A high molecular weight chitosan material with controllable molecular weight suitable for 3D printing and its molding method
A high-molecular weight, 3D printing technology, applied in the field of 3D printing materials and their forming, can solve problems such as difficult to meet the mechanical strength of bone materials, and achieve the effect of shape control
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
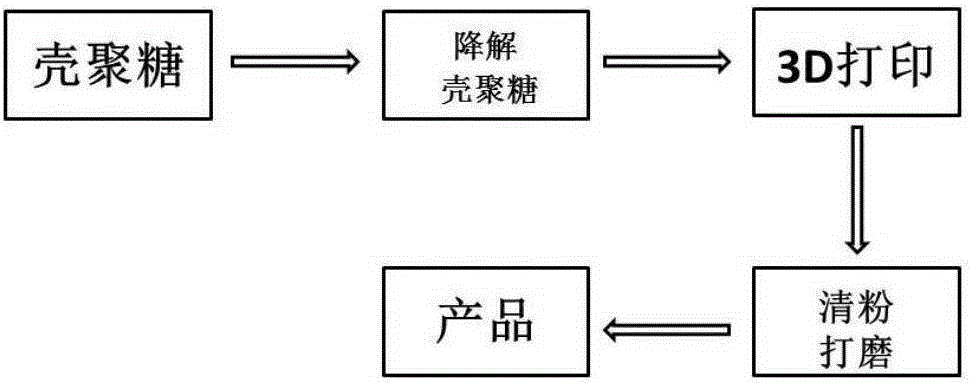
[0038] The preparation method that the present invention applies:
[0039] 1. Add 25 parts by weight of 600KD chitosan finished product to 75 parts by weight so that the weight fraction is 1.3×10 -4 HCl solution. 25 parts by weight of chitosan solution were obtained after reflux and stirring degradation reaction in a constant temperature water bath at 50° C. for 6 hours.
[0040] 2. Add 0.1 part by weight of heat stabilizer to 25 parts by weight of chitosan solution, and dry in vacuum at 70° C. for 24 hours. To obtain chitosan powder.
[0041] The forming technique that the present invention applies:
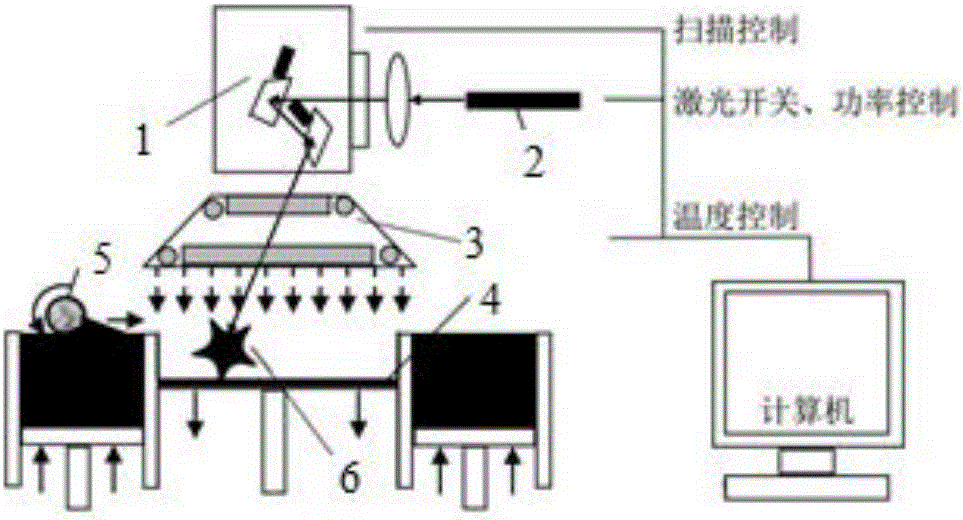
[0042] Spread the chitosan powders with different molecular weights obtained in step 2 on the workbench of the laser sintering 3D printer FORMIGAP110 from EOS, Germany, and control the sintering temperature to 100 °C. The component model is made through computer CAD-aided design, and then the computer (equipped with Windows operating system) controls the 3D printer to scan t...
Embodiment 2
[0048] The preparation method that the present invention applies:
[0049] 1. Add 25 parts by weight of 600KD chitosan finished product to 75 parts by weight so that the weight fraction is 1.3×10 -4 HCl solution. 25 parts by weight of chitosan solution were obtained after reflux and stirring degradation reaction in a constant temperature water bath at 50° C. for 12 hours.
[0050] 2. Add 0.1 part by weight of heat stabilizer to 25 parts by weight of chitosan solution, and dry in vacuum at 70° C. for 24 hours. To obtain chitosan powder.
[0051] The forming technique that the present invention applies:
[0052] Spread the chitosan powders with different molecular weights obtained in step 2 on the workbench of the laser sintering 3D printer FORMIGAP110 from EOS, Germany, and control the sintering temperature to 100 °C. The component model is made through computer CAD-aided design, and then the computer (equipped with Windows operating system) controls the 3D printer to scan th...
Embodiment 3
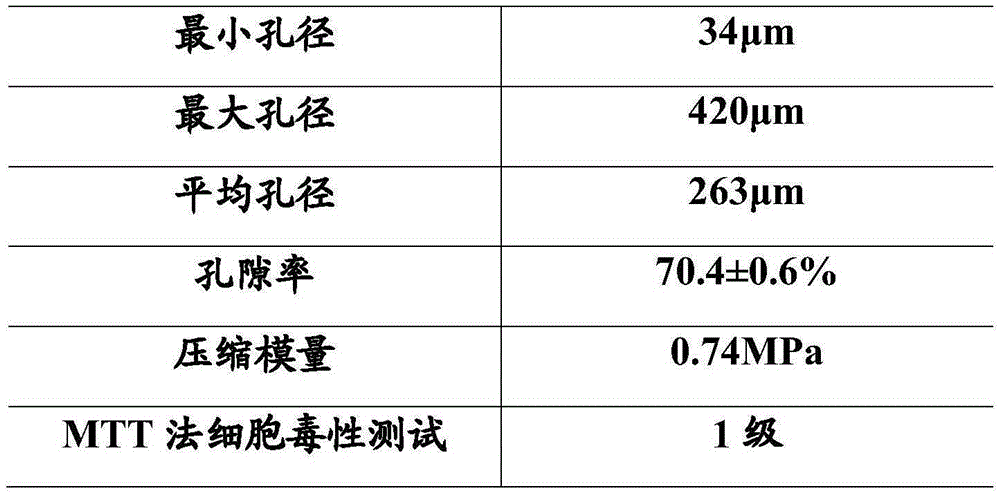
[0057] Embodiment 3: As an optimization of the above embodiment, a porous composite material is made, the raw material includes a high molecular weight chitosan substrate, and the toughening agent includes carbon nanotubes, hydroxyapatite, and nano-calcium carbonate.
[0058] The specific preparation method is as follows:
[0059] 1. Add 25 parts by weight of 600KD chitosan finished product to 5 parts by weight of toughening agent (carbon nanotubes: hydroxyapatite: nano calcium carbonate = 2:4:4) and 70 parts by weight. The weight fraction is 1.3× 10 -4 HCl solution. A 25% chitosan solution was obtained after the degradation reaction was carried out under reflux and stirring in a constant temperature water bath at 50° C. for 12 hours.
[0060] 2. Add 0.1 parts by weight of heat stabilizer to the 25% chitosan solution prepared in step 1, and vacuum dry at 70° C. for 24 hours to obtain chitosan powder.
[0061] The forming technique that the present invention applies:
[006...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com