Application method of papermaking wet-strength agent
An application method and technology of wet strength agent, applied in the application field of papermaking wet strength agent, can solve the problems of paper product strength reduction, unfavorable environmental protection, PAE papermaking pollution, etc., to ensure the strength of paper products, reduce waste water pollution, weaken The effect of corrosion
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
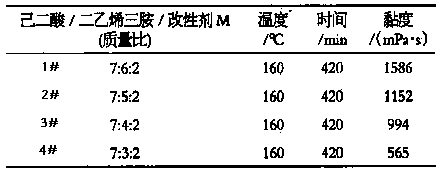
[0019] See the 1# experiment in Table 1. Dissolve diethylenetriamine in water to make a 30% solution, then add adipic acid. At this time, the temperature rises automatically, and the water evaporates. The temperature can reach 110-120°C, and then add Modifier M, continue heating to 140-180°C under stirring. After a certain period of time, the heating can be stopped. Slowly add water, lower the temperature to 70°C, add epichlorohydrin to the above intermediate, react for about 2 hours, and keep the pH of the system at 7.5-8.5. When the viscosity reaches the requirement, immediately add hydrochloric acid to adjust the pH and terminate the reaction. In 1#, the mass ratio of adipic acid, diethylenetriamine and modifier M is 7:6:2. The molar ratio between polyamide polyamine and epichlorohydrin is 1:1.4.
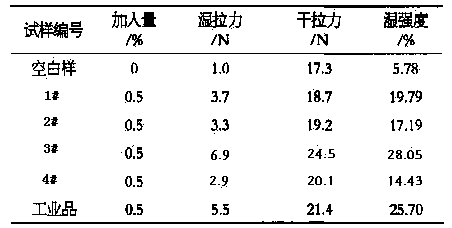
[0020] See the 1# experiment in Table 2, using the modified PAE wet strength agent prepared by 1# in Table 1, with a solid content of 12.5%, diluted with water to 1:10, and add...
Embodiment 2
[0022] See the 2# experiment in Table 1. Dissolve diethylenetriamine in water to make a 30% solution, and then add adipic acid. At this time, the temperature rises automatically, and the water evaporates. The temperature can reach 110-120°C, and then add Modifier M, continue heating to 140-180°C under stirring. After a certain period of time, the heating can be stopped. Slowly add water, lower the temperature to 70°C, add epichlorohydrin to the above intermediate, react for about 2 hours, and keep the pH of the system at 7.5-8.5. When the viscosity reaches the requirement, immediately add hydrochloric acid to adjust the pH and terminate the reaction. In 1#, the mass ratio of adipic acid, diethylenetriamine and modifier M is 7:5:2. The molar ratio between polyamide polyamine and epichlorohydrin is 1:1.4.
[0023] See the 2# experiment in Table 2, using the modified PAE wet strength agent prepared by 1# in Table 1, with a solid content of 12.5%, diluted with water to 1:10, and...
Embodiment 3
[0025] See experiment 3# in Table 1. Dissolve diethylenetriamine in water to make a 30% solution, and then add adipic acid. At this time, the temperature rises automatically, and the water evaporates. The temperature can reach 110-120°C, and then add Modifier M, continue heating to 140-180°C under stirring. After a certain period of time, the heating can be stopped. Slowly add water, lower the temperature to 70°C, add epichlorohydrin to the above intermediate, react for about 2 hours, and keep the pH of the system at 7.5-8.5. When the viscosity reaches the requirement, immediately add hydrochloric acid to adjust the pH and terminate the reaction. In 1#, the mass ratio of adipic acid, diethylenetriamine and modifier M is 7:4:2. The molar ratio between polyamide polyamine and epichlorohydrin is 1:1.4.
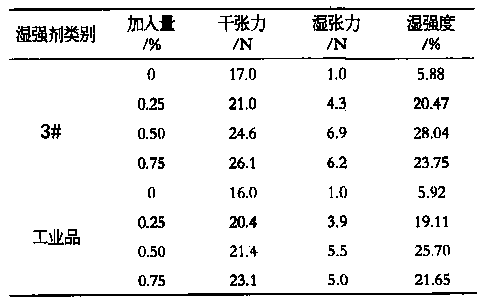
[0026] See the 3# experiment in Table 2, using the modified PAE wet strength agent prepared by 1# in Table 1, with a solid content of 12.5%, diluted with water to 1:10, and add...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| viscosity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| solid content | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com