Intra-domain dynamic multipath generating method based on generating tree
A multi-path and spanning tree technology, applied in the Internet field, can solve problems such as high algorithm time complexity, increase algorithm complexity, increase communication overhead, etc., and achieve the effect of reducing complexity and high reliability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 example
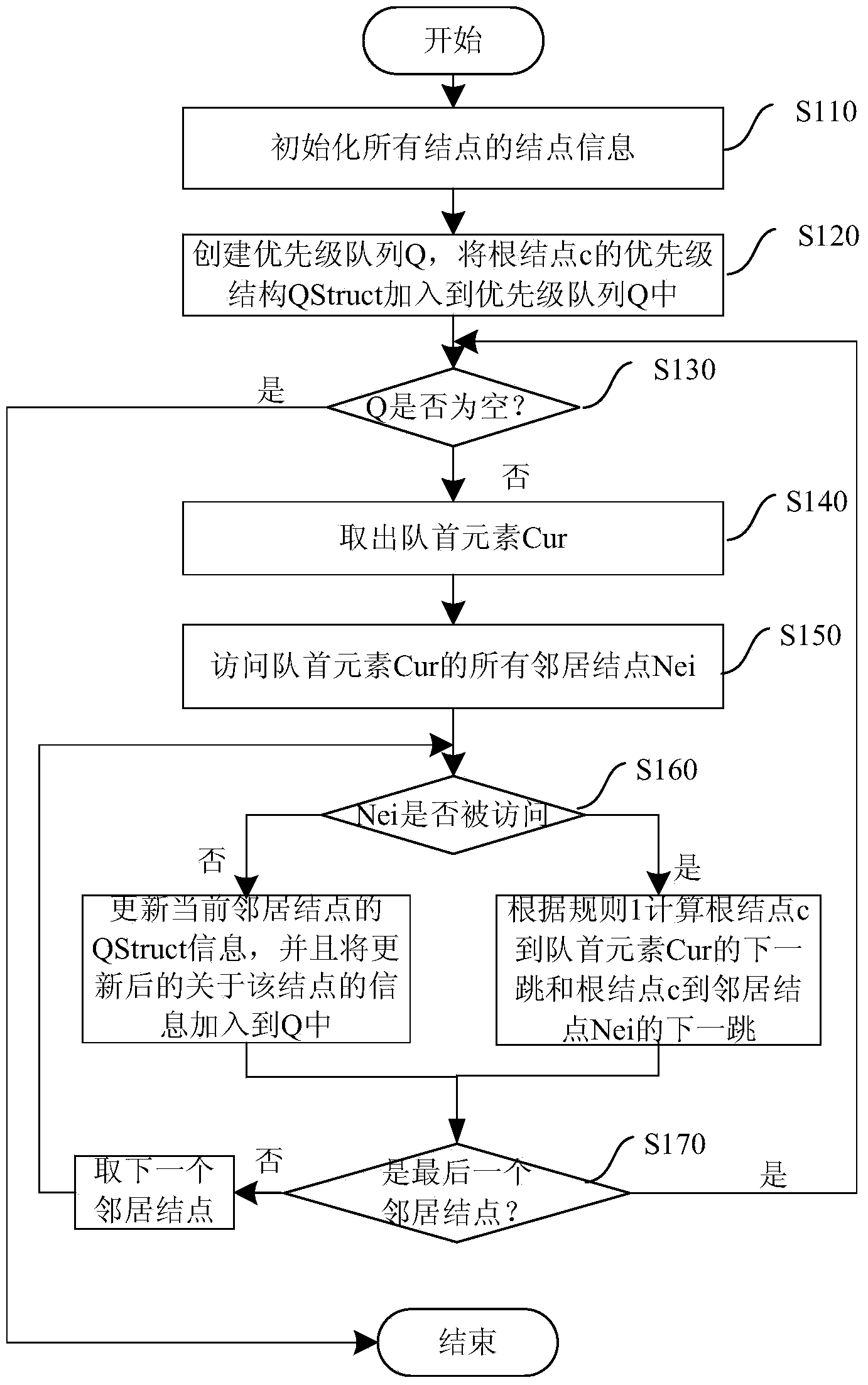
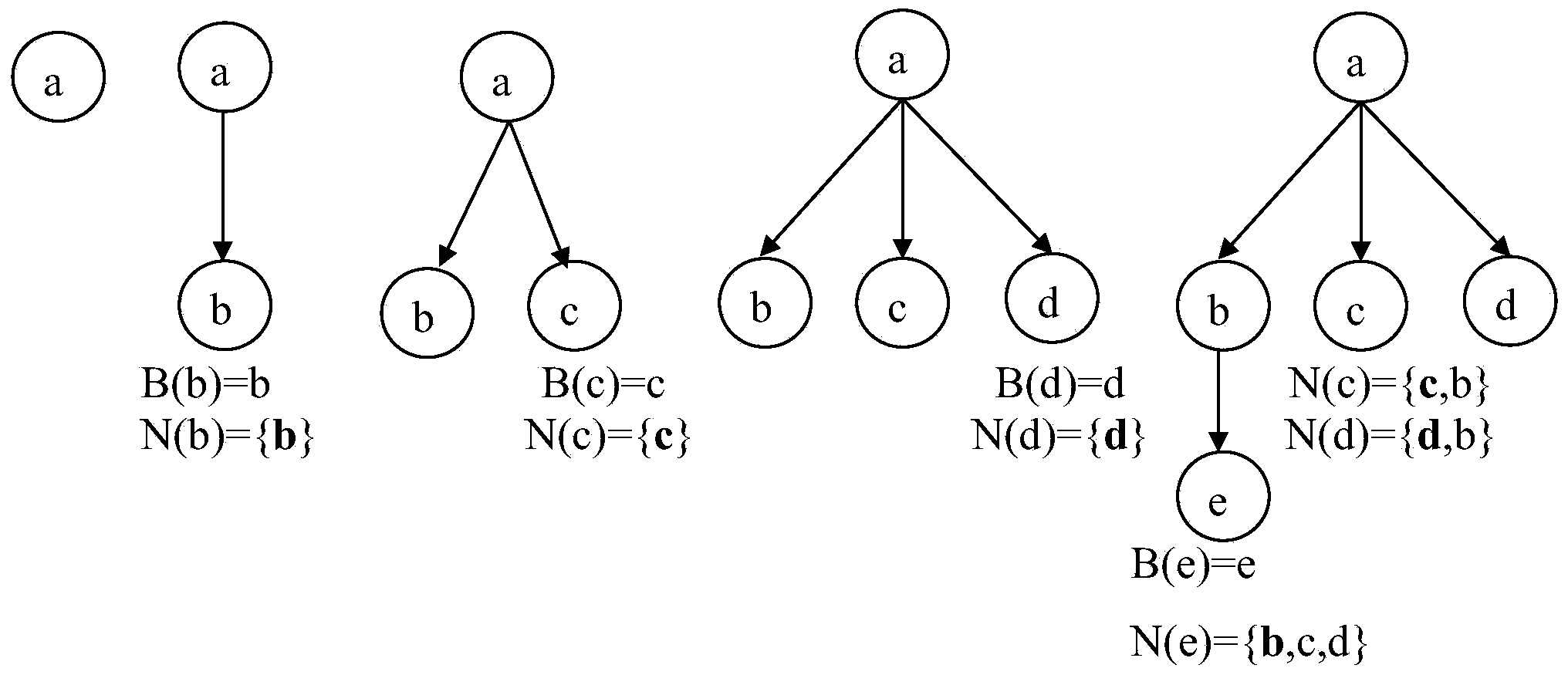
[0058] figure 1 is a schematic flowchart of a spanning tree-based intra-domain dynamic multi-path generation method according to the first embodiment of the present invention. This embodiment is a multi-path generation method in a static situation. Refer to figure 1 To explain in detail the steps of constructing an SPT rooted at a certain node. Multiple next hops from the root node to all other nodes can be calculated during the construction of the SPT. And the construction of SPT is an iterative process, each time a node is selected to join the SPT.
[0059] Step S110, initializing node information of all nodes in a network.
