Method for manufacturing rotor and cutting apparatus
A manufacturing method and rotor technology, applied in the field of cutting device for cutting magnet base material, manufacturing of rotor, and cutting device, can solve the problems of lower yield, more chips, higher manufacturing cost, etc., and achieve high contact resistance and lower cost , the effect of reducing eddy loss
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 Embodiment approach
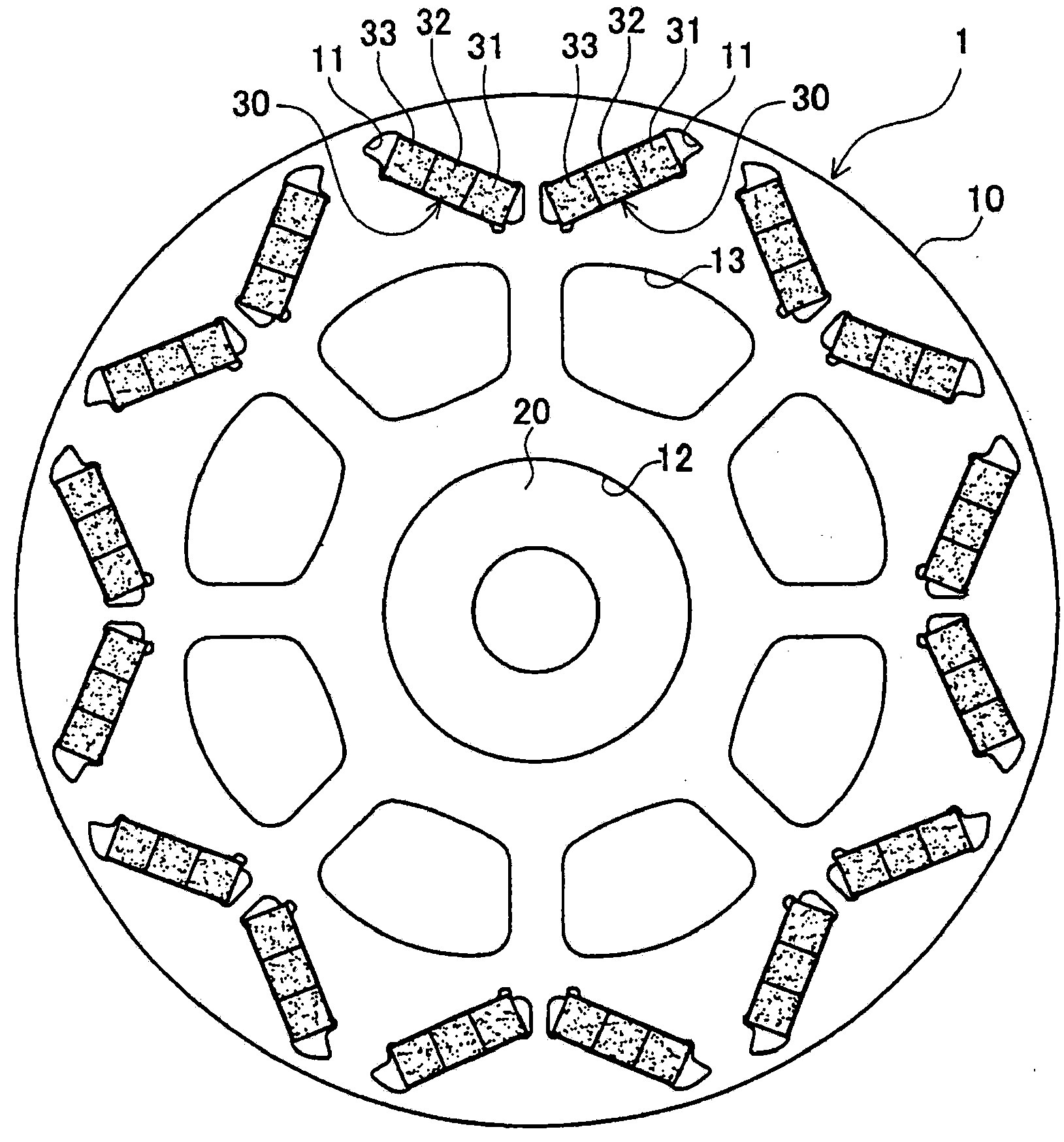
[0062] Hereinafter, a method for manufacturing a rotor and a cutting device according to the present invention will be described with reference to the drawings. figure 1 is a plan view showing the rotor 1 . Such as figure 1 As shown, the rotor 1 includes a rotor shaft 20, a cut-off magnet 30, and a rotor core 10 as a main body of the rotor.
