Flexible organic light emitting diode and method for manufacturing same
A luminescent and diode technology, applied in the field of organic electroluminescent devices, can solve the problems affecting the luminous stability of OLED devices, weak bonding force of flexible substrates, and high surface resistance of conductive films, so as to be easy to popularize and use, and enhance luminous stability Good performance and stability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
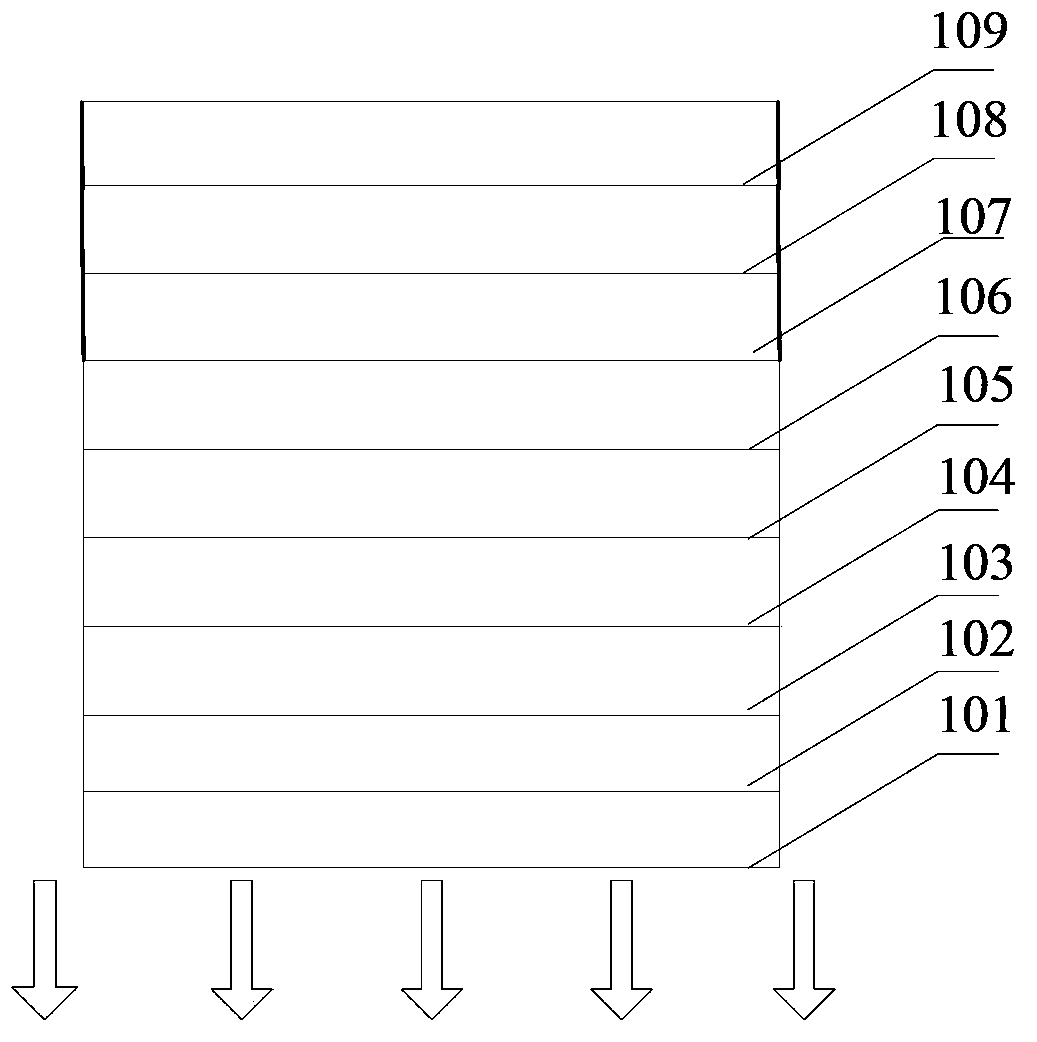
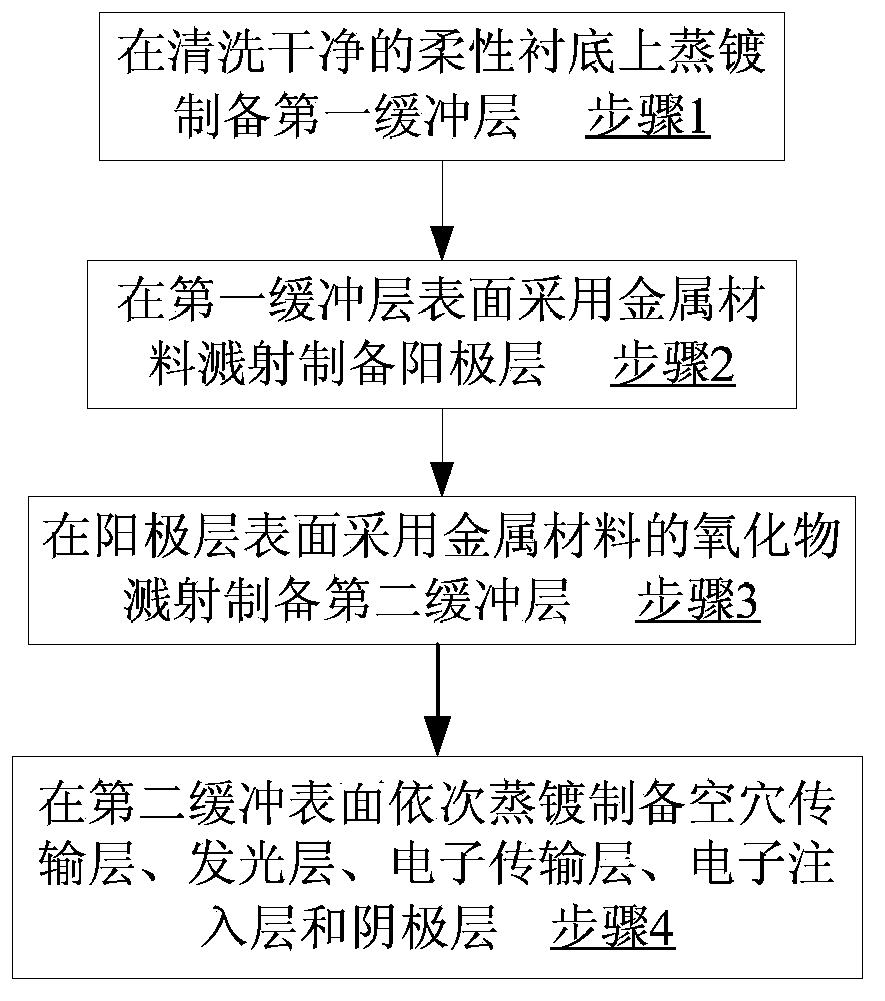
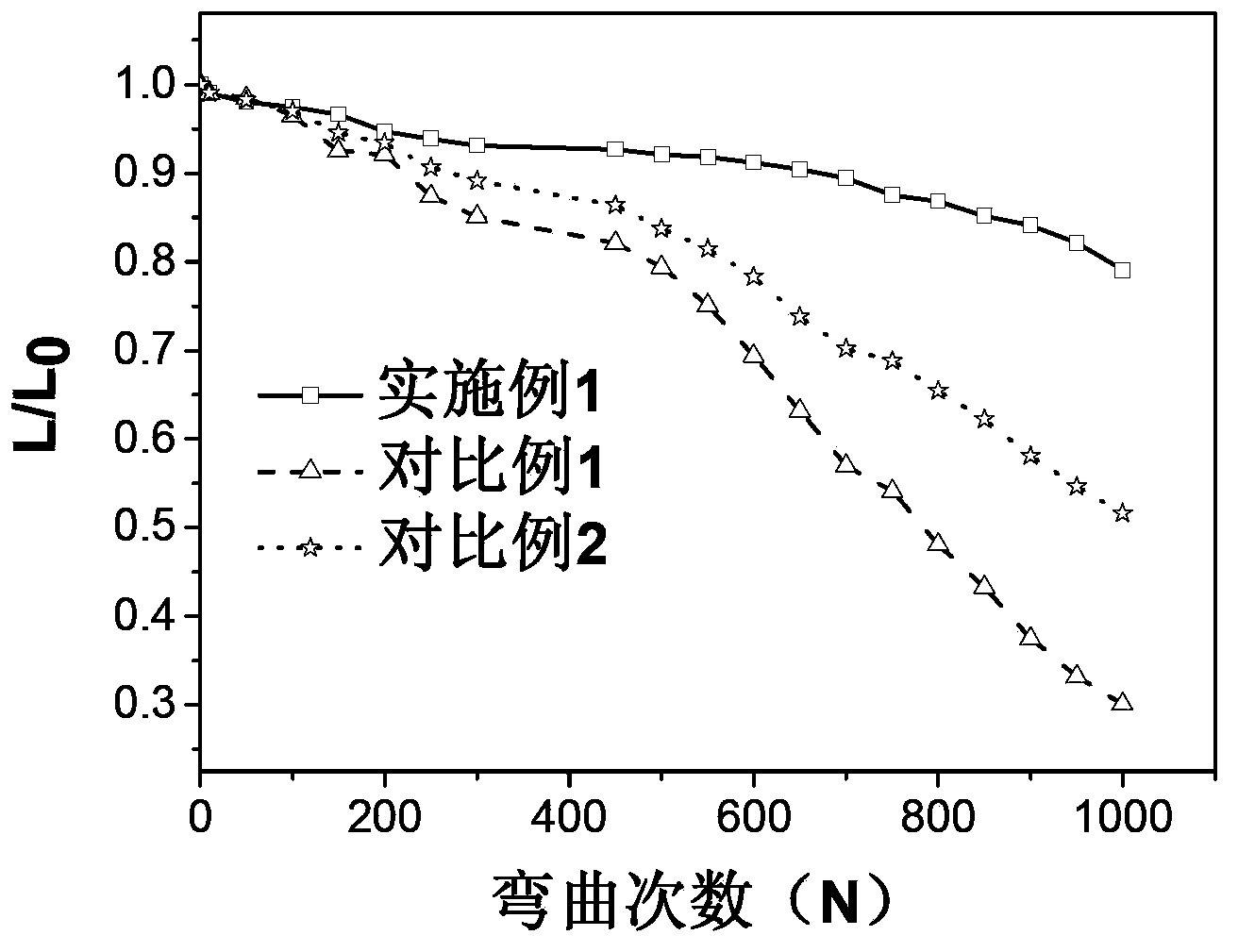
[0039] A flexible OLED with a layered structure ( Figure 1a ), consisting of sequentially stacked flexible substrate 101, first buffer layer 102, anode layer 103, second buffer layer 104, hole transport layer 105, light emitting layer 106, electron transport layer 107, electron injection layer 108 and cathode layer 109 Composition, wherein the flexible substrate 101 is PEN, the first buffer layer 102 is 200nm SiO, the anode layer 103 is 18nm Al, the second buffer layer is 1nm aluminum oxide, and the hole