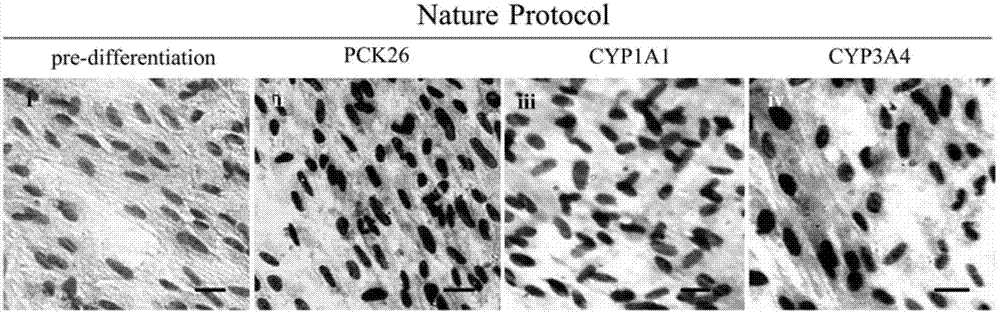
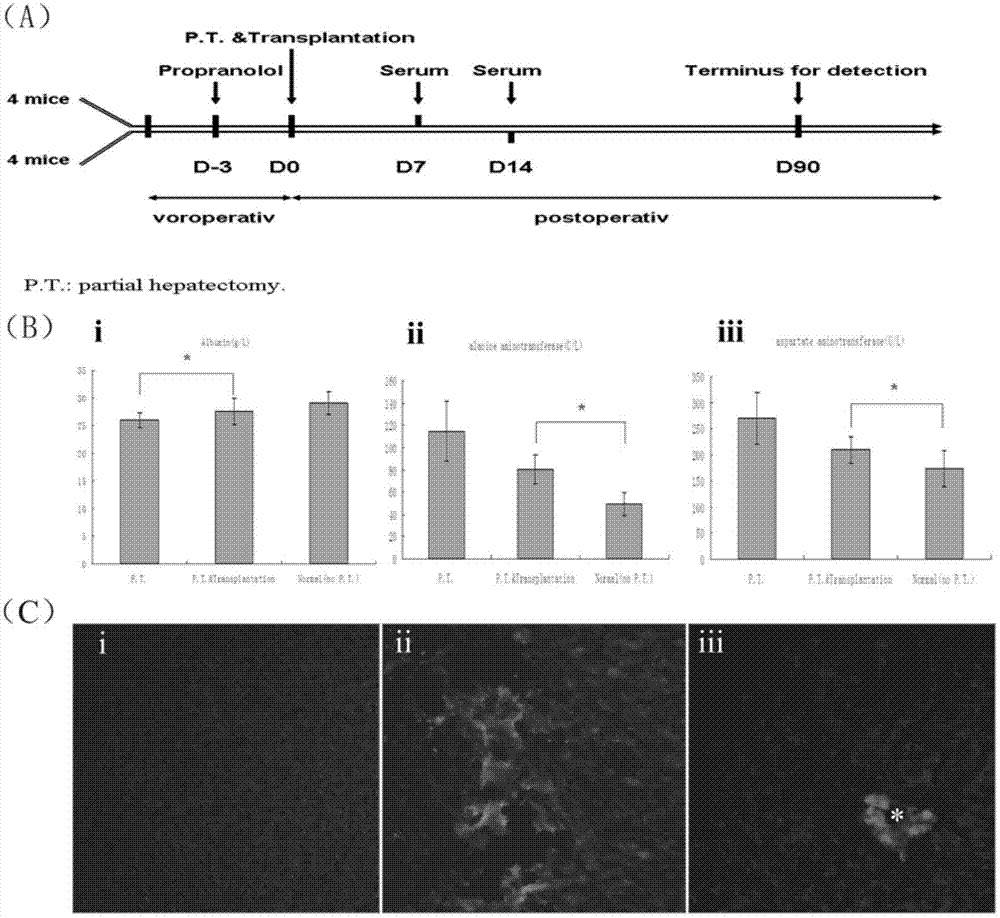
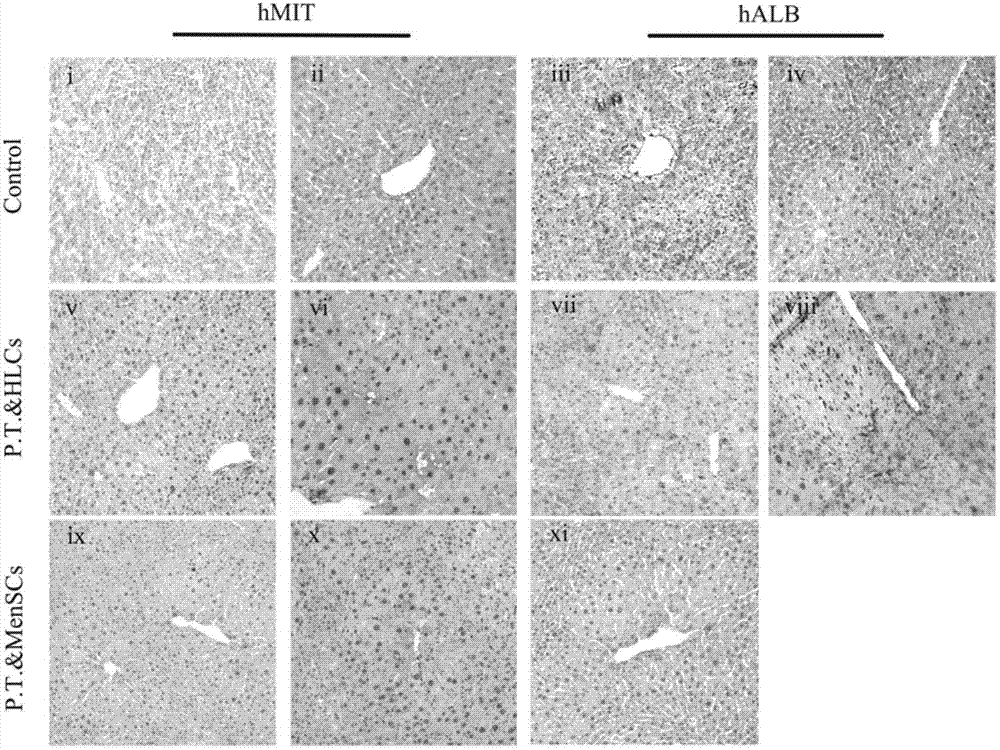
Method for induced differentiation of liver cells by using endometrium stem cells
A technology of endometrial stem cells and liver cells, applied in the field of using endometrial stem cells to induce differentiation of liver cells, to achieve the effect of enriching the source of cells
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0064] Example 1. Isolation, cultivation and expansion of menstrual blood mesenchymal stem cells:
[0065] Ten menstruating women of different ages were recruited to donate menstrual blood samples on a completely voluntary basis. After 24 hours of antibiotic treatment, microbiological testing and infectious disease pathogen safety testing were carried out. After centrifugation, the supernatant was removed, and then inoculated, using Chang's general medium in 5% CO 2 , cultured in an incubator at 36-38°C (for example, 37°C) with 95% saturated humidity. Change the medium after 5-7 days to remove non-adherent cells, and then change the medium every 2-4 days (for example, 3 days). Once the cells grew to 80% confluence, they were passaged by trypsin / EDTA digestion. Then use flow cytometry to identify the molecular phenotypes of CD117, CD34, CD44, CD45, CD73, CD90, CD105, CD29, HLA-DR, etc. on menstrual blood mesenchymal stem cells.
[0066] The specific operating procedures are...
Embodiment 2
[0130] Embodiment 2, in vitro induced differentiation and detection:
[0131] The specific operating procedures are as follows:
[0132] 1. Directed induction of endometrial stem cells to differentiate into liver cells in vitro
[0133] 1) Take the third-generation cells in good growth condition, which are characterized by vigorous growth, large cell bodies, clear nuclei, rich cytoplasm, and strong refraction under the microscope, and digest them with trypsin-EDTA digestion solution (0.25%) Under the microscope, when the cells become a single round shape, stop the digestion with DMEM medium containing 10% (volume concentration) fetal bovine serum, gently pipette and centrifuge to obtain cell pellets, PBS (PBS washing solution without calcium and magnesium ions) Wash 2 times (the purpose is to wash away trypsin, fetal bovine serum and other substances).
[0134] 2) Inoculate the above-mentioned cell pellet after washing with PBS in a 6-well plate for induction culture, and inoc...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com