[0063] The rotor core 10 is formed by laminating a plurality of annular electromagnetic steel sheets. Such as figure 1 As shown, the rotor core 10 has a plurality of slots 11 on the outside in the radial direction, a central hole 12 in the center of the shaft, and a plurality of lightening holes 13 in the middle in the radial direction.
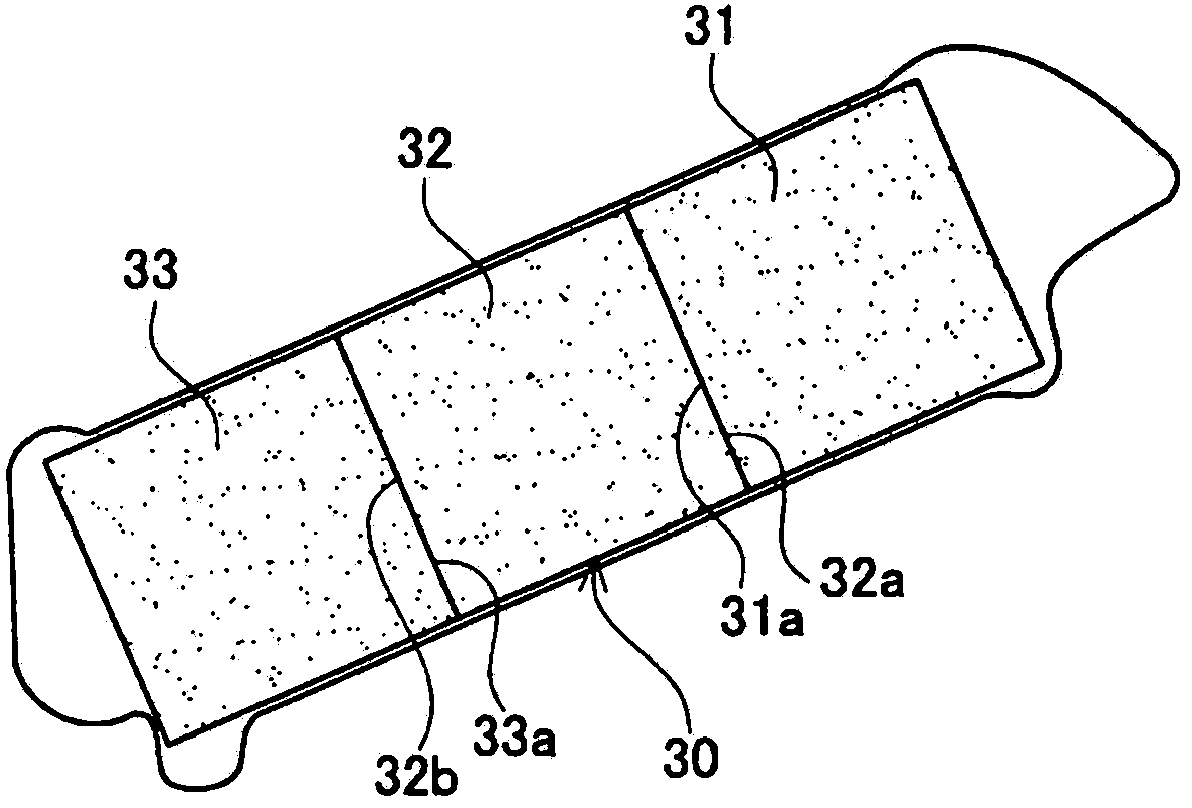
[0064] Each slot 11 is used for assembling the split magnet 30 , and each slot 11 penetrates the rotor core 10 in the axial direction. A pair of adjacent slots 11 are arranged at equal intervals along the circumferential direction of the rotor core 10 and are substantially V-shaped in plan view. ...
no. 2 Embodiment approach
[0106] Next, use Figure 11 to Figure 14 The second embodiment will be described. Figure 11 It is a schematic overall configuration diagram of a cutting device 40A in the second embodiment. exist Figure 11 In , the state where the magnet base material 30A is divided into the first magnet piece 31 and the second magnet piece 32 is shown. Such as Figure 11 As shown, the cutting device 40A has a surface processing mechanism 90 . here, Figure 12 yes Figure 11 The Z-Z section view.
