Method for producing grain-oriented magnetic steel strip or steel sheet for electrical purposes
A grain-oriented, magnetic steel plate technology, applied in the direction of magnetic materials, magnetic objects, circuits, etc., can solve the problem of not achieving magnetic properties
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0069] A slab was cast from a melt which, in addition to iron and unavoidable impurities, had (shown in % by weight) 3.05% Si, 0.045% C, 0.052% Mn, 0.010 % of P, 0.030% of S, 0.206% of Cu, 0.067% of Cr, 0.030% of Al, 0.001% of Ti, 0.003% of N, 0.011% of Sn, 0.016% of Ni, divided by the continuous casting slab into a thin steel ingot having a thickness of 63 mm and a width of 1100 mm. After free, uncontrolled cooling to about 900° C., a homogenization annealing is carried out in which the thin steel ingot is completely heated to 1050° C. The thin steel ingot was then hot-rolled in a hot-rolling train comprising seven successive hot-rolling stands one behind the other to form a hot-rolled strip having a hot-rolled strip thickness of 2.30 mm. The temperature of the rolled stock was in the range of 960-980° C. in the first rolling pass and 930-950° C. in the second rolling pass. The final temperature of hot rolling is 840°C.
[0070] The hot-rolled steel strip thus obtained was...
example 2
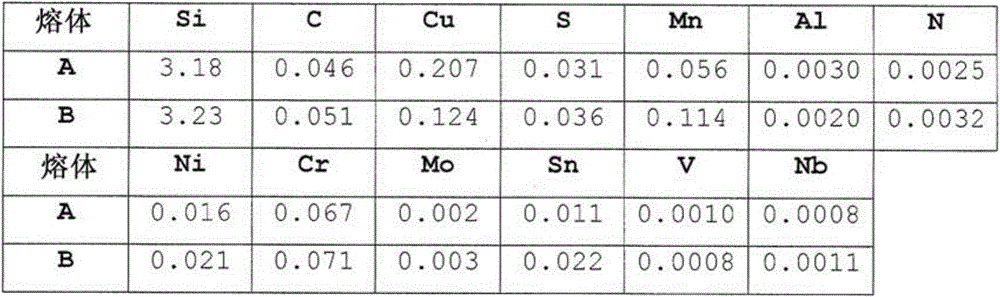
[0074] Melt A according to the invention and melt B not according to the invention were melted, Table 1 gives the composition of these two melts.
[0075] These melts were cast into thin steel ingots having a thin steel ingot thickness of 63 mm in a continuous casting method. The superheat temperature of the melt in the tundish is 25-45K. The casting rate during continuous casting was in the range of 3.5-4.2 m / min. The slab is then cooled to about 900°C before entering the roller hearth furnace.
[0076] The thin ingots divided from the continuous cast slabs are reheated for 20 minutes in the leveling furnace to a temperature between 1030 and 1070° C. and then transported to the hot rolling station. Table 2 gives the reheating temperature SRT for specific settings, and the ratios of %Mn / %S and %Cu / %S in the alloys of melts A and B.
[0077] On the way from the leveling furnace to the first hot deformation pass, the temperature of the thin steel slab drops to a value of appr...
example 3
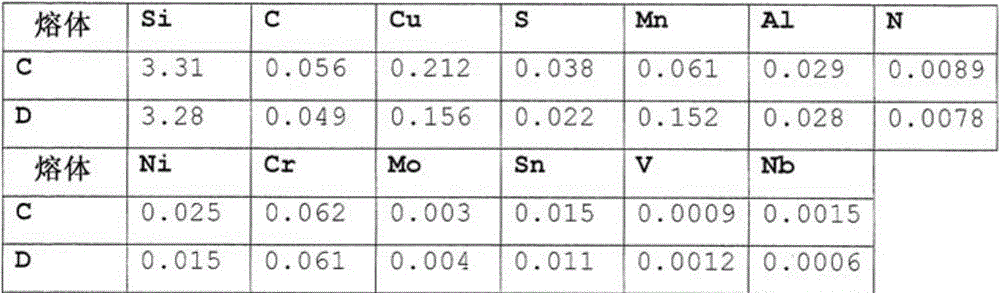
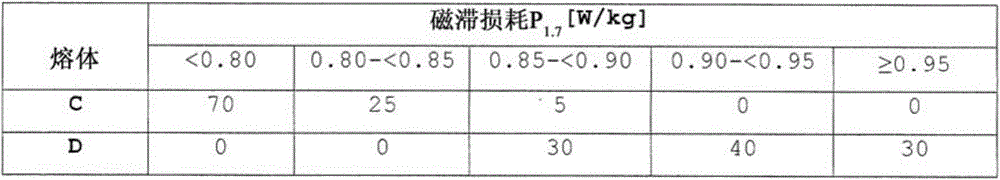
[0083] Like melts A and B, melts C formed according to the invention and melts not formed according to the invention having the compositions given in Table 4 were cast in the same manner as described above and processed into hot strip. This is followed by annealing and rapid cooling of the hot strip in the same manner as described above for the production of hot strip from steels A and B.
[0084] The following process is carried out by cold rolling to the nominal thickness of the finished steel strip of 0.23mm in one step and then performing an annealing treatment capable of recrystallization and decarburization, wherein during the decarburization process by adding 15% NH 3 Used as an annealing gas while performing nitriding treatment. Then an annealing separator consisting essentially of MgO is applied as a bond protector and annealed in a high-temperature bell annealing furnace for secondary recrystallization. An insulating layer is then applied and a stress-relieving stra...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com