Zero-cross detection circuit and detection method used for synchronous buck converter
A zero-crossing detection circuit and synchronous step-down technology, applied in the direction of converting DC power input to DC power output, instruments, electrical components, etc., can solve the problems of increasing circuit power consumption, error, and large fluctuation range of the zero-crossing point of the inductor current. Achieve the effect of realizing automatic correction and reducing circuit power consumption
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
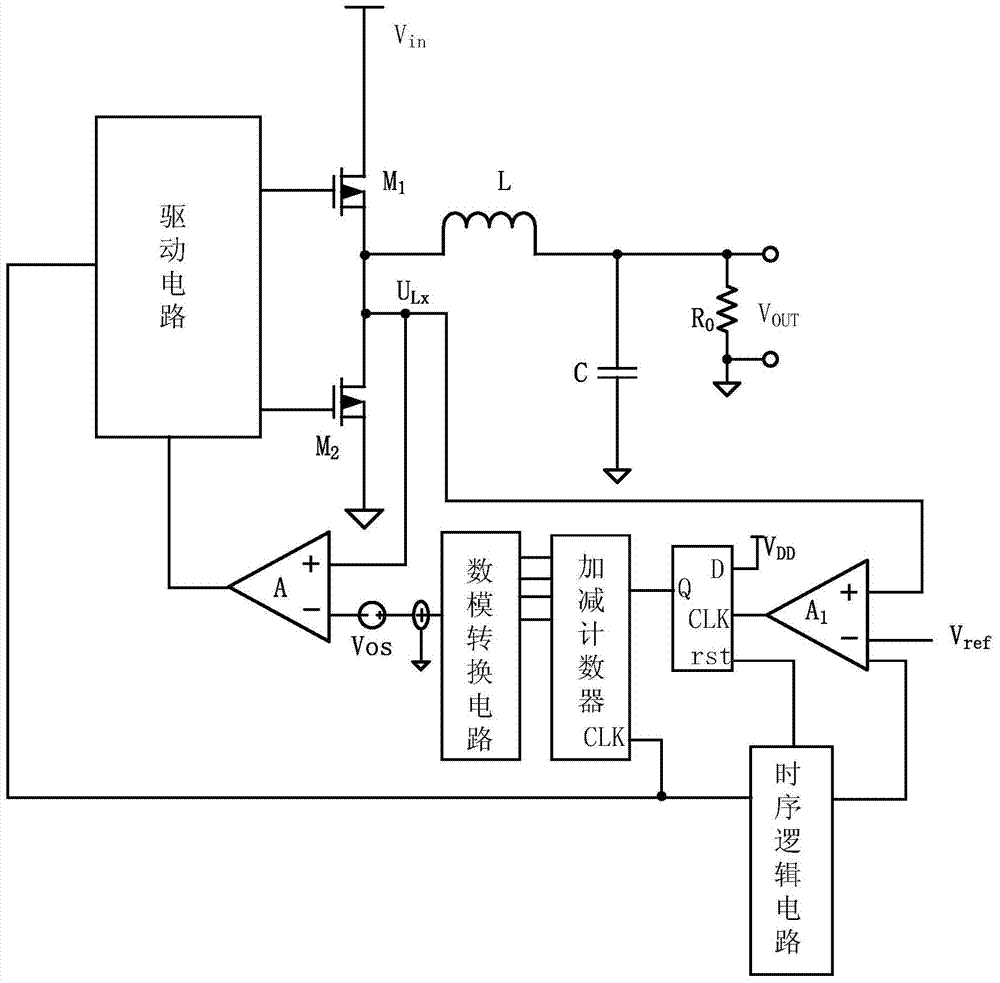
[0043] Such as figure 2 shown, using the first comparator A 1As a state judging circuit, the state judging refers to judging the synchronous tube M 2 Whether the body diode in is turned on; after the zero-crossing comparator is triggered, the synchronous tube M is turned off through the drive circuit 2 , then the first comparator A 1 Detect the drain voltage U of the synchronous tube within a sampling time Lx , compare the voltage with the reference voltage;
[0044] Since when the sync tube M 2 When the body diode is turned on, its voltage drop is 0.7v. You can set the value of the reference voltage to -0.3~-0.5v or +0.3~0.5v for comparison. The inductor current is positive from left to right. When When the body diode conducts, U Lx The voltage at the point is roughly -0.7v, U Lx The voltage at the point is connected to the non-inverting input terminal of the first comparator, and the reference voltage value -0.4v is connected to the first comparator A 1 The invertin...
