Identification method and equipment for sensibility of bacteria on antibiotic
An identification method and antibiotic technology, applied in the field of microorganisms, can solve complex problems and achieve the effect of shortening the time required for identification
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
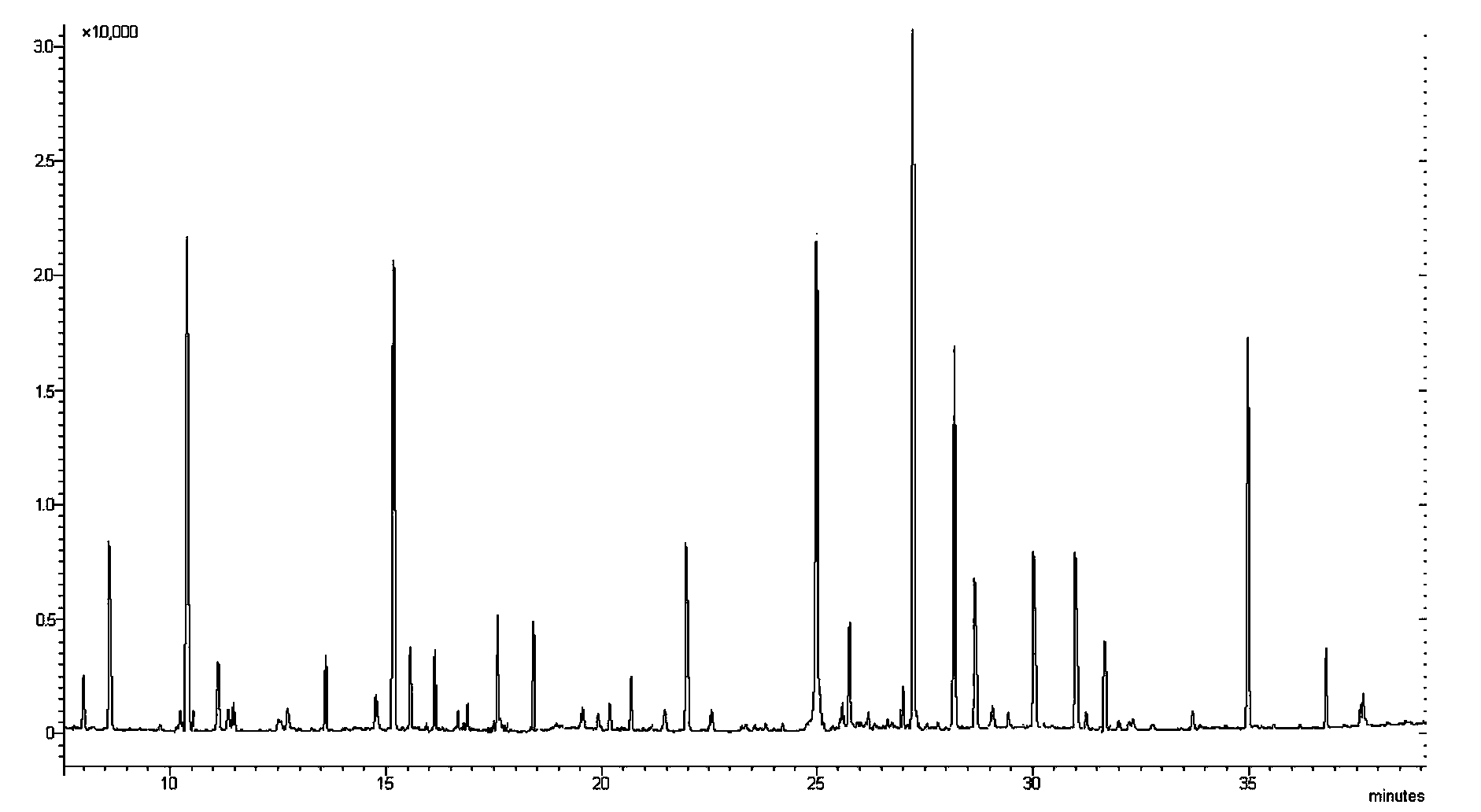
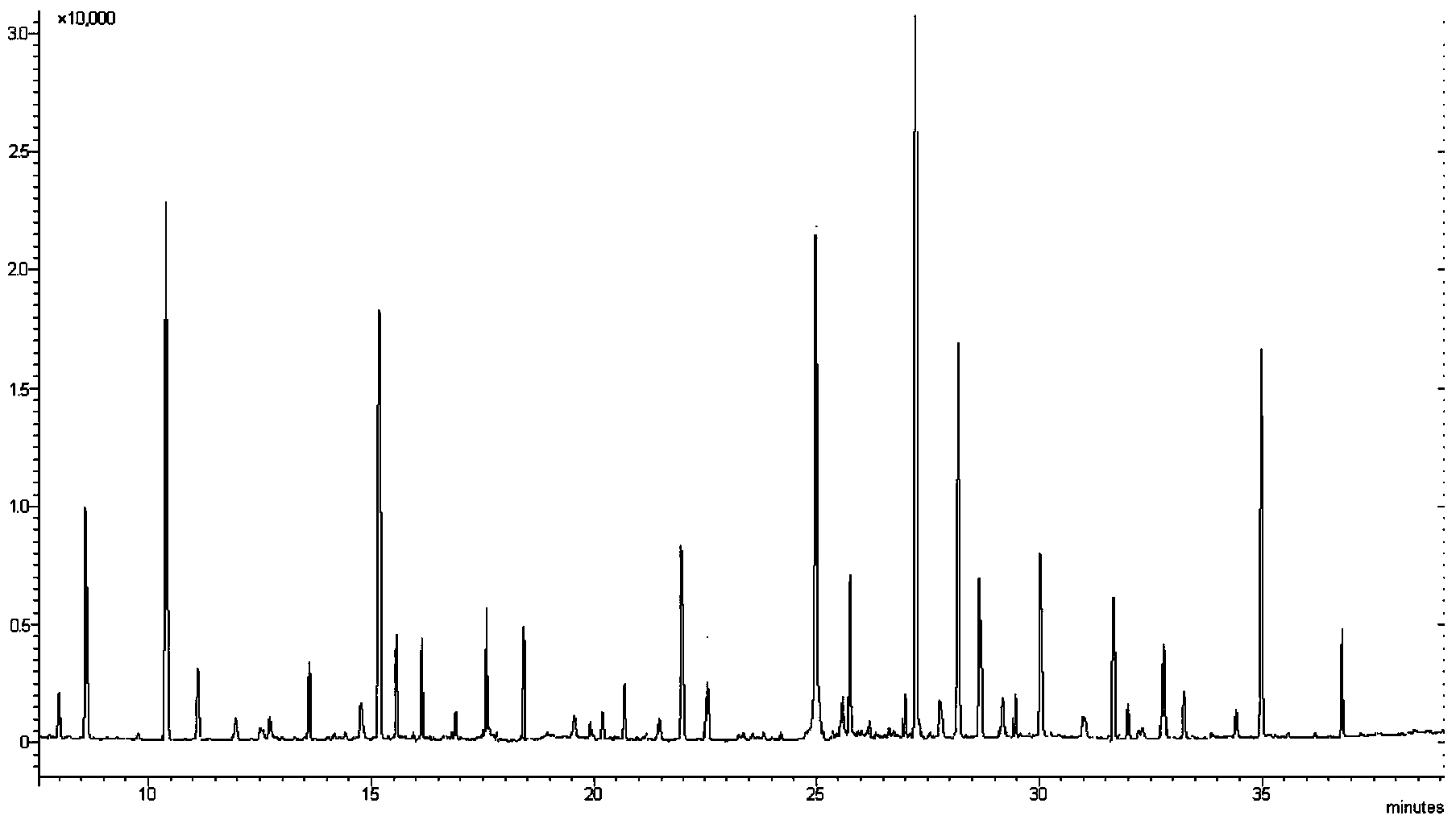
[0079] Establishment of Escherichia coli susceptibility database to ceftazidime and identification of Escherichia coli susceptibility to ceftazidime.
[0080] (a) Take 60 strains of Escherichia coli known to be sensitive to ceftazidime, 50 strains of Escherichia coli known to be moderately sensitive to ceftazidime, and 30 strains of Escherichia coli known to be resistant to ceftazidime; The ceftazidime-resistant MIC configuration was used to induce antibiotics for the strains, specifically: each strain was prepared with 0.9% normal saline to make 0.5 McFarland units; 0.4ml of ceftazidime with a concentration of 80μg / ml was added to 1.6ml of MH broth, and then Add 1ml of the strain suspension respectively, and incubate at 37°C for 4 hours.
[0081] (b) Centrifuge the culture solution at 4°C to obtain a precipitate, add 1.5ml-45°C cold methanol (inactivation and extraction dual function) and 0.75ml cold pure water, vortex and shake to mix, then add -45°C chloroform 1.5ml Vortex...
