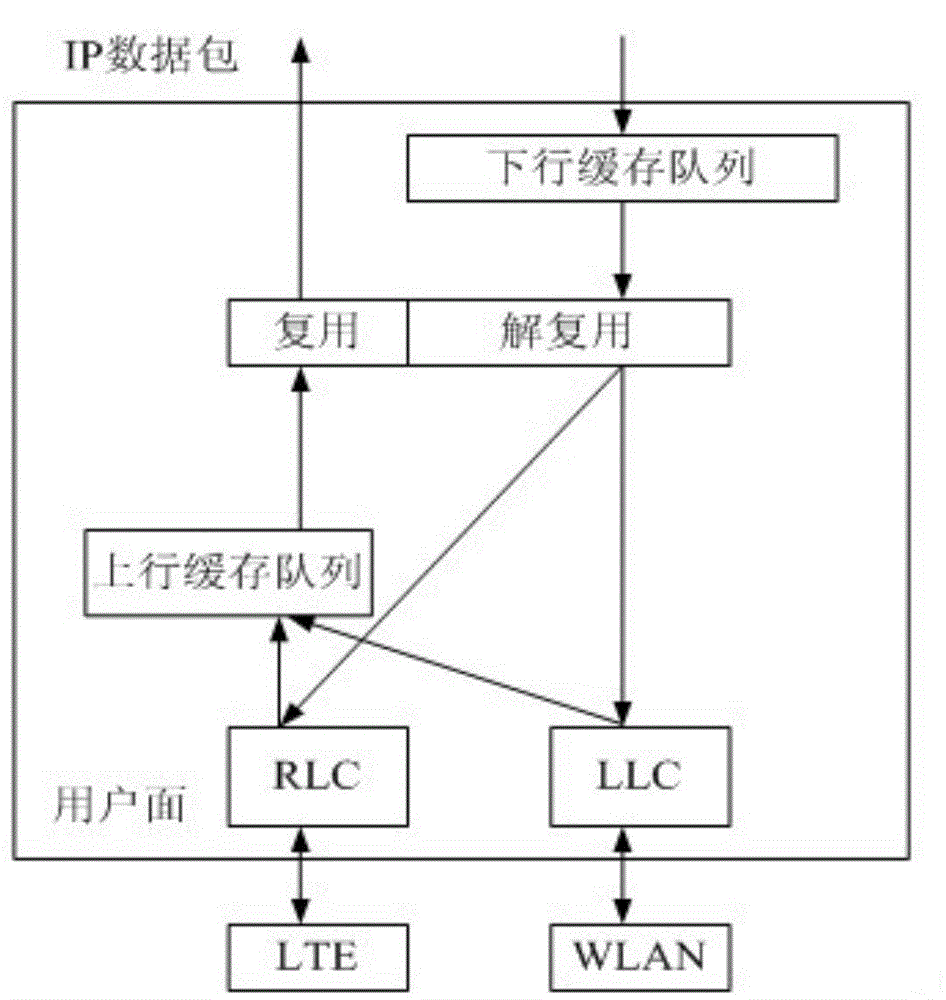
[0115] Step 1: In order to ensure that the data is not lost and processed in an orderly and reasonable manner, the IP data packets from the core network first arrive at the downlink buffer area of the RMC layer, so that the IP data packets wait for processing in a certain order.
[0116] Step 2: Report the state of the downlink buffer queue to the relevant resource scheduling module and traffic offloading module of the control plane, adjust the resource scheduling strategy according to the queuing situation, and ensure that no packet loss is caused when the demultiplexing module at the RMC layer is processed. And optimize resources to the greatest extent.
[0117] Step 3: The multi-mode base station periodically measures the networ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com