Coated slow-release compound fertilizer and preparation method thereof
A slow-release compound fertilizer and compound fertilizer technology, which is applied in fertilization devices, fertilizer mixtures, applications, etc., can solve the problems of difficulty in achieving compatibility between price and output, high price of final products, and high cost of slow/controlled release fertilizers , to solve the environmental pollution and the quality decline of agricultural products, avoid the problem of secondary environmental pollution, and improve the germination rate and crop quality.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
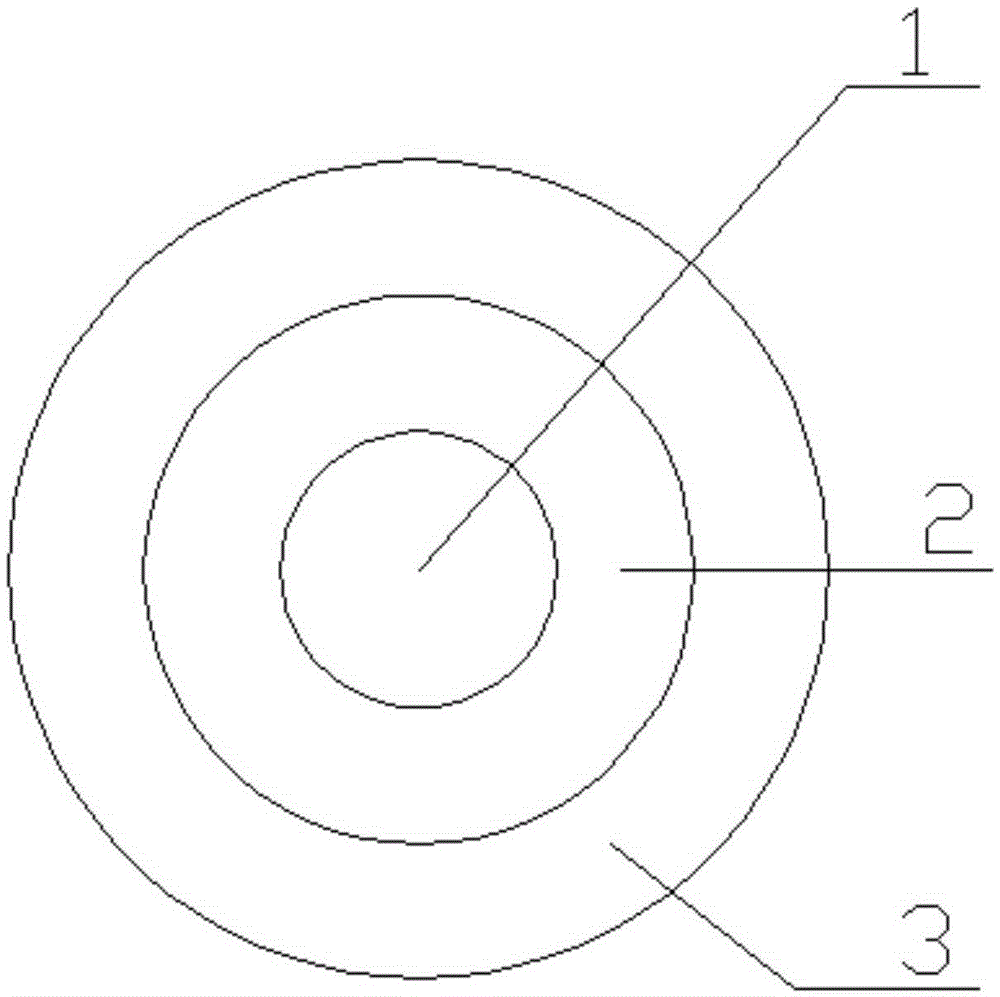
[0055] A coated slow-release compound fertilizer, including a urea core, a coating layer and a hydrophobic layer that coat the urea core from the inside to the outside, the particle size of the urea core is 2 mm, the thickness of the coating layer is 1.3 mm, and the hydrophobic layer The thickness is 0.03mm; the coating layer is formed by high-temperature mixing and melting of powdery nitrogen, powdery phosphorus and powdery potassium, and the powdery nitrogen in the coating layer accounts for 15-25% of the total nitrogen content of the coated slow-release compound fertilizer Wherein the powdery nitrogen is urea, the powdery phosphorus is monoammonium phosphate, and the powdery potassium is potassium chloride; when used for wheat, the weight ratio of nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium in the coating is 19:21:5 , The specific proportions of nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium vary according to the growth needs of different crops, and you can refer to relevant national standards ...
Embodiment 2
[0061] The difference between this embodiment and embodiment 1 is that the weight ratio of nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium in the coating layer 2 is 20:8:12; this embodiment is suitable for planting field corn.
Embodiment 3
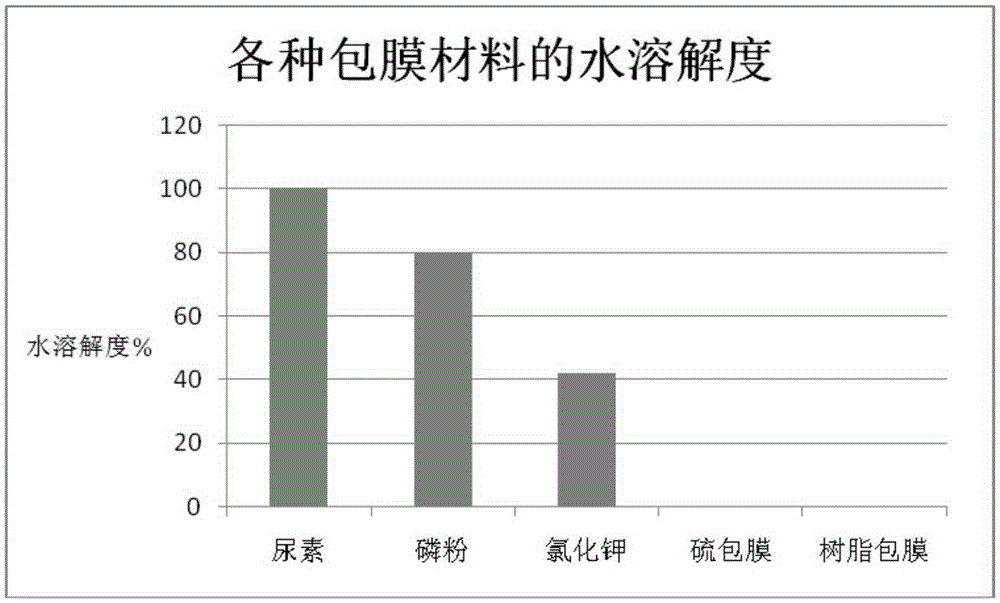
[0062] Embodiment 3, the water solubility test research of different cladding materials
[0063] By comparing the solubility (water solubility) of the coating layer material of the present invention and the sulfur coating and resin coating material in the prior art in water, the specific results are as follows figure 2 As shown, it can be known that the water solubility of the coating layer material of the present invention is much better than that of sulfur-coated and resin-coated slow-release fertilizers.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com