Method and device for obtaining cross-domain end-to-end routing, and sub-routing calculation entity
A cross-domain, routing technology, applied in the field of communications, can solve problems such as low computational efficiency, difficulty in finding the optimal route, and no solution proposed, to achieve the effect of improving accuracy
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
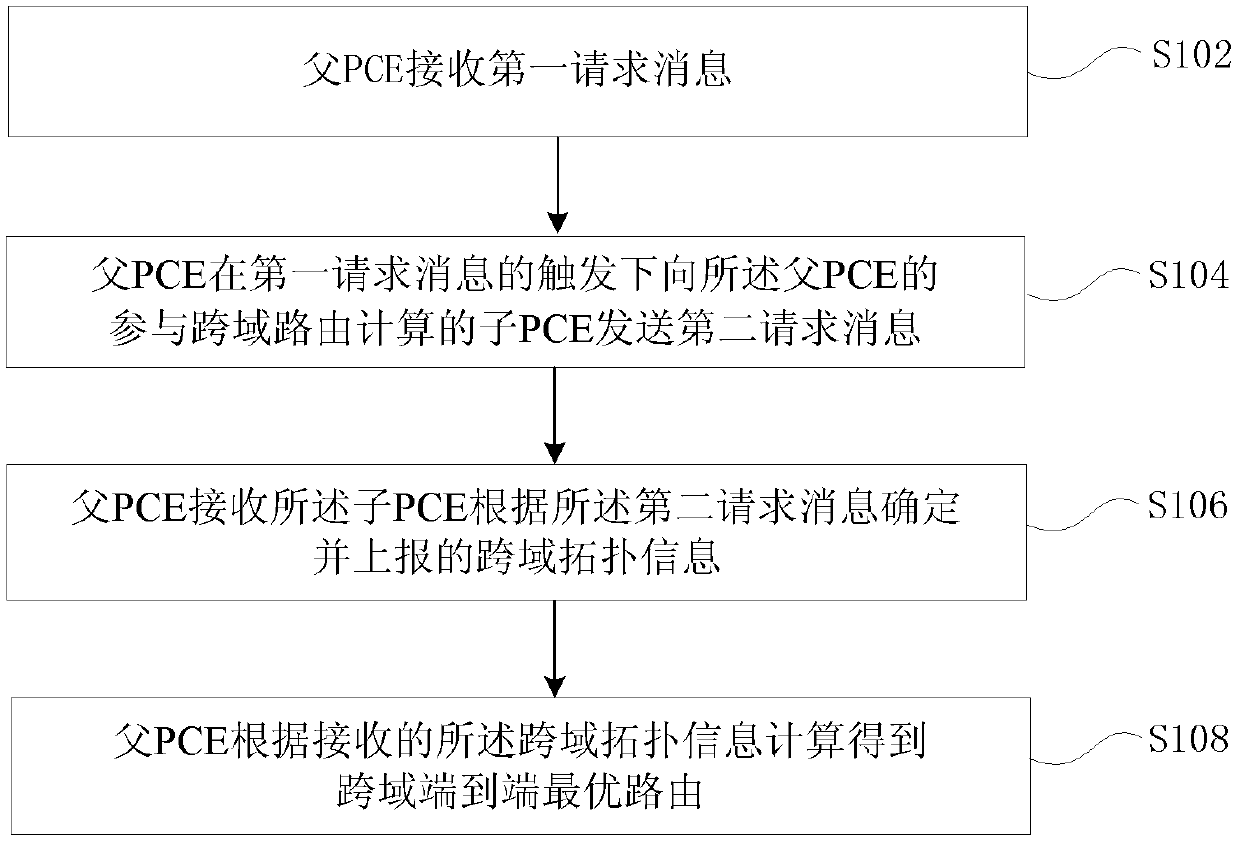
[0081] In order to calculate the optimal route that meets the routing request conditions and domain local policies, the topology of the entire network is composed of the following types of links: inter-domain links; virtual links corresponding to the optimal path in the domain; physical links corresponding to the optimal path in the domain Link: a cross-domain intra-domain link planned in advance by domain local policy (the two endpoints of the link are in the same domain)
