Micro-power-consumption M-bus slave end circuit for intelligent instrument communication and communication method thereof
A smart instrument, micro-power consumption technology, applied in the direction of instruments, computer control, general control systems, etc., can solve the problems of slow communication speed, poor circuit stability of simple discrete components, complex peripheral devices, etc., to reduce power consumption and communication speed unaffected effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
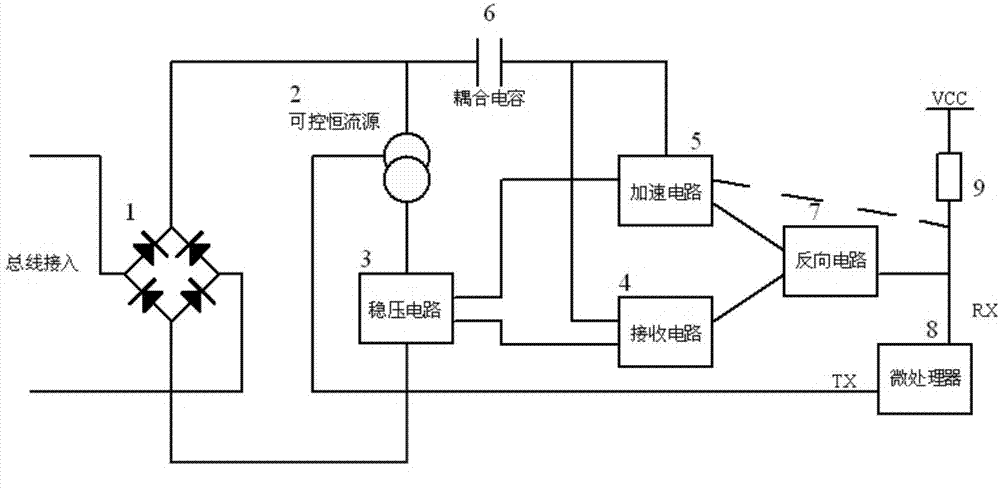
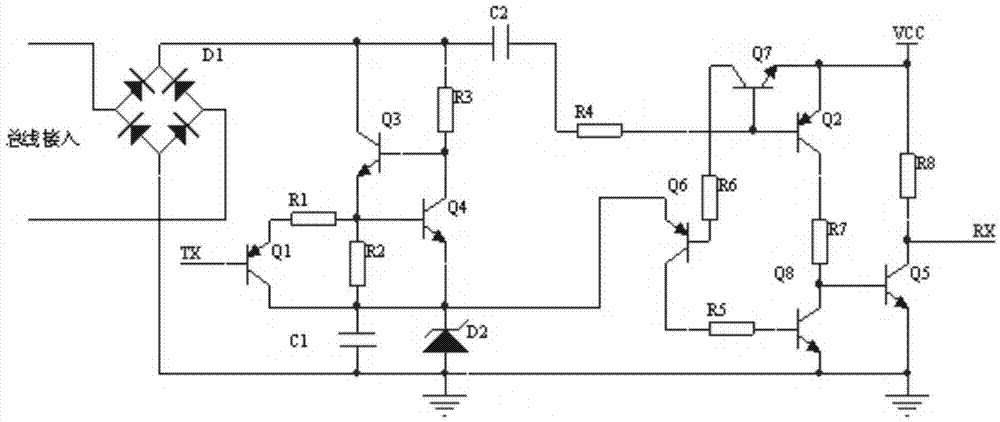
[0018] Such as figure 1 , 2 shown, corresponding to figure 2 In the embodiment circuit, the controllable constant current source 2 circuit is composed of triode Q1, triode Q3, triode Q4, resistor R2, and resistor R3, wherein the constant current source circuit is composed of triode Q3, triode Q4, resistor R2, and resistor R3. R1 and transistor Q1 are constant current source control circuits. Capacitor C1 , voltage regulator tube D2 and the controllable constant current source circuit constitute a voltage regulator circuit 3 , and capacitor C2 and resistor R4 constitute a coupling circuit 6 . Transistor Q2 and resistor R7 form receiving circuit 4, triode Q6, triode Q7, triode Q8, resistor R5 and resistor R6 form acceleration circuit 5, triode Q5 and resistor R8 form reverse circuit 7.
Embodiment 2
[0020] On the basis of the circuit in Embodiment 1, the data communication method provides a stable initial voltage on the bus. When there is data, a falling edge appears on the bus, the voltage decreases, and the receiving circuit 4 receives the signal from high to low. A high potential is output from the transistor Q2, which is passed through the resistor R7 to the reverse circuit 7, and then output to the low level of RX after inversion; when the bus returns to the initial voltage and the voltage rises, there will be a rising edge signal from low to high, and the receiving In the circuit, the transistor Q2 is turned off, the receiving circuit 4 is turned off, the transistor Q7 in the acceleration circuit 5 is turned on, the transistor Q6 is turned on, and the transistor Q8 is turned on, so that the accelerated transistor Q5 is cut off, and RX outputs a high level. This completes the physical circuit for the entire process of receiving data. The sending circuit is composed o...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com