System and method for calculating time lag stability upper limit based on generalized eigenvalue
A generalized eigenvalue and time-delay system technology, applied in the field based on generalized eigenvalues, can solve high conservatism problems
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
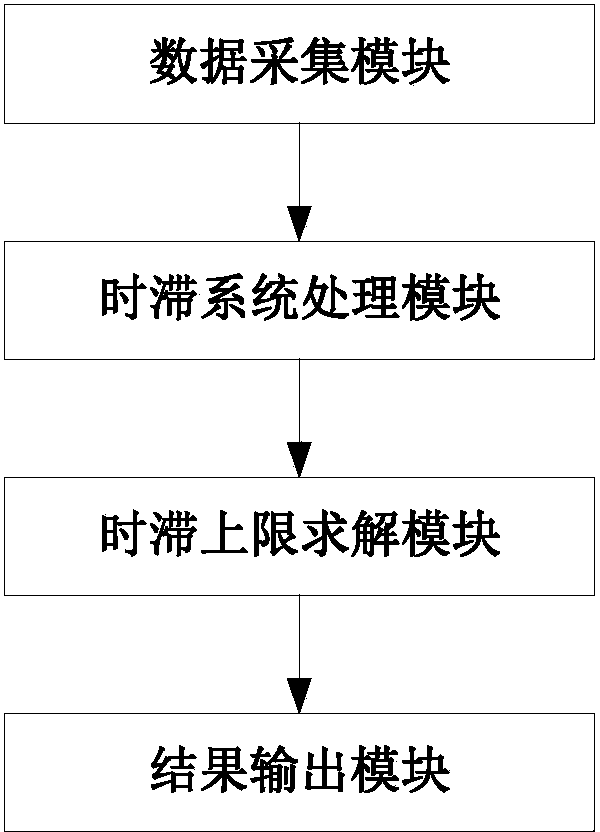
[0060] figure 1 It is a structural diagram of the calculation system of the time-delay stability upper limit based on the generalized eigenvalue provided by the present invention. Such as figure 1 As shown, the structure diagram of the time-delay stability upper limit calculation system based on generalized eigenvalues provided by the present invention includes sequentially connected data acquisition modules, time-delay system processing modules, time-delay upper limit solution modules and result output modules.
[0061] The data collection module is used to collect network structure parameters, generator frequency and generator power angle, and send the collected data to the time-delay system processing module. Among them, the network structure parameters are the parameters needed to establish the state equation of the time-delay system, and the generator frequency and generator power angle are the state vectors in the state equation of the time-delay system.
[0062] The...
Embodiment 2
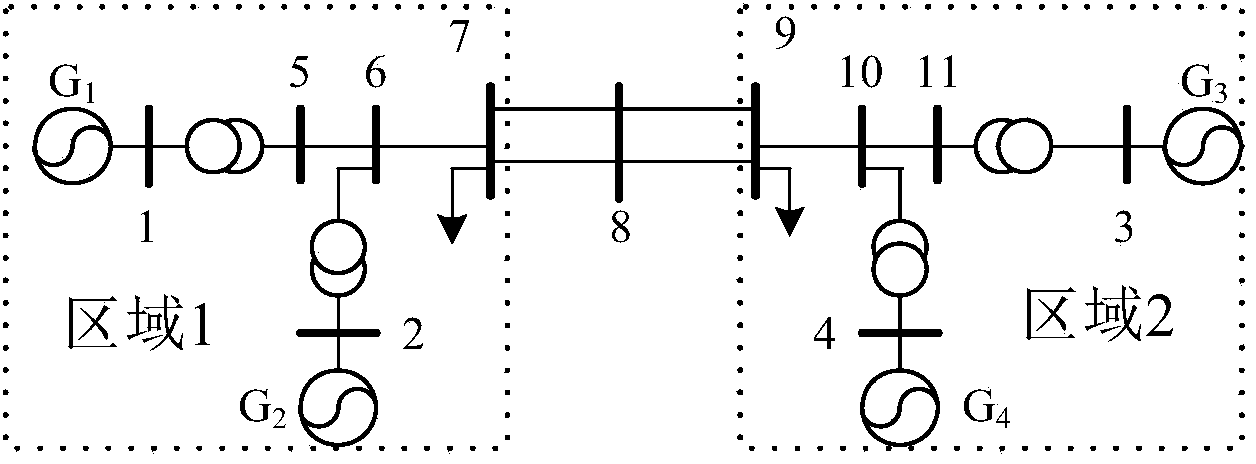
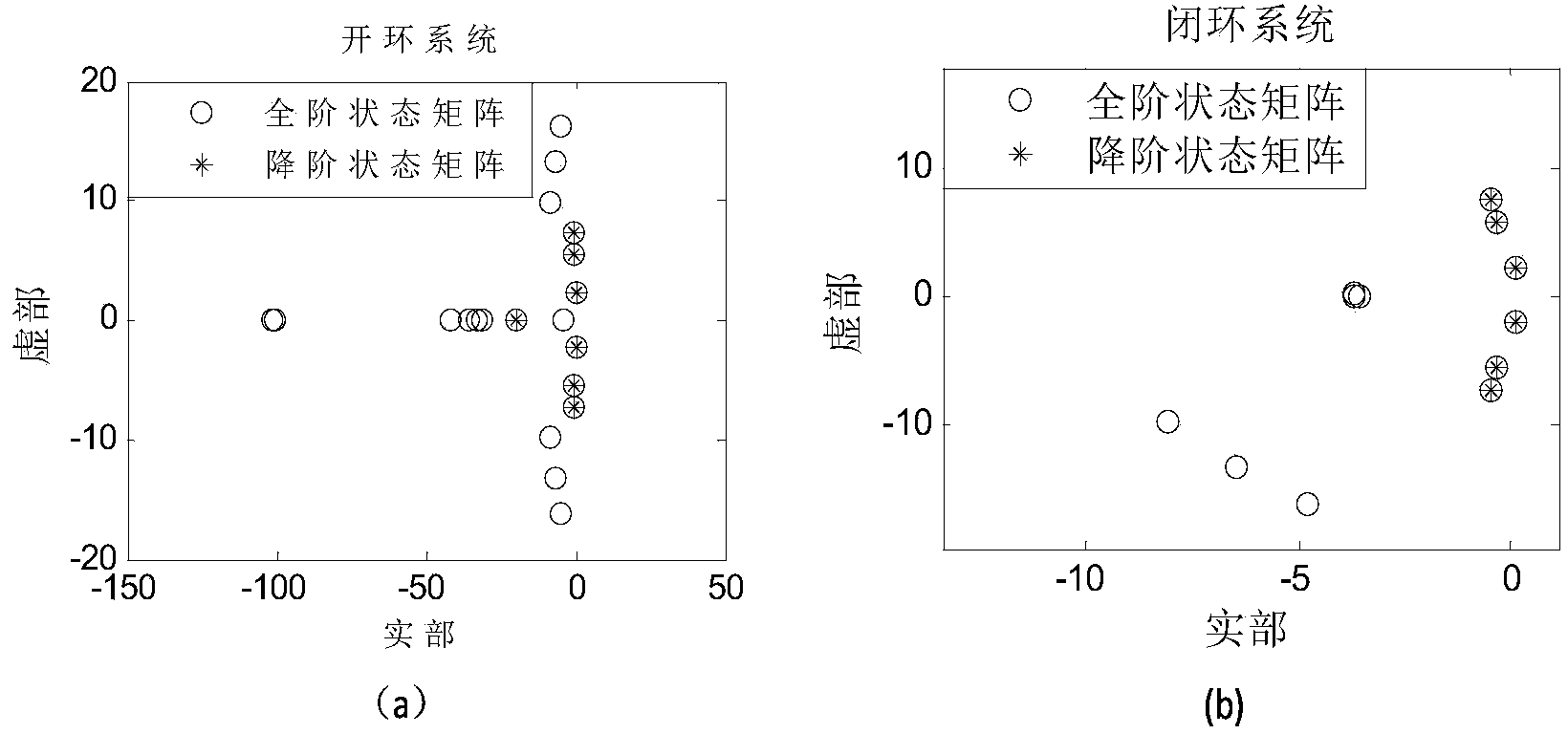
[0145] Built based on MATLAB simulation software figure 2 In the IEEE4-machine 11-node system shown, the generator adopts a 6-order detailed model, the excitation system adopts fast excitation, and the load under the benchmark model adopts a 50% constant impedance and 50% constant current model. First, the state matrix of the four-machine system is obtained by the modal analysis method, and the SMA method is used to reduce the order of the open-loop and closed-loop state matrices, as shown in image 3 shown.
[0146] image 3 (a) is a comparison diagram of the characteristic roots of the full-order open-loop state matrix and the reduced-order open-loop state matrix, and (b) is a comparison diagram of the characteristic roots of the full-order closed-loop state matrix and the reduced-order closed-loop state matrix. Depend on image 3 It can be seen that the low-frequency oscillation components in the system are retained after the order reduction of the open-loop and closed-...
Embodiment 3
[0154] Built based on MATLAB simulation software Figure 8 The shown IEEE16-machine 68-node system further examines the validity and versatility of the maximum time-delay solution method based on the generalized eigenvalue method. The important connection lines of this system are the connection lines 1-2, 1-27 and 8-9 of Area 4 and Area 5. The generator adopts a 6-order detailed model, the excitation adopts IEEE-DC1 type excitation, the load model is 15% constant active power, 25% constant active current and 15% constant reactive power, 25% constant reactive power and 60% constant impedance. First, the Schur balance reduction method is used to reduce the order of the system under the premise that the input and output characteristics of the frequency band of interest remain unchanged, such as Figure 9 shown.
[0155] Figure 9 (a) The solid line is the frequency response of the open-loop full-order system, and the dashed line is the frequency response of the open-loop redu...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com