Method for removing total cholesterol in animal fat
A technology of animal fat and total cholesterol, which is applied in the field of improved animal fat processing technology to remove cholesterol from animal fat, can solve the problems of cumbersome operation steps, complex reactant system, and low operability, and achieve the effect of simple operation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0124] Chemical method esterification + adsorption
[0125] Heating the animal fat, adding an esterification reaction catalyst, and carrying out the esterification reaction for a period of time at a certain temperature and keeping the vacuum degree below 10mbar. After the reaction of the reaction system is completed, centrifuge to separate the solid from the liquid, and take the liquid phase; then heat the above animal fat to 100-200° C., add an adsorbent, and react under vacuum for 1-120 minutes. After the reaction of the reaction system is finished, the solid and liquid are separated by suction filtration to obtain animal fat with low total cholesterol and low free cholesterol. The experimental conditions of Example 1 are shown in Table 3.
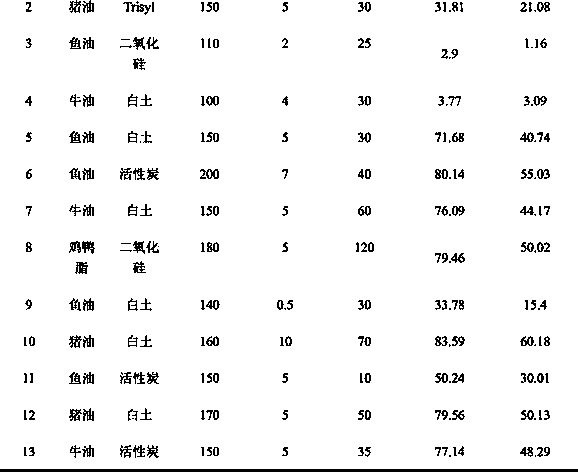
[0126] Table 3: Experimental conditions of Example 1
[0127]
[0128]
[0129]The results of each experiment in Example 1 are compared with the results of Comparative Example 1 in Table 4.
[0130] Table 4: Each experimental re...
Embodiment 2
[0135] Enzymatic esterification + adsorption
[0136] The animal fat is heated, and an enzymatic esterification reaction catalyst is added, and at a certain temperature, the vacuum degree is kept below 10mbar to carry out the esterification reaction for a period of time. After the reaction system is completed, centrifuge to separate the solid from the liquid, and take the liquid phase; then heat the liquid phase obtained in the previous step to 100-200° C., add an adsorbent, and react under vacuum for 1-120 minutes. After the reaction of the reaction system is finished, the solid and liquid are separated by suction filtration to obtain animal fat with low total cholesterol and low free cholesterol. The experimental conditions of embodiment 2 are shown in table 5.
[0137] The experimental condition of table 5 embodiment 2
[0138]
[0139]
[0140] The experimental results in Example 2 are compared with the results of Comparative Example 1 in Table 6.
[0141] Table 6...
Embodiment 3
[0145] In the aforementioned method, in order to avoid the influence on the adsorption, separation was carried out after the esterification reaction. In order to investigate the impact of this step, the inventors treated the corresponding oils and fats according to the methods of Examples 1 and 2, but directly used the esterification product for adsorption operation after the esterification reaction instead of using the solid-liquid separation obtained in advance. The liquid phase product is adsorbed, and the removal rate of free cholesterol and total cholesterol is detected respectively, and is compared with the free cholesterol and the removal rate of the oil processed by the method of Examples 1 and 2 and the oil processed with the existing method A comparison was made.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com