Embodiment 2
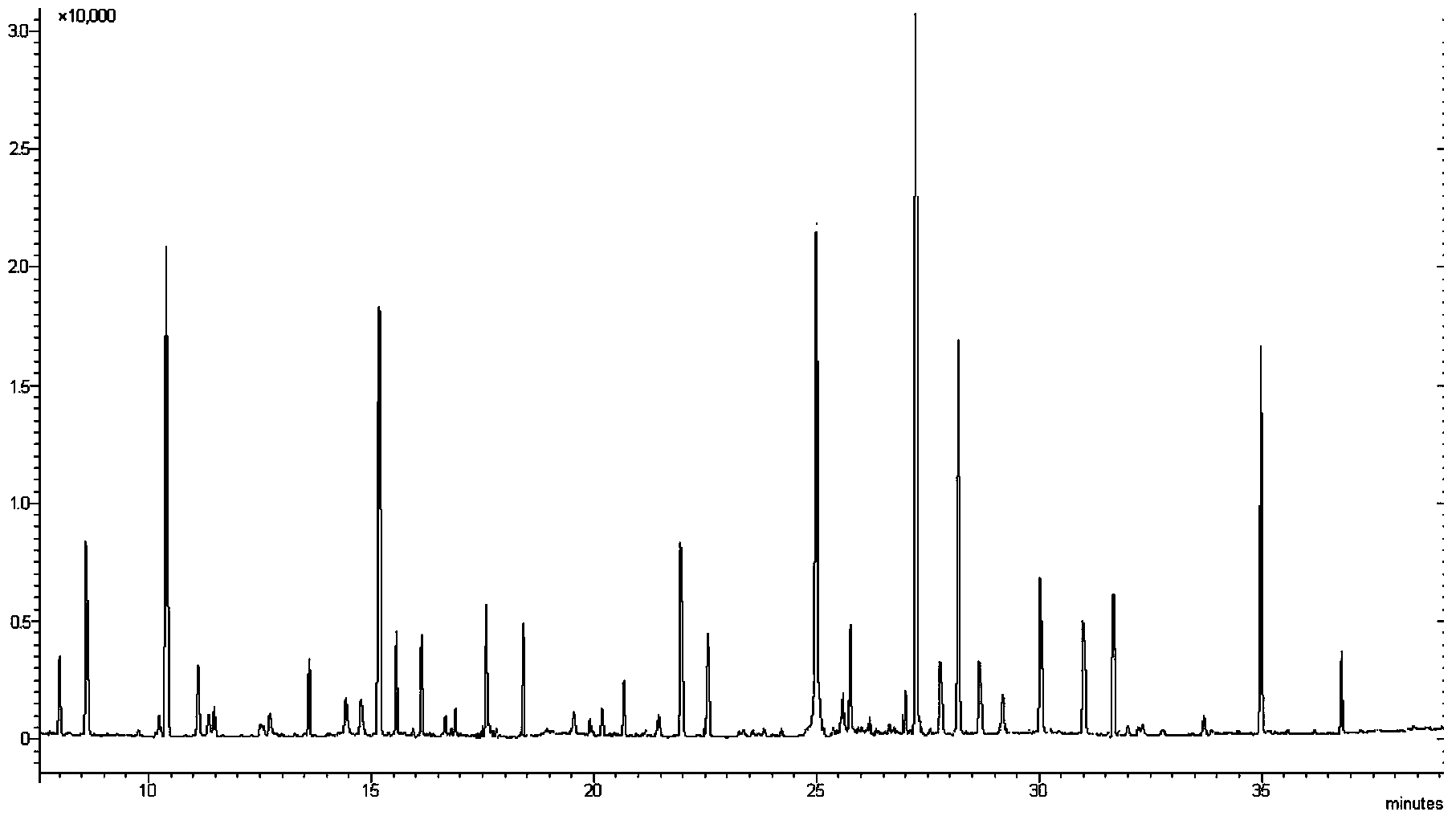
[0087] Establishment of Penicillin G Sensitivity Database of Staphylococcus aureus and Identification of Staphylococcus aureus Sensitivity to Penicillin G.
[0088] (a) Take 60 strains of Staphylococcus aureus known to be sensitive to penicillin G, 50 strains of Staphylococcus aureus known to be moderately sensitive to penicillin G, and 30 strains of Staphylococcus aureus known to be resistant to penicillin G; as recommended by CLSI ATCC29213 is resistant to penicillin G with the MIC configuration to induce antibiotics for the strains, specifically: each strain is prepared with 0.9% normal saline to make 0.5 McFarland units; respectively take 0.4ml of penicillin G with a concentration of 1.25μg / ml and add 1.6 ml MH broth, and then add 1ml of strain suspension respectively, and incubate at 37°C for 4 hours.
[0089] (b) Centrifuge the culture solution at 4°C to obtain a precipitate, add 1.5ml-45°C cold methanol (inactivation and extraction dual function) and 0.75ml cold pure wa...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com