Low-cost sulfur-tolerant shift catalyst and preparation method thereof
A sulfur-resistant shift, catalyst technology, applied in chemical instruments and methods, physical/chemical process catalysts, metal/metal oxide/metal hydroxide catalysts, etc. To solve the problems of large amount and other problems, it can achieve the effects of simple process, good structure and activity stability, and reduced preparation cost.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
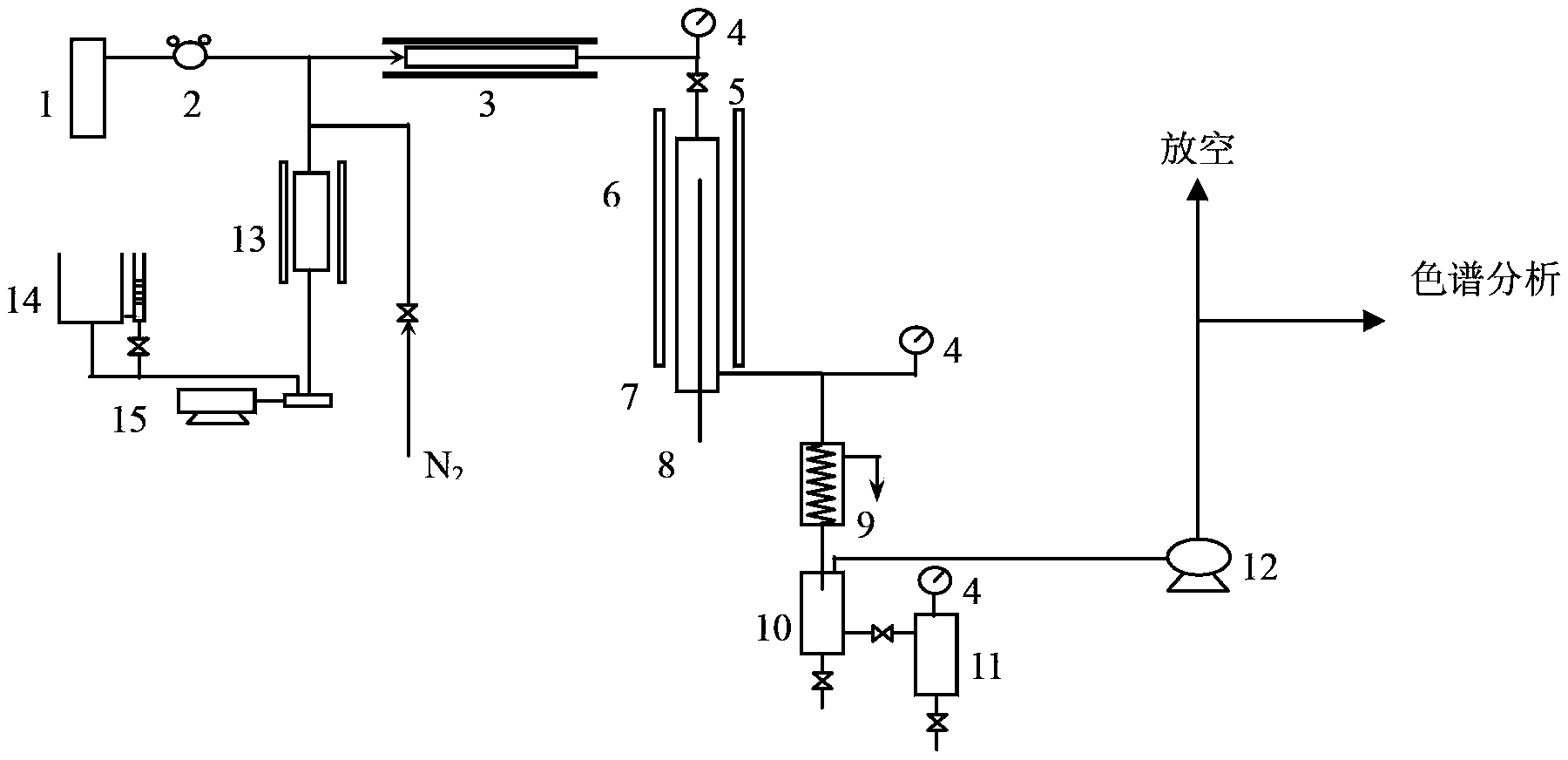
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0038] The attapulgite clay was first calcined at 800°C for 2 hours, and then crushed through a 160-mesh sieve.
