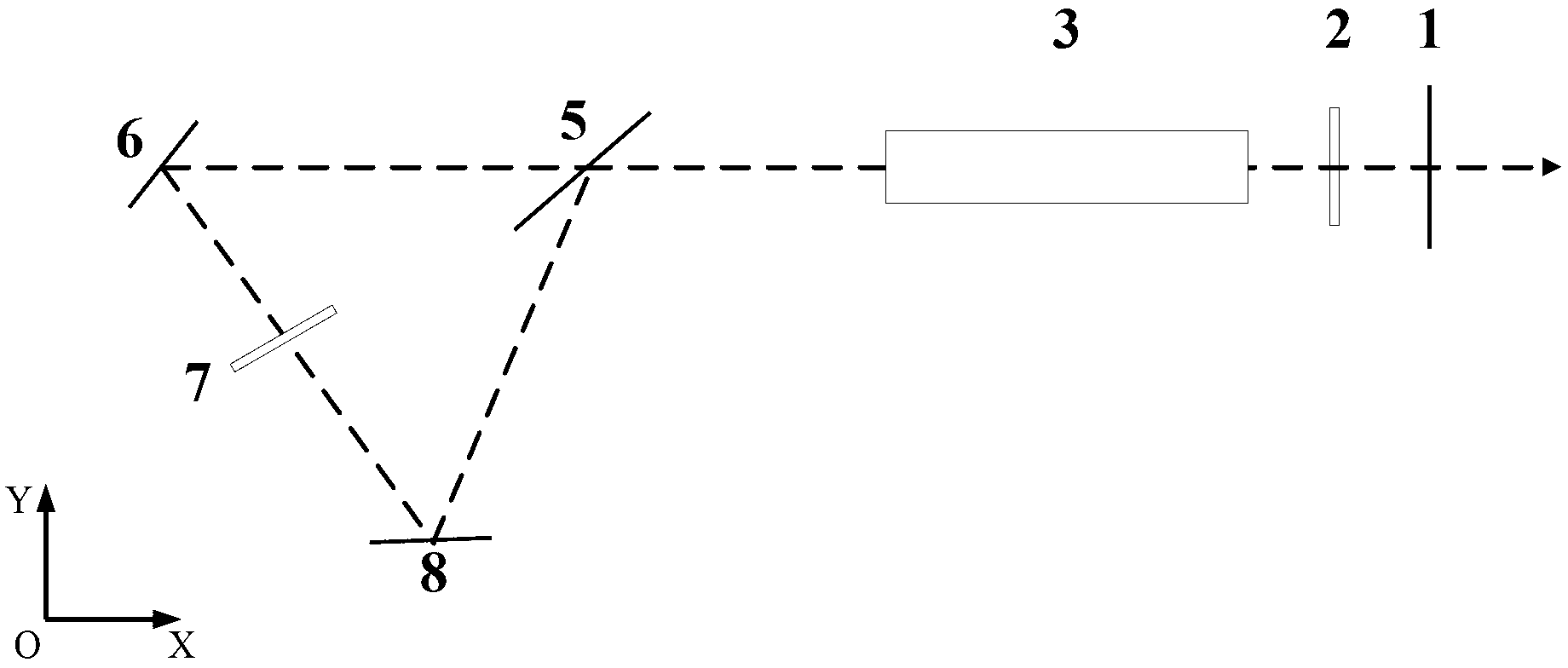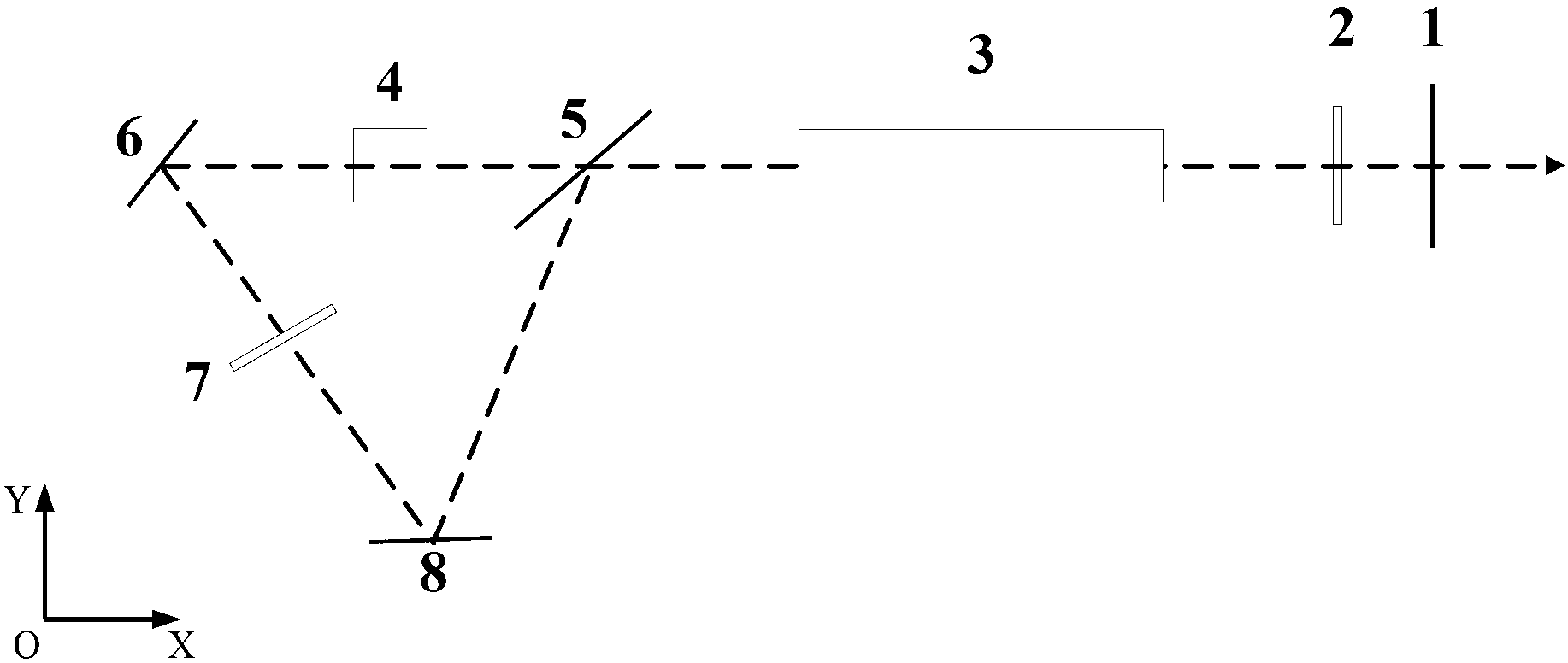Solid laser with annular polarization compensation
A solid-state laser and polarization technology, which is applied to lasers, laser components, phonon exciters, etc., can solve the problems of increasing resonant cavity depolarization loss, laser power and laser mode decline, and achieve high electro-optical conversion efficiency and high peak value Effect of power, high beam quality
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0019] figure 1 As shown, the laser includes a laser output mirror 1 , a λ / 4 wave plate 2 , a laser gain medium 3 , a polarizing beam splitter 5 , a first reflection mirror 6 , a λ / 2 wave plate 7 , and a second reflection mirror 8 . Wherein the laser output mirror 1, the polarization beam splitter mirror 5, the first mirror 6, and the second mirror 8 constitute a laser resonant cavity. The optical path between the laser beam splitter 5 and the laser output 1 is the main optical path of the resonant cavity.
[0020] The laser output mirror 1 is a semi-transparent and half-reflective mirror, which realizes laser output while improving sufficient reflection and amplification of the resonant cavity.
[0021] The λ / 4 wave plate 2 is located on the main optical path of the laser resonator, and controls the ratio and composition of the polarization state of the laser output from the resonator.
[0022] The laser gain medium 3 is located on the main optical path of the laser resonat...