[0060] Specifically, the initialized node information includes the cost of each node, the parent node, the descendant node, and the visited flag attribute (visited). Define an access flag attribute for each node, set the initial value to unvisited false, when the node is added to the SPT, set the access flag attribute to visited true.
[0061] More ...
no. 2 example
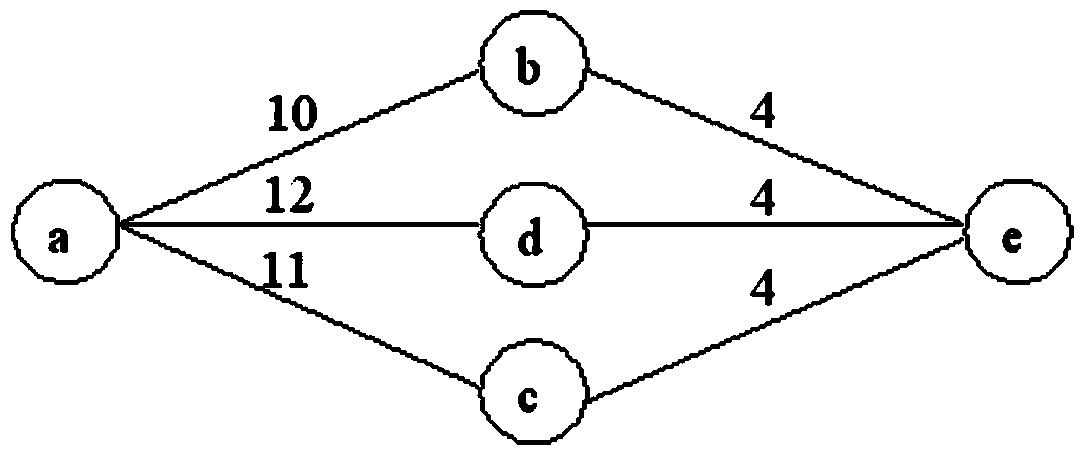
[0085] Figure 6 It is a schematic flow chart of a spanning tree-based intra-domain dynamic multi-path generation method according to the second embodiment of the present invention. This embodiment is a dynamic multi-path generation method when the link state changes. Refer to Figure 6 to describe each step in detail.
[0086] For the convenience of description, we assume the minimum cost C from root node c to node s c (s) ≥ the minimum cost C from root node c to node e c (e).
[0087] Step S210, analyze the cost change of the link (edge) L(s, e), when the cost of the edge L(s, e) increases, execute step S220, otherwise execute step S230.
[0088] Step S220, judging whether the structure of the statically constructed shortest path tree SPT with respect to the root node c has changed.
[0089] Specifically, if the judgment result is negative, that is, when the edge is not on the SPT, the next hops from the root node c to nodes s and e will be affected. There are two situa...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com