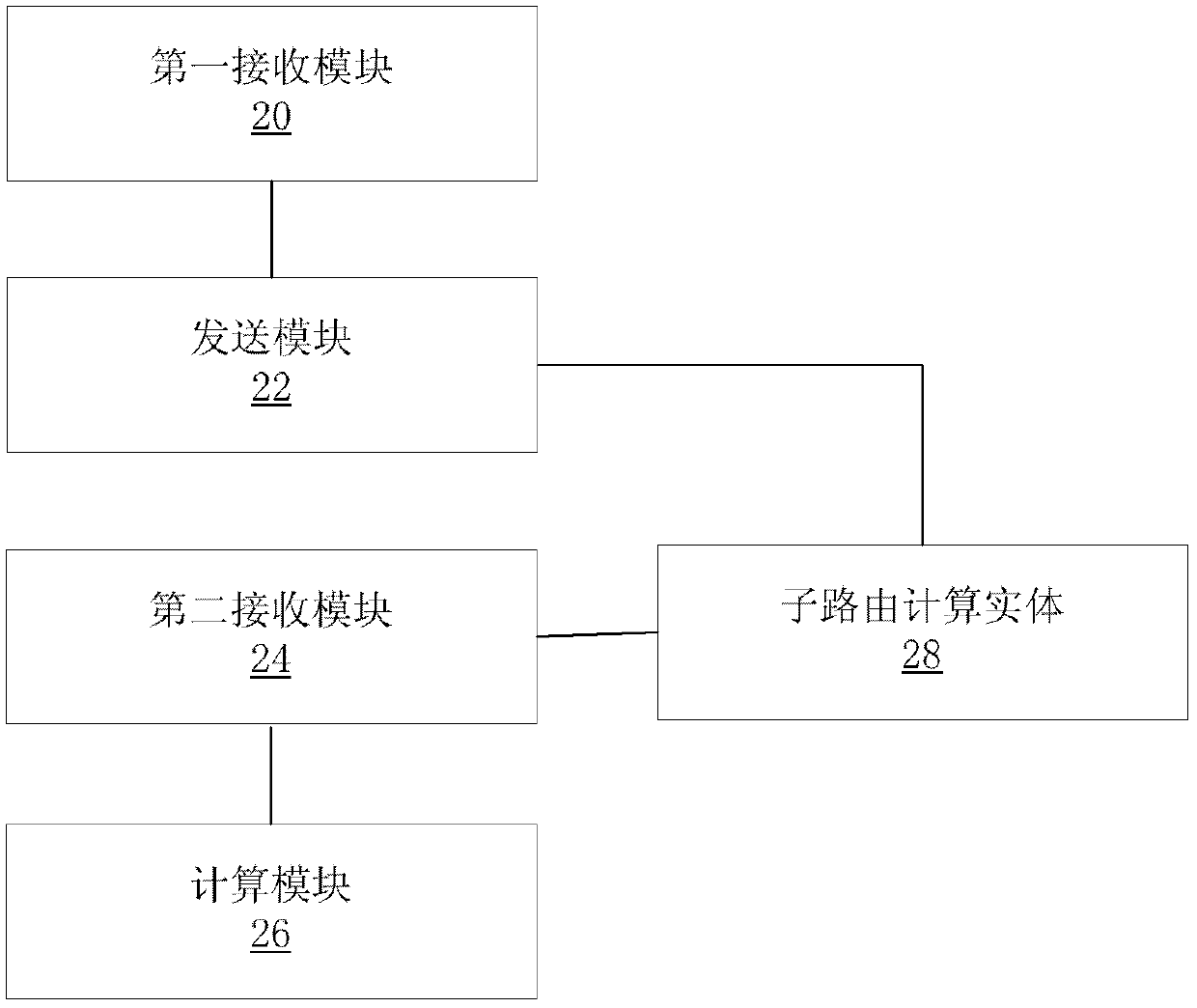
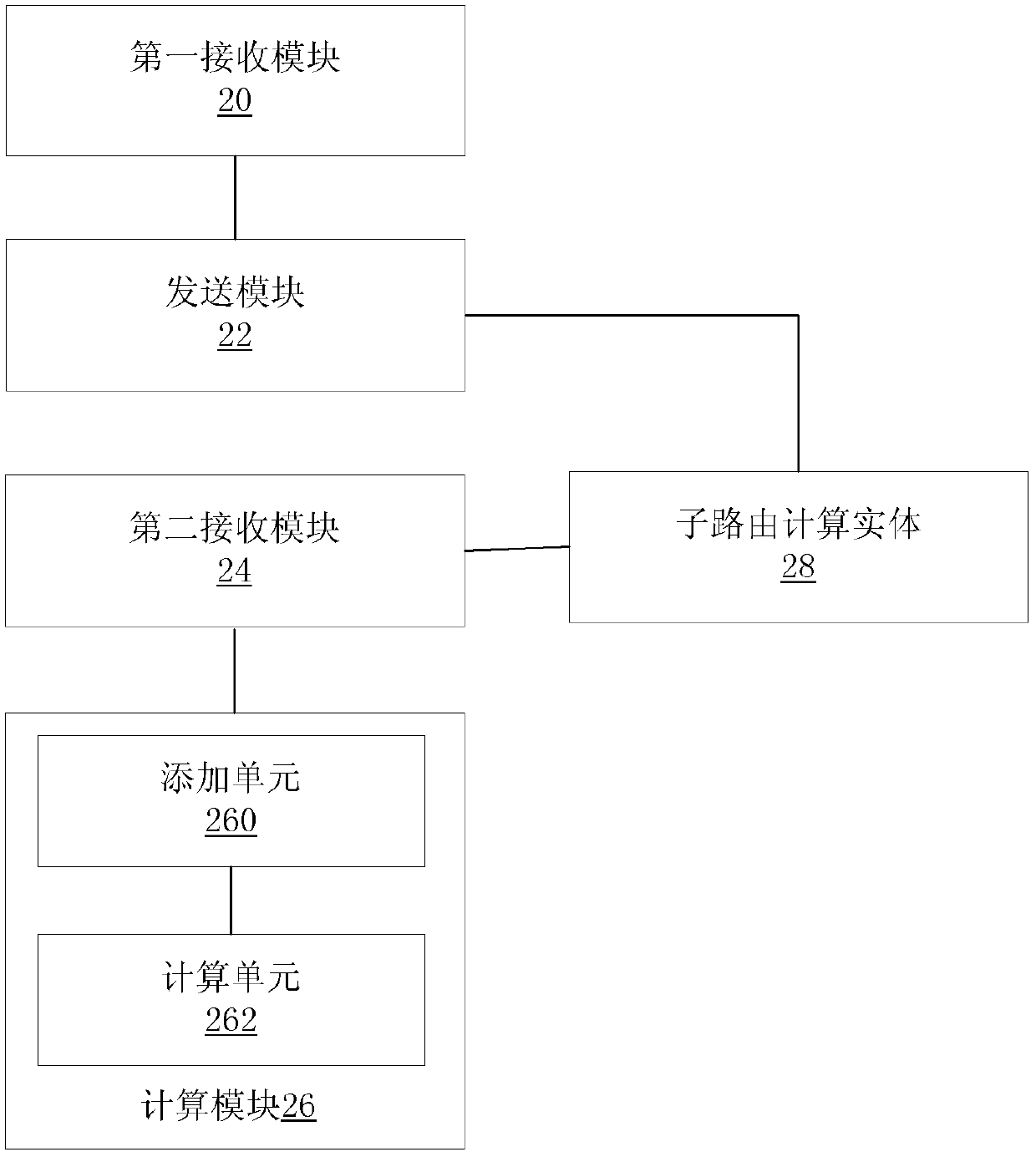
[0082] In this embodiment, two types of routing calculation entities are involved, the parent PCE and the child PCE. The parent PCE is responsible for calculating cross-domain end-to-end routes according to the network topology of the entire network. The sub-PCE is responsible for calculating intra-domain routes according to the network topology of the domain it serves. A sub-PCE is allowed to serve multiple domains, that is, to calculate intra-domain routes for multiple domains.
[0083] Considering tha...
Embodiment 2
[0099] This embodiment relates to a connection-oriented network, including a connection-oriented packet switching network multi-protocol label switching (Multi-Protocol Label Switching, referred to as MPLS), such as MPLS / MPLS_TP (Transport profile, transport plane) network, synchronous digital system (Synchronous Digital Hierarchy (referred to as SDH) network, Optical Transport Network (Optical Transport Network, referred to as OTN), etc., are technologies for calculating cross-domain end-to-end optimal routes in connection-oriented multi-domain networks.
[0100] In this example, if Image 6As shown, the parent PCE and the child PCE run on different servers, and the parent PCE has been configured with {Domain1, child PCE1}, {Domain2, child PCE2}, {Domain3, child PCE3}, {Domain4, child PCE4}, { Domain5 and sub-PCE5} respectively correspond to domain information and sub-PCE information, the domain information includes a domain identifier, and the sub-PCE information includes a s...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com