[0039] Dissolve 1.23g of ammonium molybdate in 40.0ml of deionized water to obtain solution A containing molybdenum; dissolve 1.94g of cobalt nitrate in 30.0ml of deionized water, then add 2.87g of manganese nitrate and 6.00g of citric acid into the above solution , stirring and dissolving to obtain solution B containing cobalt, manganese and binder.
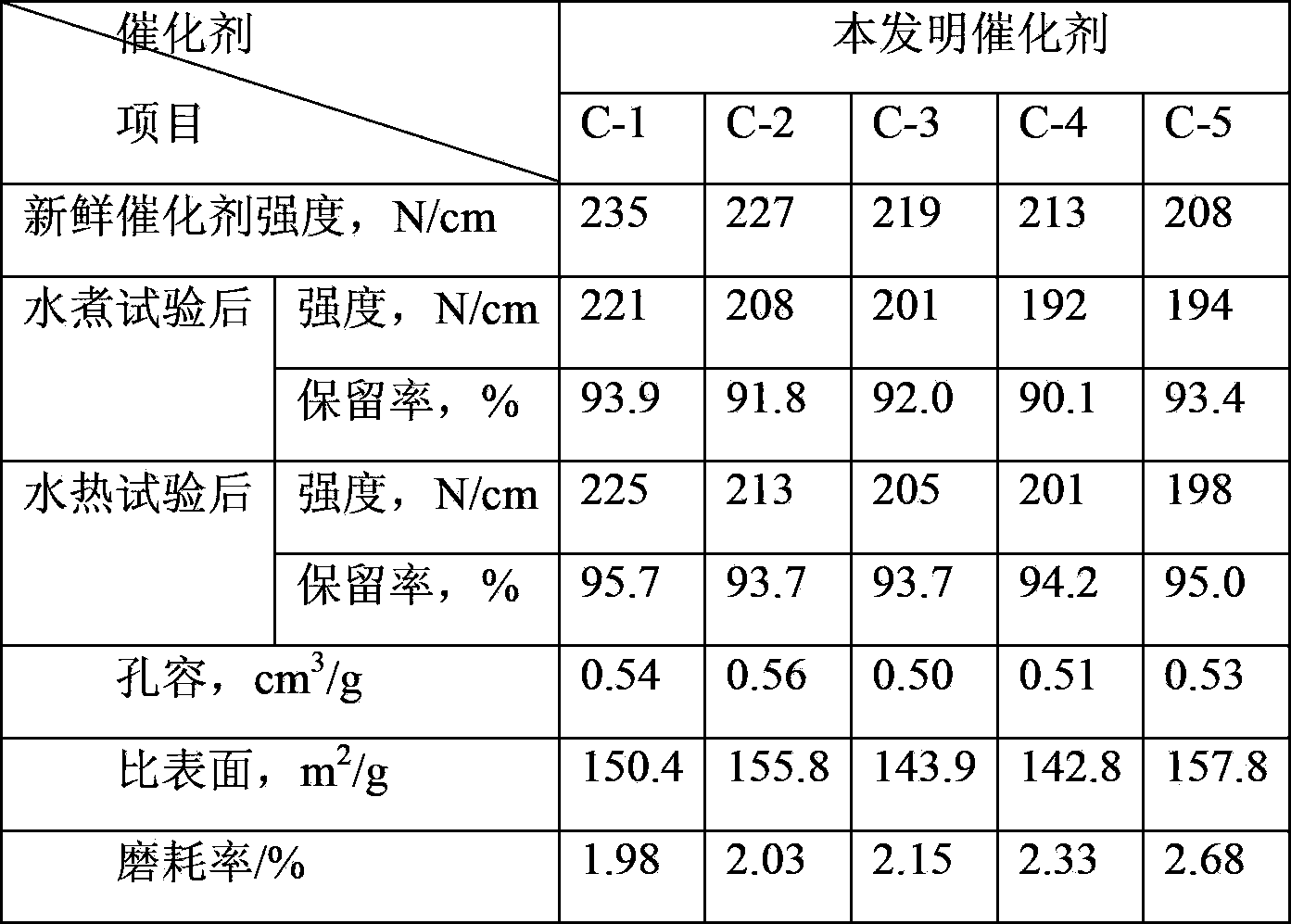
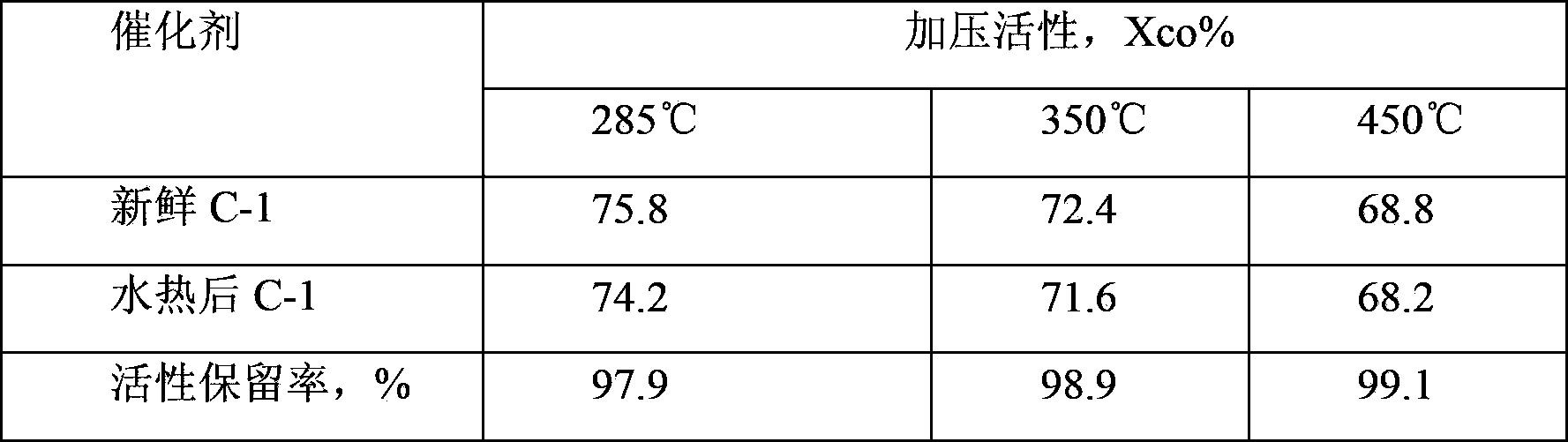
[0040] Weigh 97.50g of the treated attapulgite clay and 8.00g of safflower powder and mix evenly, add solution A to the mixture, knead evenly; then add solution B, knead evenly and shape, dry naturally, at 500°C Calcined for 5 hours to obtain the finished sulfur-tolerant shift catalyst C-1. Its strength, pore structure and activity data are shown in Table 1 and Table 2.
Embodiment 2
[0042] The attapulgite clay was first calcined at 760°C for 2.5 hours, and then crushed through a 160-mesh sieve.
[0043]Dissolve 2.08g ammonium molybdate with 40.0ml deionized water to obtain solution A containing molybdenum; dissolve 2.33g cobalt nitrate with 30.0ml deionized water, then add 4.02g manganese nitrate and 4.00g citric acid to the above solution respectively , stirring and dissolving to obtain solution B containing cobalt, manganese and binder.
[0044] Weigh 96.30g of treated attapulgite clay and 4.0g of starch and mix evenly, add solution A to the mixture, knead evenly; then add solution B, knead evenly, shape, dry naturally, and roast at 530°C for 3.5h , to obtain the finished sulfur-tolerant shift catalyst C-2. Its strength, pore structure and activity data are shown in Table 1 and Table 2.
Embodiment 3
[0046] The attapulgite clay was first calcined at 740°C for 3.5 hours, and then crushed through a 160-mesh sieve.
[0047] Dissolve 2.33g of ammonium molybdate in 40.0ml of deionized water to obtain solution A containing molybdenum; dissolve 3.11g of cobalt nitrate in 30.0ml of deionized water, then add 4.60g of manganese nitrate and 3.00g of citric acid into the above solution , stirring and dissolving to obtain solution B containing cobalt, manganese and binder.
[0048] Weigh 95.70g of treated attapulgite clay and 3.00g of starch and mix evenly, add solution A, knead evenly; then add solution B, knead evenly, shape, dry naturally, and roast at 550°C for 2.5h to obtain the finished sulfur resistant Change Catalyst C-3. Its strength, pore structure and activity data are shown in Table 1 and Table 2.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| specific surface area | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| specific surface area | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com