Gallium stibino mid-infrared circular spot output low divergence angle edge photon emission crystal laser
A low divergence angle and photonic crystal technology, applied in the structure of optical waveguide semiconductors, etc., can solve the problems of large far-field emission angle, small beam waist size of fundamental mode beam, and reduced optical confinement factor, so as to increase the optical field area , high repeatability, and the effect of reducing the divergence angle of the far field
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
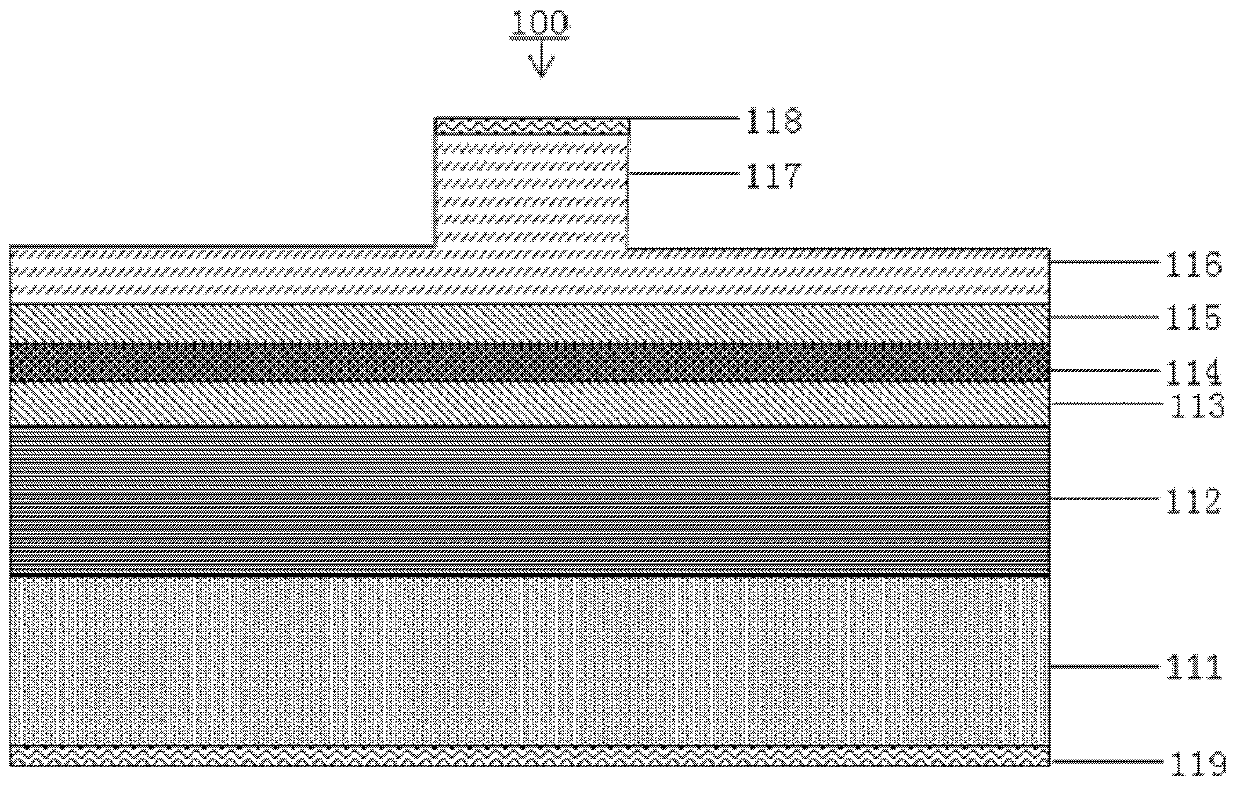
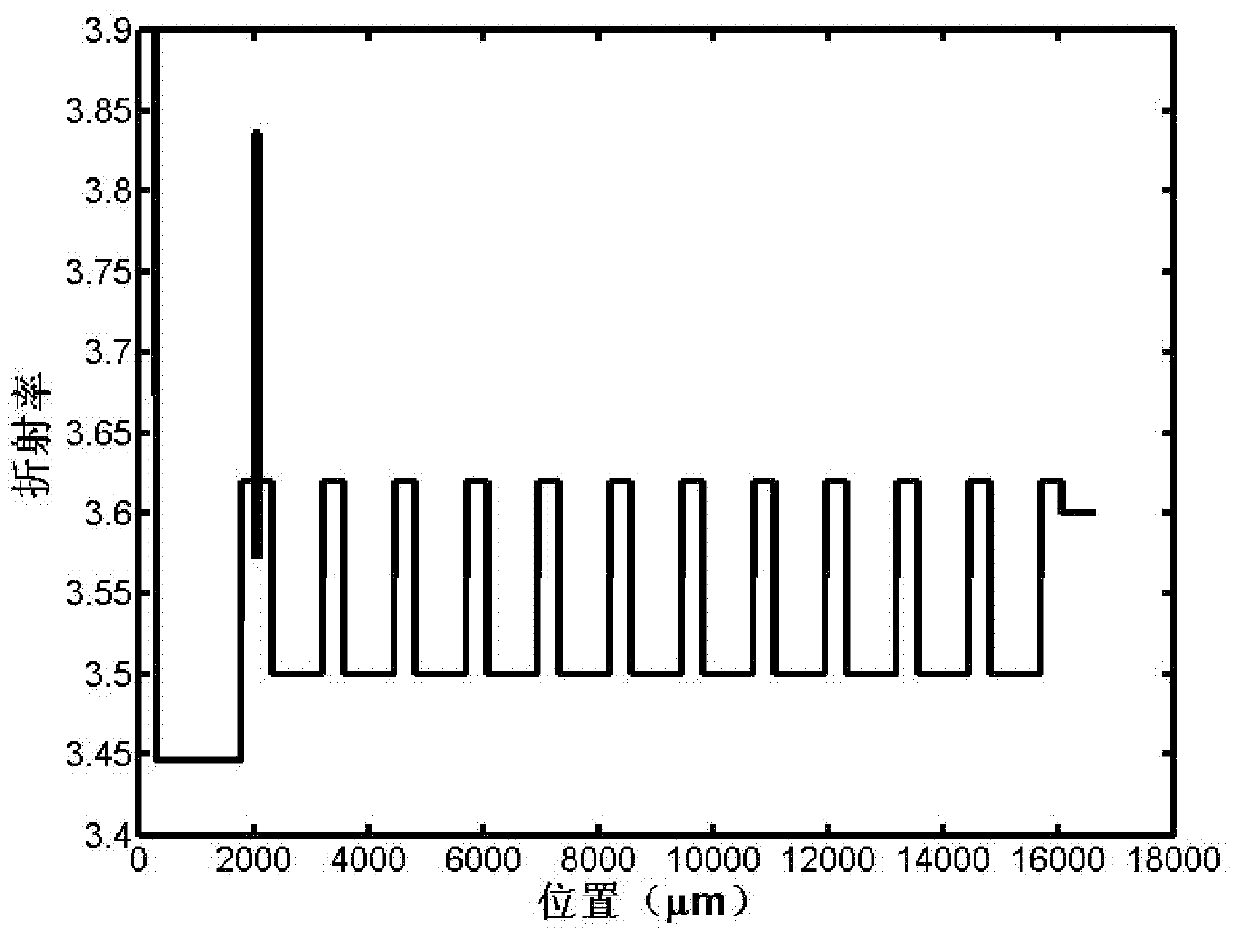
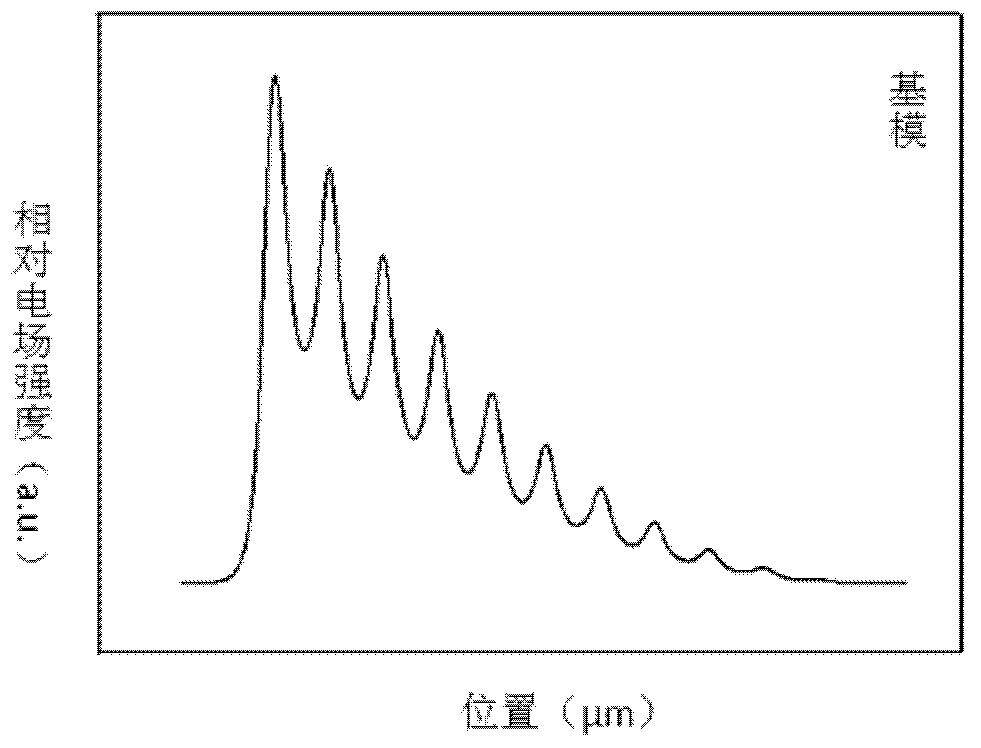
[0024] In order to make the object, technical solution and advantages of the present invention clearer, the present invention will be described in further detail below in conjunction with specific embodiments and with reference to the accompanying drawings.
[0025] It should be noted that, in the drawings or descriptions of the specification, similar or identical parts all use the same figure numbers. Implementations not shown or described in the accompanying drawings are forms known to those of ordinary skill in the art. Additionally, while illustrations of parameters including particular values may be provided herein, it should be understood that the parameters need not be exactly equal to the corresponding values, but rather may approximate the corresponding values within acceptable error margins or design constraints. In addition, the directional terms mentioned in the following embodiments, such as "upper", "lower", "front", "rear", "left", "right", etc., are only re...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com