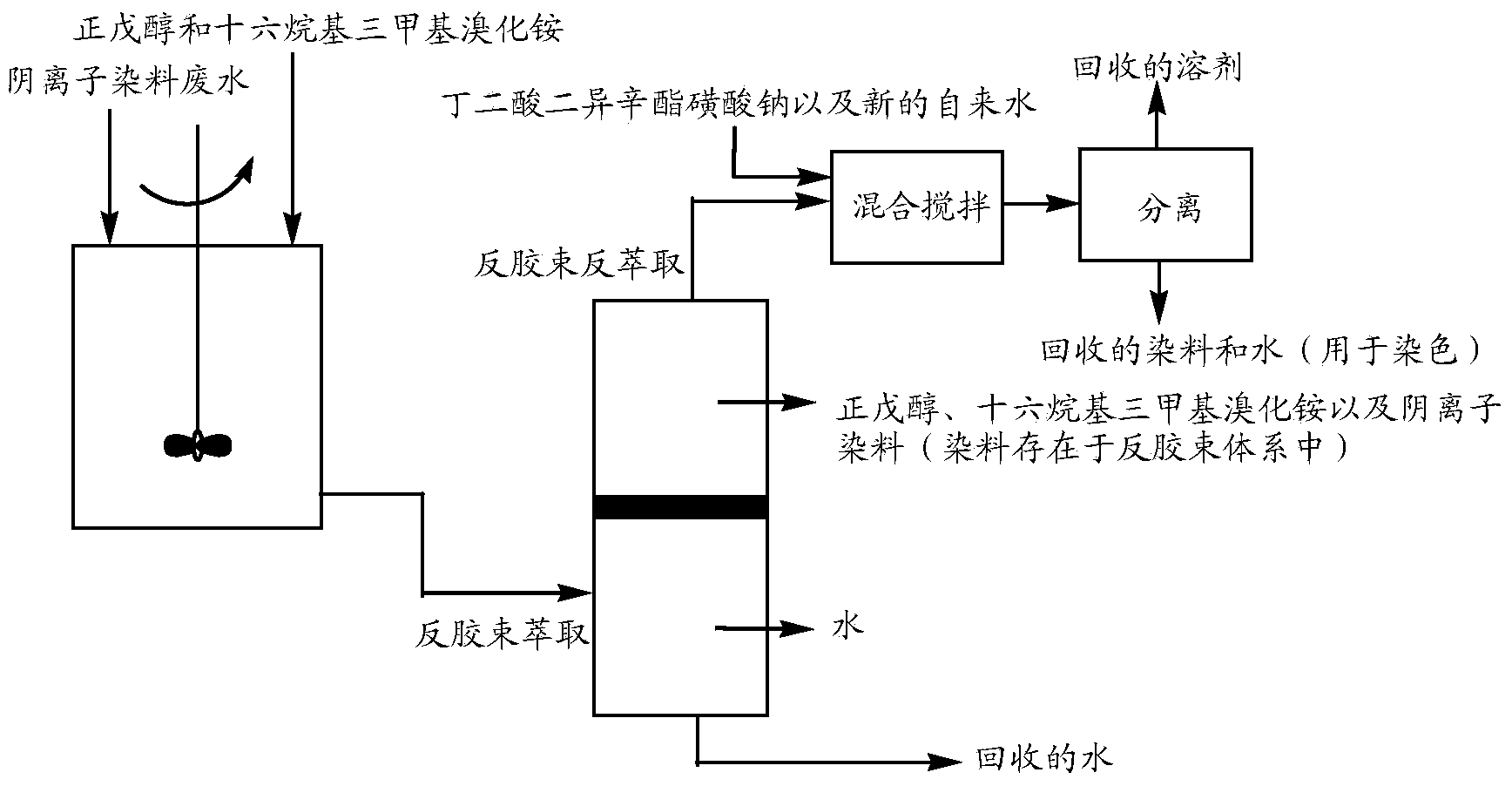
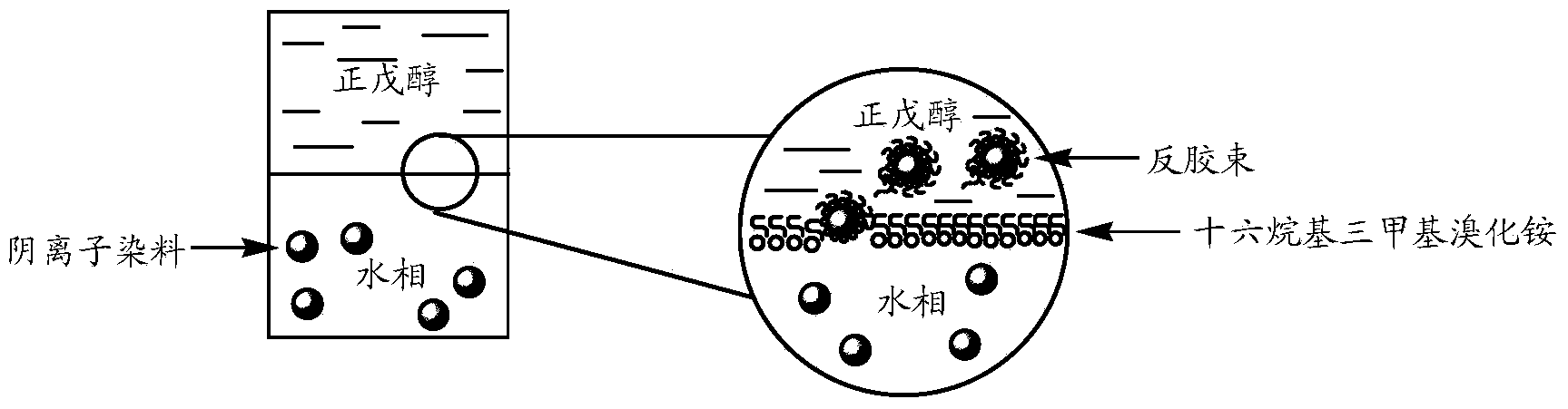
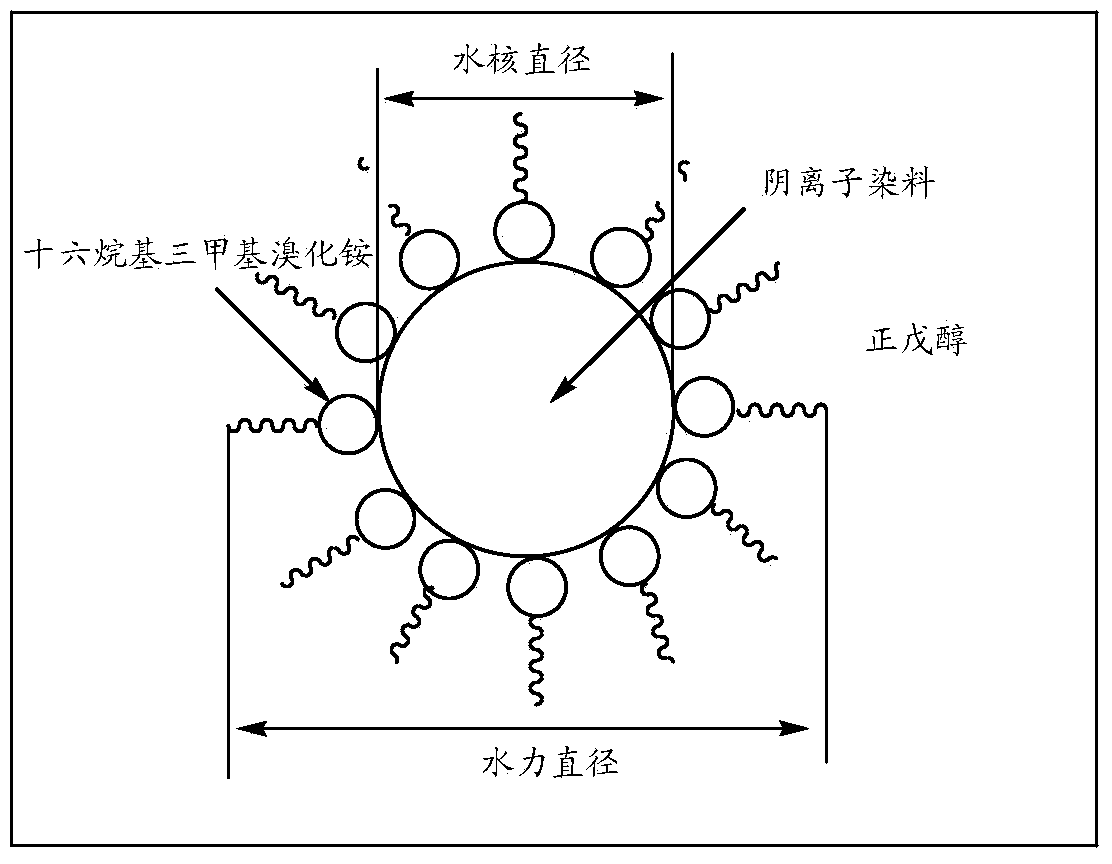
Reverse micelle dye extraction and recycling method for textile dyeing waste water
A technology of dyeing wastewater and reverse micelles, which is applied in textile industry wastewater treatment, organic dyes, extraction water/sewage treatment, etc., can solve the problem that dyes cannot be reused, achieve significant cost advantages, simple preparation process, and low cost Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0040] The present embodiment extracts the reactive red 195 dyeing waste water of 100ml concentration 0.2g / L, pre-extraction 300ml, wherein each component in pre-extraction and back-extraction is:
[0041] Pre-extraction: cetyltrimethylammonium bromide and n-pentanol, the weight ratio is 1:2000;
[0042] Post-extraction: sodium dioctyl sulfonate succinate, the weight ratio of the dosage to n-amyl alcohol in the pre-extraction is 1:2000.
[0043] The specific steps are:
[0044] 1) Filtration treatment of textile dyeing wastewater, mainly to remove fiber debris generated during the dyeing process;
