Method for re-mining residual floor coal in fully-mechanized top coal caving face
A fully-mechanized caving and coal body technology, applied in the field of re-mining residual bottom coal, can solve the problems of low recovery efficiency, threats to re-mining safety, and high investment costs, and achieve the effect of alleviating the pressure of enterprises, releasing resource potential and improving economic benefits
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
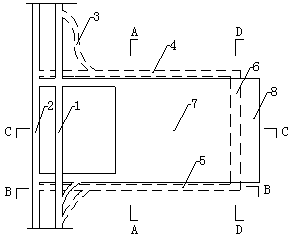
[0043] Such as figure 1 As mentioned above, excavate the detour 3, upper level roadway 4, lower level roadway 5 and cut eye 6 for mining residual bottom coal on the original track uphill 1 and transportation uphill 2, and delineate the re-mining working face 7 (the roadway and working face are indicated by dotted lines) , where the upper and lower level roadways 4 and 5 on the re-mining working face are staggered by a distance of 1~2 roadway widths. In the figure, the solid line indicates the goaf 8, the dotted line indicates the re-mining roadway and the re-mining working face, and the range indicated by the dotted line is below the range of the solid line.
[0044] figure 2 , 3 The spatial position relationship of the roadway layout in the re-production working face and the layout of the exploration and drainage boreholes 9 are described respectively from the direction of inclination and direction. Such as figure 2 As shown, the upper drift 4 and the lower drift 5 are ...
Embodiment 2
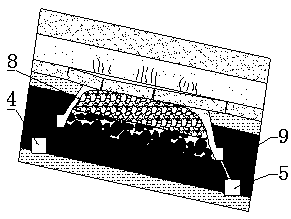
[0046] Such as Figure 4 As shown, the re-mining working face is arranged on the residual bottom coal floor, and a certain thickness of control coal seam 10 is left on the upper part. Controlling the setting of the coal seam 10 solves the problems of low rebonding strength of coal and rock in the goaf, difficult maintenance of the roof, and easy roof fall, etc., and ensures the safety of re-mining. During the re-mining process, the control coal seam 10 and the upper broken coal body 12 are released through the fully-mechanized caving equipment 11, which improves the recovery rate of the residual bottom coal. When the thickness of the remaining bottom coal becomes thinner, the ratio of mining and caving can be properly adjusted to ensure the stability of the control coal seam 10, and when it is too broken, it can be appropriately injected with chemical slurry for reinforcement. This solves the problem of safe and efficient recovery of residual bottom coal.
Embodiment 3
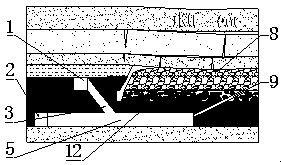
[0048] Such as Figure 5 As shown, after multiple layers of mining, there will be a large number of broken coal bodies 12 left at the bottom of the original goaf 8, which will cause the complete residual bottom coal at the bottom of the coal seam to be relatively thin, and the thickness of the remaining coal seam after the reserved control coal seam 10 is relatively small . At this time, the upper and lower level roadways 4 and 5 are arranged undercover to form a semi-coal and rock roadway, and the thin residual coal re-mining caving support and its supporting equipment are developed for mining.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com