Flexible photoelectric device substrate, flexible photoelectric device and preparation method
A kind of optoelectronic device, flexible technology, applied in the direction of electrical solid device, semiconductor/solid device manufacturing, photovoltaic power generation, etc., can solve the problems of small device mobility, residual glue, alignment difficulties, etc., and achieve the effect of preventing falling off
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0031] The present invention provides a flexible optoelectronic device substrate, a flexible optoelectronic device and a preparation method. In order to make the purpose, technical solution and effect of the present invention clearer and clearer, the present invention will be further described in detail below. It should be understood that the specific embodiments described here are only used to explain the present invention, not to limit the present invention.
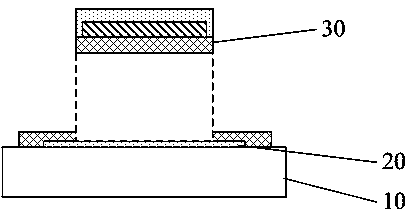
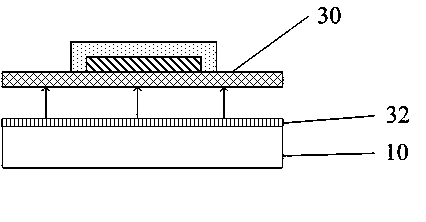
[0032] In the process of studying the properties between polymer materials and various metal surfaces, the present invention confirms through experiments that some metal materials and polymer films have good adhesion properties, thus proposing a flexible optoelectronic device for the production of flexible optoelectronic devices. A device substrate and a preparation method thereof. The flexible optoelectronic device substrate is not only suitable for the preparation of large-scale flexible optoelectronic devices, but al...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com