[0045] 2) Pre-extraction of reverse micelles: First, add the extract to the dyeing wastewater, and fully stir it at a temperature of 15 degrees for 60 minutes. In 60 minutes, the anionic dye in the dyeing wastewater gradually entered the organic solvent n-amyl alcohol under the electrostatic attraction of the cationic surfactant cetyltrimethylammonium bromide. figure 2 As shown,...
Embodiment 2
[0050] The present embodiment extracts the reactive red 195 dyeing waste water of 100ml concentration 0.6g / L, pre-extraction 165ml, wherein each component in pre-extraction and back-extraction is:
[0051] Pre-extraction: cetyltrimethylammonium bromide and n-pentanol, the weight ratio is 1:1500;
[0052] Post-extraction: sodium dioctyl sulfonate succinate, the weight ratio of the dosage to n-amyl alcohol in the pre-extraction is 1:1500.
[0053] The specific steps are:
[0054] 1) Filtration treatment of textile dyeing wastewater, mainly to remove fiber debris generated during the dyeing process;
[0055] 2) Pre-extraction of reverse micelles: First, add the extract to the dyeing wastewater, and fully stir it at a temperature of 25 degrees for 30 minutes, then make the mixed solution static and layered under gravity, and the static time is In 30 minutes, the anionic dye in the dyeing wastewater gradually entered the organic solvent n-amyl alcohol under the electrostatic attr...
Embodiment 3
[0060] The present embodiment extracts the reactive red 195 dyeing waste water of 100ml concentration 1.0g / L, pre-extraction 30ml, wherein each component in pre-extraction and back-extraction is:
[0061] Pre-extraction: cetyltrimethylammonium bromide and n-pentanol, the weight ratio is 1:2500;
[0062] Post-extraction: sodium dioctyl sulfonate succinate, the weight ratio of the dosage to n-amyl alcohol in the pre-extraction is 1:2500.
[0063] The specific steps are:
[0064] 1) Filtration treatment of textile dyeing wastewater, mainly to remove fiber debris generated during the dyeing process;
[0065] 2) Pre-extraction of reverse micelles: First, add the extract to the dyeing wastewater, and fully stir it at a temperature of 35 degrees for 10 minutes, and then make the mixed solution static and layered under the action of gravity, and the static time is In 10 minutes, the anionic dyes in the dyeing wastewater gradually entered the organic solvent n-amyl alcohol under the ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com