Screening and identification and application of bacillus for efficiently degrading phthalate
A technology for Bacillus subtilis and strains, which is applied in the field of screening and identification of efficiently degrading Bacillus phthalates, and can solve the problems of refractory degradation, slow rates of hydrolysis and photolysis, and long half-life of phthalates.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
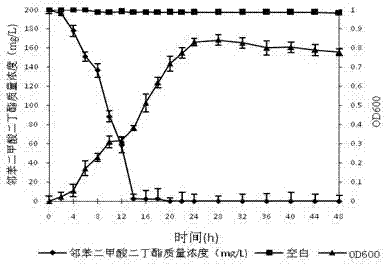
[0027] Example 1: Determine the relationship between the growth of phthalate-degrading bacterial strain JF and the degradation of dibutyl phthalate
[0028] Activation of strains: pick the strain JF that degrades phthalates into LB liquid medium, 35°C, 180r / min shaking culture for 24h; then continuously streak, pick a single colony and culture twice (35°C), Pick a single colony and inoculate it on an LB slope at 35°C for 2 days for later use.
[0029] Wash the bacterial cells on the lower slant with sterile saline and adjust the cell concentration to 10 8 cfu / mL, made into seed solution.
[0030] Determination of the growth curve: Inoculate the seed liquid of the degrading strain JF into LB liquid medium containing 200 mg / L dibutyl phthalate (DBP) according to the inoculum amount of 5%, and divide into 30 mL / 250 mL Erlenmeyer flasks, Cultivate at 35°C and 180r / min for 48h. The sampling time is 1 bottle every 2h during 0h-36h, and 1 bottle every 4h during 36h-48h. Store the s...
example 2
[0033] Example 2: Degradation characteristics of strain JF degrading dibutyl phthalate
[0034] Effect of substrate concentration on the degradation rate of dibutyl phthalate by strain JF: According to the inoculum amount of 5.0% (v / v), the seed solution (1.0×10 8 individual / mL) inoculated in LB liquid medium (pH7.0, 100 mg / L, 200 mg / L, 300 mg / L, 400 mg / L) with different concentrations of dibutyl phthalate, and aliquoted 30 mL / 250 mL Erlenmeyer flask, 35°C, 180 r / min shaking culture, sampling interval 4h. Use [0024] described method to measure dibutyl phthalate degradation rate.
[0035] Effect of culture temperature on the degradation rate of dibutyl phthalate by strain JF: According to the inoculation amount of 5.0% (v / v), the seed solution (1.0×10 8 / mL) inoculated in LB liquid medium (pH7.0) with a dibutyl phthalate mass concentration of 200 mg / L, divided into 30 mL / 250 mL Erlenmeyer flasks, at different temperatures (30°C, 35°C, 40°C, 45°C) 180 r / min shaking culture,...
example 3
[0038] Example 3: Degradation effect of phthalate-degrading strain JF on dibutyl phthalate in MM medium
[0039] Inoculate the seed solution of the degraded strain into 200 mg / L dibutyl phthalate (DBP) MM liquid medium according to the inoculum amount of 5%, and divide into 30 mL / 250 mL Erlenmeyer flasks, and inoculate 5% sterile water As a blank control, 35 ℃, 180r / min shaking culture.
[0040] Sampling after cultivating 60h, measure the residual amount of dibutyl phthalate (DBP) in the nutrient solution with the method described in [0024], control group dibutyl phthalate (DBP) hardly degrades, in the experimental group about 92.66% of dibutyl phthalate (DBP) was degraded by strain JF.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com