Process for removing base metals in platinum group metal containing material
A technology for platinum group metals and base metals, applied in the field of removing base metals, can solve problems such as difficulty in separating noble and base metals, and achieve the effects of reducing platinum group metal losses, reasonable connection and simple operation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
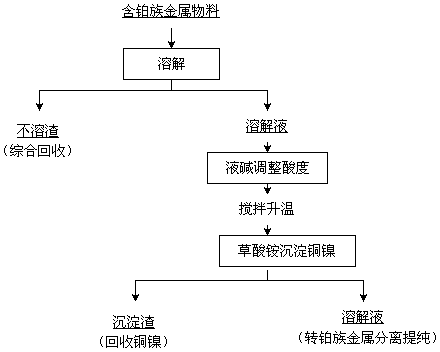
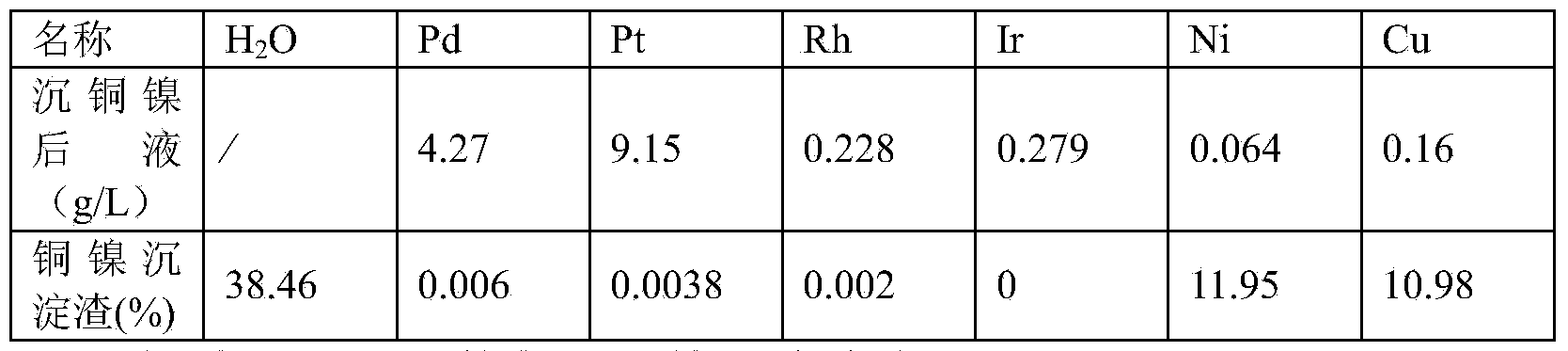
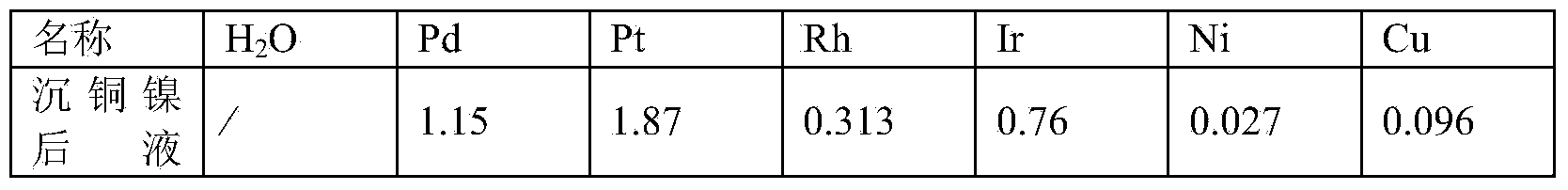
[0016] A process for removing base metals from materials containing platinum group metals. 100g of materials containing platinum group metals is added to 320ml of water for dissolution, wherein the water in the materials containing platinum group metals is 45.56g, the base metal nickel is 2.84g, and the base metals contain Copper 2.62g. Use 80ml of 12mol / L hydrochloric acid to adjust the acidity of the solution to 2.5mol / L, and the liquid-solid mass ratio of the acidity-adjusted solution obtained is 4:1. Stir and raise the temperature of the solution with adjusted acidity to 80°C on the electric heating plate. At this time, chlorine gas is introduced to start chlorination and dissolution. The flow rate of chlorine gas is 15L / h. 8 hours. After the chlorinated solution is finely filtered to remove the insoluble residue, the total volume of the filtrate plus washing water is 412ml, then add 30% sodium hydroxide solution to the filtrate to adjust the pH value of the filtrate to 0...
Embodiment 2
[0025] A process for removing base metals from materials containing platinum group metals. 100g of materials containing platinum group metals is added to 375ml of water for dissolution, wherein the water in the materials containing platinum group metals is 34.34g, the base metal nickel is 5.44g, and the base metal copper It is 16.97g. Use 125ml of 12mol / L hydrochloric acid to adjust the acidity of the solution to 3mol / L, and the liquid-solid mass ratio of the acidity-adjusted solution obtained is 5:1. Stir and raise the temperature of the solution to 75°C on the electric heating plate. At this time, chlorine gas is introduced to start chlorination and dissolution. The flow rate of chlorine gas is 18L / h. During the process of chlorination and dissolution, the temperature is maintained at 75°C. The reaction time for chlorination and dissolution is 12 hours. After the chlorinated solution is finely filtered to remove the insoluble residue, the total volume of the filtrate plus wa...
Embodiment 3
[0035] A process for removing base metals from materials containing platinum group metals. Add 100kg of materials containing platinum group metals to 320L of water for dissolution, wherein the water in the materials containing platinum group metals is 38.88kg, the base metal nickel is 2.69kg, and the base metal copper It is 21.64kg. Use 80L12mol / L hydrochloric acid to adjust the acidity of the solution to 2.5mol / L, and the liquid-solid mass ratio of the acidity-adjusted solution obtained is 5:1. Stir and feed chlorine gas to raise the temperature of the solution to 75°C. At this time, feed chlorine gas to start chlorination and dissolution. The flow rate of chlorine gas is 24L / h. During the process of chlorination and dissolution, the temperature is maintained at 80°C. The reaction time for chlorination and dissolution is 8 hours. After the chlorinated solution is finely filtered to remove the insoluble residue, add a total of 450L of washing water to the filtrate and transfer...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com