Microbial strain expressing glycosidase and application technique thereof to biological enzyme papermaking
A thermophilic glucosidase and papermaking pulp technology, applied in the direction of microorganism-based methods, biochemical equipment and methods, microorganisms, etc., can solve problems such as poor thermal stability and unstable organic solvents
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0041] [Example 1] Using crops and leaves as the ratio screening of papermaking raw material pulp
[0042] In this embodiment, the alkaloid sodium ethoxide is used, and the raw materials are corn stalks, wheat stalks, and banana leaves, and a ratio experiment of different raw materials is carried out. The purpose of raw material slurry ratio screening is to explore for the subsequent enzymatic papermaking and reduce papermaking pollution.
[0043] The specific proportioning schemes are shown in Table 1 to Table 4 below. The ratio of corn stalks: wheat is from 1:1 to 10:1; banana leaves: fishbone leaves are from 4:1 to 9:1; 1:1 to 5:1.
[0044] Table 1: Biological enzymatic papermaking experiment with the ratio of two crops
[0045]
[0046] Table 3 Proportion of crops and leaves for bio-enzymatic papermaking experiment (corn stalks and banana leaves)
[0047]
[0048] The results of the bio-enzymatic papermaking experiment with the ratio of the above two crops show t...
Embodiment 2
[0049] [Example 2] Screening of technological conditions of enzymatic method combined with organic alkali papermaking method
[0050] The cellulase used in this example: the model is 1.4 million U / g, the batch number is 20120280008YX, and the manufacturer is Xiasheng Industrial Group Co., Ltd.
[0051] β-glucanase: the model is 30 million U / g, the batch number is 20120280008YX, and the manufacturer is Xiasheng Industrial Group Co., Ltd.
[0052] The results of the research on the environmental protection process conditions of enzymatic method + organic alkali are shown in Table 5:
[0053] Table 5: Exploration of enzymatic papermaking conditions
[0054]
[0055] It can be seen from Table 5 that the required action time is also significantly different when the concentration of the enzyme is different. According to the cost, the group with a smaller amount of enzyme and a shorter action time is preferred. Because the amount of enzyme added is directly related to the produc...
Embodiment 3
[0056] [Example 3] Construction of a vector expressing a biological enzyme gene
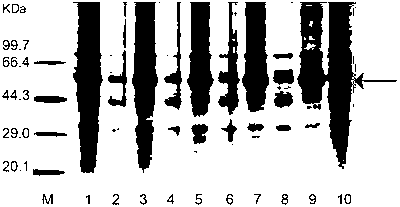
[0057] The gene thermophilic glycosidase 0602, also called TN0602 in this paper, was extracted from the genome of Thermotoga naphthophila (Thermotoga naphthophila, Japan Collection of Microorganisms, RIKEN BioResource Center) by conventional PCR. Ferment hyperthermophilic archaea, collect the bacteria by centrifugation, extract the gene with a kit, transfer the thermophilic glycosidase 0602 gene from the genome by PCR, and then transfer it into Escherichia coli (E.coli BL21 (DE3)) for further Expression, purification and characterization of basic enzymatic properties.
[0058] Experimental materials and methods
[0059] Genome extraction: Escherichia coli cells transformed with the thermophilic glycosidase 0602 gene were collected by centrifugation, and their genomes were extracted with a kit (Hangzhou Viteje Co., Ltd.) according to the instructions of the kit.
[0060] Primer design: Using the...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com