Yeast beta-D-glucan derivative and preparation method and application thereof
A technology of glucan and derivatives, applied in the field of glucan derivatives, can solve problems such as small specific surface area and application limitation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0039] Preparation of esterification agent: Place a four-neck flask with a condenser, a stirring device and a temperature measuring device in a brine ice bath, add pyridine, stir, and cool it below 0°C, then use a constant pressure dropping funnel to slowly Slowly add chlorosulfonic acid, and the dropwise addition is completed in about 30 minutes. A large amount of light yellow solid appears in the flask, and the esterification agent is obtained.
[0040] A certain amount of yeast β-D-glucan was weighed and dissolved in dimethylformamide, stirred and suspended at room temperature, and then added to the prepared esterification agent. Quickly move the four-necked flask into a hot water bath, stir at constant temperature, react for a certain period of time, then transfer it to an ice-water bath to cool to room temperature, pour the reaction solution into ice water, neutralize it to about pH 7.5 with 2.5% NaOH, add Water ethanol 1:3 (V / V), a light yellow precipitate was precipitat...
Embodiment 1
[0056] Example 1 Preparation of yeast β-D-glucan
[0057] Add an appropriate amount of distilled water to the yeast cell wall, add papain, incubate at 55°C for 24h, centrifuge at 4500r / min for 10min, add 3% NaOH solution (3:1, V / W) to the sediment for 2h at 90°C, centrifuge, and precipitate The product was washed twice with water (2:1, V / W), once with absolute ethanol (2:1, V / W), twice with ether (2:1, V / W), freeze-dried, and obtained.
[0058] The prepared product was qualitatively and quantitatively analyzed. The results of thin-layer chromatography and infrared spectroscopy showed that the prepared product was β-D-glucan, and the content of glucan reached 87.36%.
experiment example 1
[0059] Experimental example 1 single factor experiment of different sulfation conditions affecting degree of substitution
[0060] Taking the degree of substitution of sulfuric acid group as an index, the effects of sulfation conditions (volume ratio of chlorosulfonic acid to pyridine, reaction temperature and reaction time) on the degree of substitution were investigated.
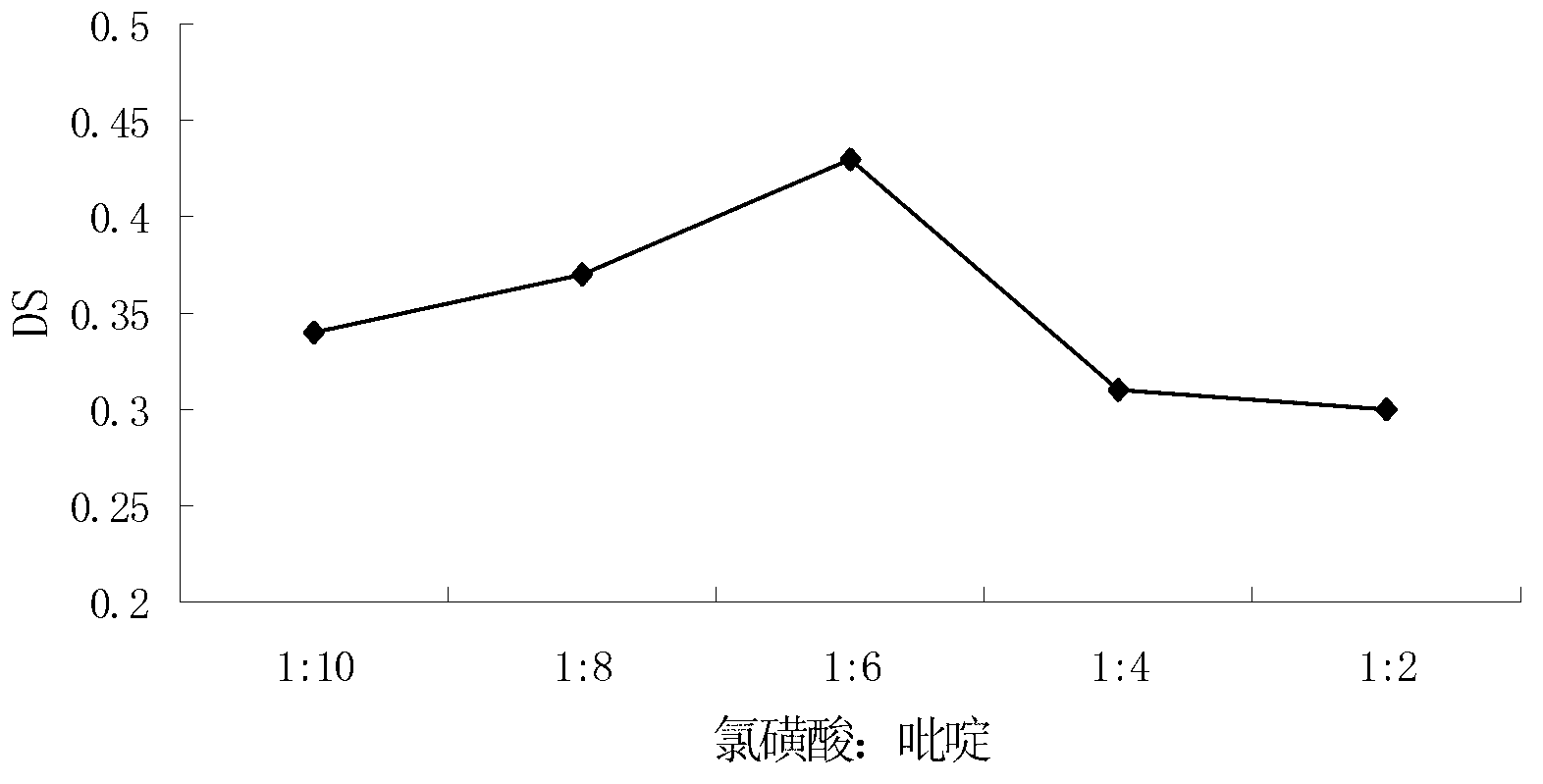
[0061] 1. Effect of different ratios of chlorosulfonic acid and pyridine on the degree of substitution
[0062] Prepare the esterification agent according to the volume ratio of chlorosulfonic acid to pyridine: 1:2, 1:4, 1:6, 1:8, 1:10, the reaction temperature is 60°C, and the reaction time is 3h. The degree of substitution was used as an indicator, and the sulfation reaction was carried out according to method 3.2.2. see results figure 2 .
[0063] Depend on figure 2 It can be seen that when the ratio of chlorosulfonic acid to pyridine is 1:10, the degree of substitution of yeast β-glucan sulfate ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| adsorption capacity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| degree of substitution | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com