[0107] Such as Figure 12 As shown, the surface processing mechanism 90 includes a spacer 91 , a connecting pin 92 , a holding member 93 , an actuator 94 , a vibrating device 95 , a connecting pin 96 and a nut 97 . The partition 91 restricts or allows the central wall 61 to move relative to the side walls 52 , 53 in the axial direction of the rotation shaft 64 (hereinafter simply referred to as “axial direction”). exist Figure 12 , the spacer 91 fills the gap D1 between the side wall 52...
no. 3 Embodiment approach
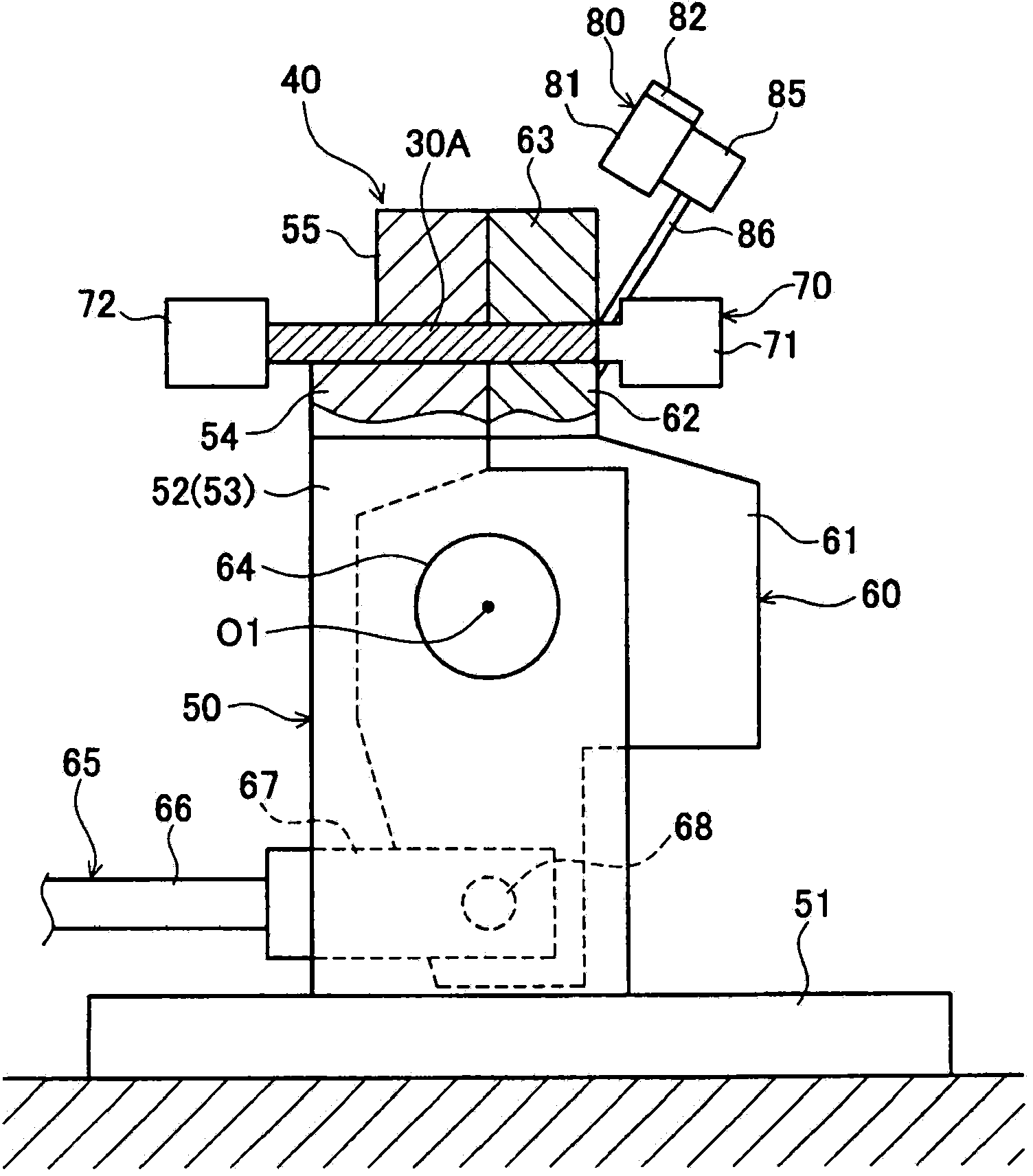
[0117] Next, use Figure 15 ~ Figure 17 The third embodiment will be described. Figure 15 It is a schematic overall configuration diagram of the cutting device 40B in the third embodiment. exist Figure 15 In , the state before cutting the magnet base material 30A is shown. This cutting device 40B does not have the surface processing mechanisms 80 and 90 of the first and second embodiments.
[0118] and, if Figure 15 As shown, in this cutting device 40B, between the fixed lower jig 54 and the movable lower jig 62 and between the fixed upper jig 55 and the movable upper jig 63 , the magnet base material 30A is cut. ( Figure 15 left and right direction) is formed with a gap D3. Other configurations of the third embodiment are the same as those of the first and second embodiments, and therefore descriptions of these configurations are omitted.
[0119] Next, the process of surface-processing the fractured surface 31a of the 1st magnet piece 31 in 3rd Embodiment is demon...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com