A kind of preparation method of transferable mercury cadmium telluride thin film
A mercury cadmium telluride and thin-film technology, which is applied in semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturing, electrical components, circuits, etc., can solve problems such as failure to meet device requirements, high temperature resistance, difficulty in film growth, etc., and achieve the effect of convenient selection
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
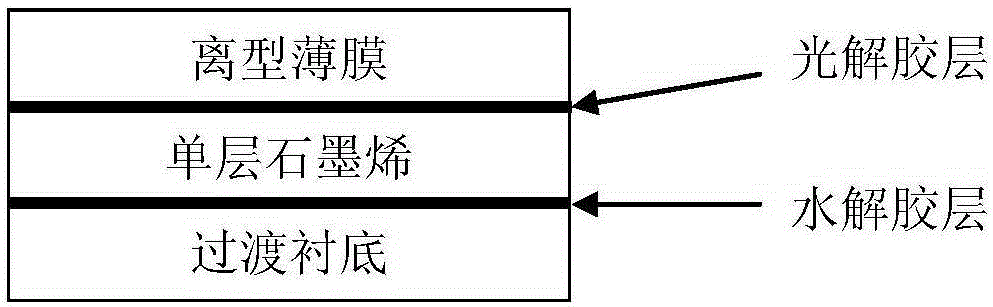
[0030] (1) Preparation of graphene
[0031] Put the copper foil into a vacuum chemical vapor deposition (CVD) system composed of a high-temperature tube furnace and a compound molecular pump, pump the system to below 10Pa, and start heating up. When the temperature rises to 300°C, H is introduced into the 2 (Flow rate 50sccm), continue to heat up to 1050°C, keep the temperature for 20 minutes and then pass CH 4 (Flow 50sccm), after 50 minutes of ventilation, turn off CH 4 , after keeping the constant temperature for 15 minutes, turn off the H 2 , followed by rapid cooling to obtain single-layer graphene.
[0032] (2) Pre-exfoliation of graphene layer
[0033] Put the graphene obtained in step (1) and the release film evenly coated with UV photolytic glue on the surface, put it in an oven at 80°C for 1 minute, take it out, and after a period of time, put it in FeCl 3 Soak in the solution at room temperature until the Cu substrate is completely corroded. The "graphene + re...
Embodiment 2
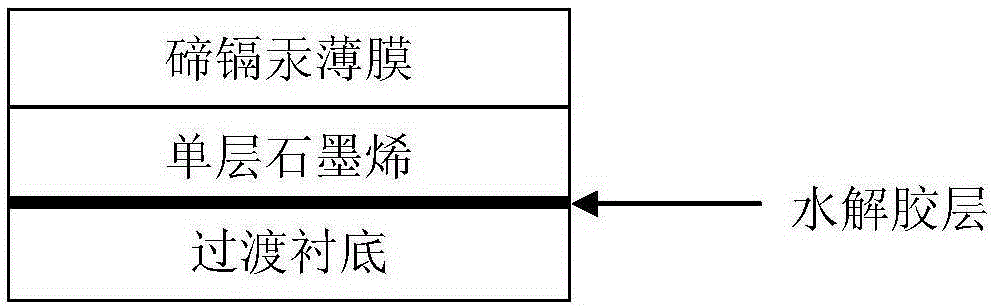
[0039] (1) Preparation of graphene
[0040]Put the copper foil into a vacuum chemical vapor deposition (CVD) system composed of a high-temperature tube furnace and a compound molecular pump, pump the system to below 10Pa, and start heating up. When the temperature rises to 300°C, H is introduced into the 2 (Flow rate 50sccm), continue to heat up to 1050°C, keep the temperature for 20 minutes and then pass CH 4 (Flow 50sccm), after 50 minutes of ventilation, turn off CH 4 , after keeping the constant temperature for 15 minutes, turn off the H 2 , followed by rapid cooling to obtain single-layer graphene.
[0041] (2) Pre-exfoliation of graphene layer
[0042] Put the graphene obtained in step (1) and the release film evenly coated with UV photolytic glue on the surface, put it in an oven at 80°C for 1 minute, take it out, and after a period of time, put it in FeCl 3 Soak in the solution at room temperature until the Cu substrate is completely corroded. The "graphene + rel...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com