Method for detecting and identifying human polyomavirus with high sensitivity
A polyoma virus and polynucleotide technology, which is applied in the detection field of pathogenic microorganisms, can solve the problems of staying, low detection throughput, and no method for detecting a variety of human polyoma viruses.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
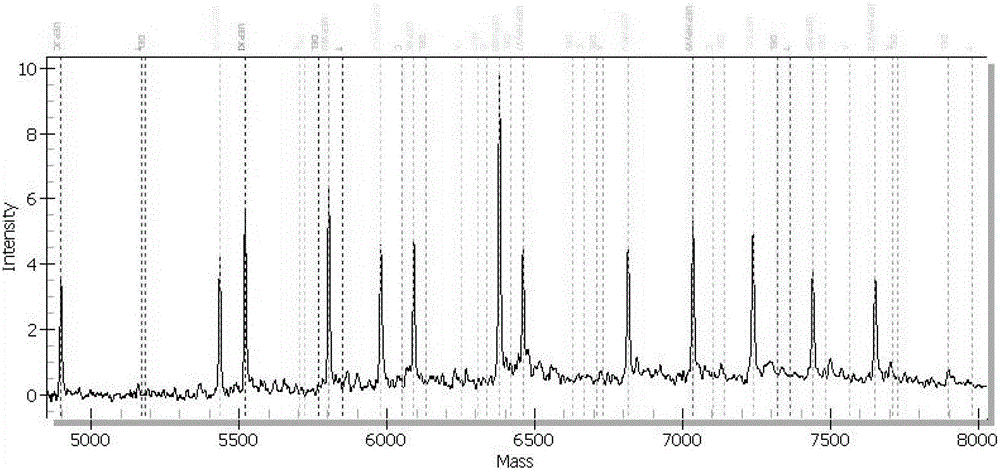
[0040] The invention includes simultaneous detection of one or more of 12 known human polyomaviruses, each genotype adopts VP1 gene region for detection. The specific embodiments described here are only used to explain the present invention, not to limit the present invention.
[0041] In the method for highly sensitive detection and / or identification of human polyomaviruses provided by the embodiments of the present invention, 12 kinds of human polyomaviruses to be detected include: BKPyV, JCPyV, KIPyV, WUPyV, MCPyV, HPyV6, HPyV7, TSPyV, HPyV9, MWPyV, STLPyV and HPyV12. Including the following steps:
[0042] (1) According to the full sequence of the human polyomavirus to be tested, obtain the VP1 gene region, select the specific conserved sequence of each type, and design a pair of PCR primers with 10 bases (ACGTTGGATG) at the 5' end of the primers Any combination of tag sequences can make the total length more than 30 bases, which is used to distinguish primers from probe...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com