Embodiment 2
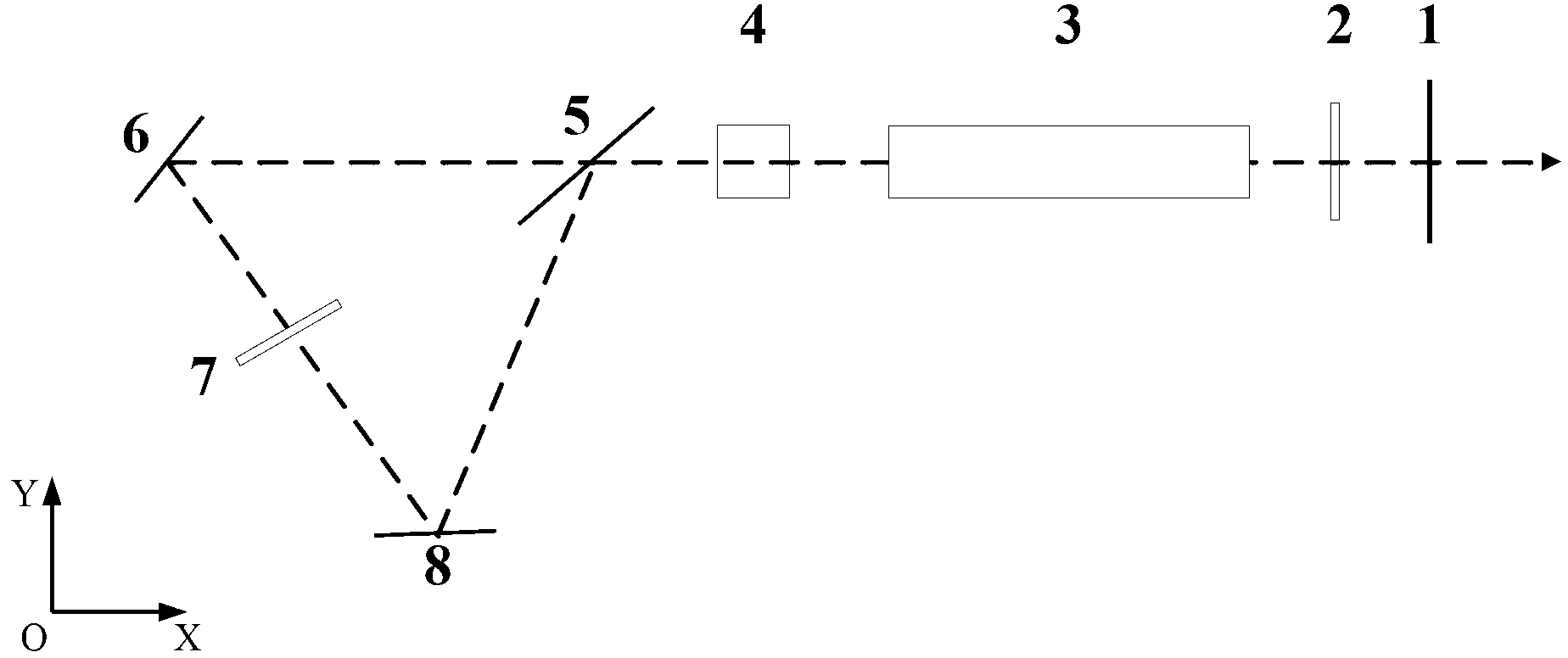
[0028] figure 2 An application example of the laser of the present invention under Q-switched operation is given, such as figure 2 As shown, the laser includes a laser output mirror 1, a λ / 4 wave plate 2, a laser gain medium 3, a Q-switching device 4, a polarizing beam splitter 5, a first reflector 6, a λ / 2 wave plate 7, and a second reflector Mirror 8. Wherein the laser output mirror 1, the polarization beam splitter mirror 5, the first mirror 6, and the second mirror 8 constitute a laser resonant cavity. The optical path between the laser beam splitter 5 and the laser output 1 is the main optical path of the resonant cavity.
[0029] The laser output mirror 1 is a semi-transparent and half-reflective mirror, which realizes laser output while improving sufficient reflection and amplification of the resonant cavity.
[0030] The λ / 4 wave plate 2 is located on the main optical path of the laser resonator, and controls the ratio and composition of the polarization state of ...
Embodiment 3
[0037] image 3 The second application example of the laser of the present invention under Q-switched operation is given, such as image 3 As shown, the laser includes a laser output mirror 1, a λ / 4 wave plate 2, a laser gain medium 3, a Q-switching device 4, a polarizing beam splitter 5, a first reflector 6, a λ / 2 wave plate 7, and a second reflector Mirror 8. Wherein the laser output mirror 1, the polarization beam splitter mirror 5, the first mirror 6, and the second mirror 8 constitute a laser resonant cavity. The optical path between the laser beam splitter 5 and the laser output 1 is the main optical path of the resonant cavity.
[0038] The laser output mirror 1 is a semi-transparent and half-reflective mirror, which realizes laser output while improving sufficient reflection and amplification of the resonant cavity.
[0039] The λ / 4 wave plate 2 is located on the main optical path of the laser resonator, and controls the ratio and composition of the polarization sta...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com