Embodiment 2
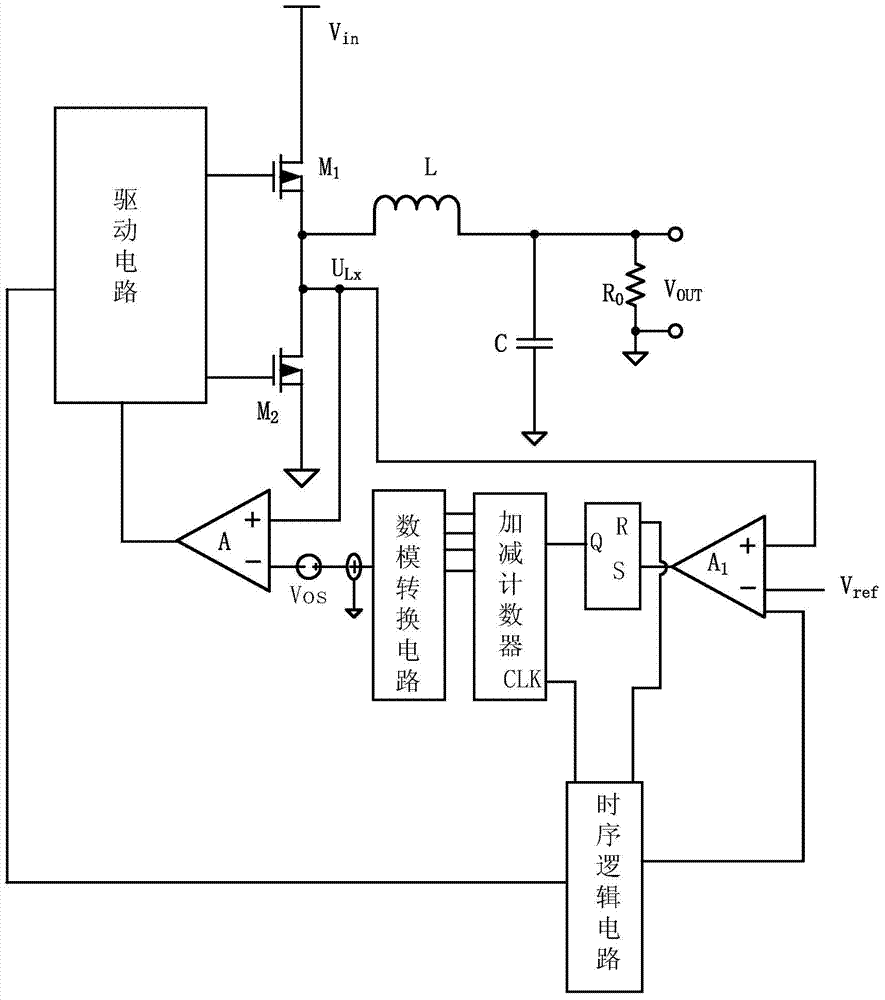
[0050] Such as image 3 As shown, the difference between embodiment 2 and 1 mainly lies in several parts such as logic circuit, sequential logic circuit and sequential signal. The logic circuit of embodiment 2 adopts an RS flip-flop, the state digital signal is connected to the S terminal of the RS flip-flop, the third timing signal is connected to the R terminal of the RS flip-flop, and the output terminal outputs counting instructions to the up-down counter.
[0051] The first timing signal is connected to the timing logic circuit, and outputs a second timing signal, a third timing signal and a fourth timing signal respectively representing the working timing of the first comparator, the logic circuit and the up-down counter. The second timing signal is a high level set for a certain sampling time on the rising edge of the first timing signal, and the third timing signal is a low level set for a certain period of time on the rising edge of the first timing signal. The fourt...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com