transport layer 105 is 40nm NPB , the light-emitting layer 106 is 25nm TCTA: Ir(ppy) 3 Doped structure (TCTA: Ir(ppy) 3 =100:3, where, TCTA:Ir(ppy) 3 It is expressed as a doped mixed material, and the description below is similar), the electron transport layer 107 is 35nm TPBi, the electron injection layer is 1nm LiF, and the cathode layer 108 is 70nm Al. The flexible OLED is a bottom emitting device. The manufacturing method of the light emitting device comprises the foll...
Embodiment 2
[0046] A flexible OLED with a layered structure, consisting of a flexible substrate, a first buffer layer, an anode layer, a second buffer layer, a hole transport layer, a light emitting layer, an electron transport layer, an electron injection layer and a cathode layer stacked in sequence, Among them, the flexible substrate is PET, the first buffer layer is 200nm ZrO 2 , the anode layer is 20nm Ag, the second buffer layer is 2nm silver oxide, the hole transport layer is 40nm NPB, and the light emitting layer is 25nm TCTA:Ir(ppy) 3 Doped structure (TCTA: Ir(ppy) 3 =100:3), the electron transport layer is 35nm TPBi, the electron injection layer is 1nm LiF, and the cathode layer is 30nm Sm. The flexible OLED is a double-sided light emitting device. Its manufacturing method is the same as that of Example 1, and will not be repeated here.
Embodiment 3
[0048] A flexible OLED with a layered structure, consisting of a flexible substrate, a first buffer layer, an anode layer, a second buffer layer, a hole transport layer, a light emitting layer, an electron transport layer, an electron injection layer and a cathode layer stacked in sequence, Among them, the flexible substrate is PES, the first buffer layer is 200nm TiO 2 , the anode layer is 70nm Ni, the second buffer layer is 5nm nickel oxide, the hole transport layer is 40nm NPB, and the light emitting layer is 25nm TCTA:Ir(ppy) 3 Doped structure (TCTA: Ir(ppy) 3 =100:3), the electron transport layer is 35nm TPBi, the electron injection layer is 1nm LiF, and the cathode layer is 30nm Yb. The flexible OLED is a top-emitting light-emitting device. Its manufacturing method is the same as that of Example 1, and will not be repeated here.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com