Method for resisting interference in multiple-group multiple-user two-way relay network
A two-way relay and multi-user technology, applied in digital transmission systems, electrical components, error prevention, etc., can solve problems such as no degree of freedom, system performance deterioration, harsh antenna configuration, etc., to improve performance and reduce system performance deterioration Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0016] In order to make the object, technical solution and advantages of the present invention clearer, the present invention will be further described in detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings and embodiments. It should be understood that the specific embodiments described here are only used to explain the present invention, not to limit the present invention.
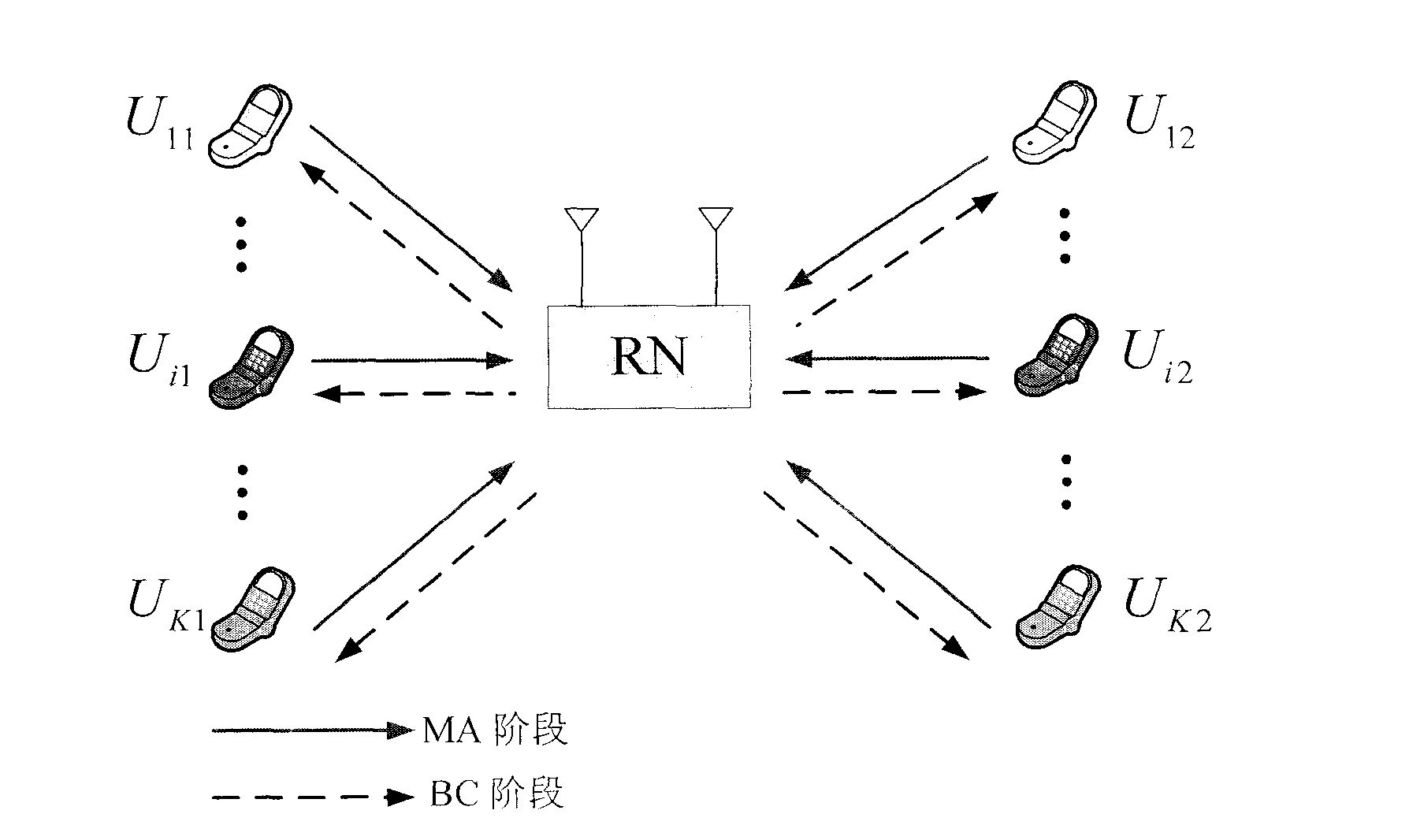
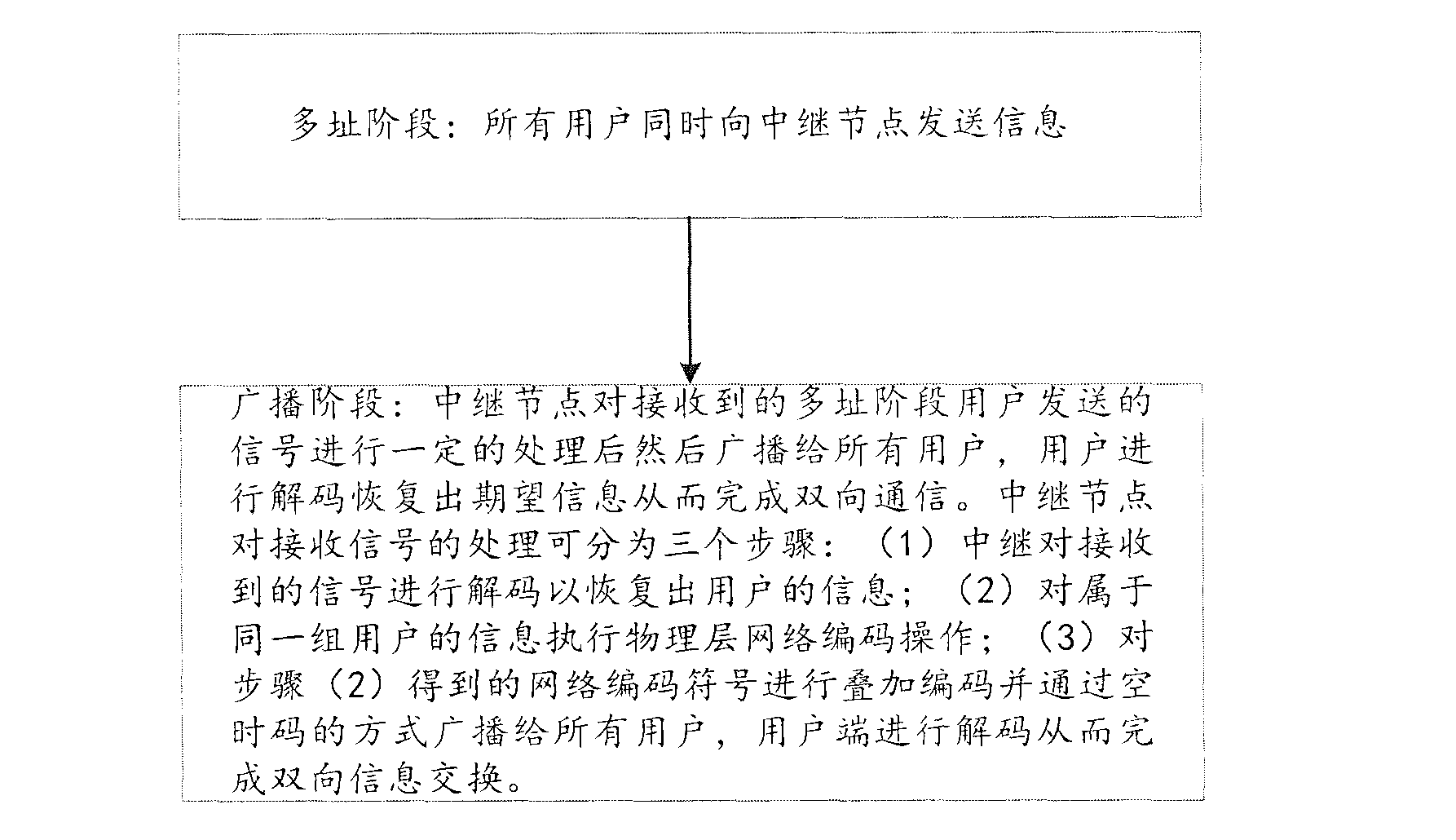
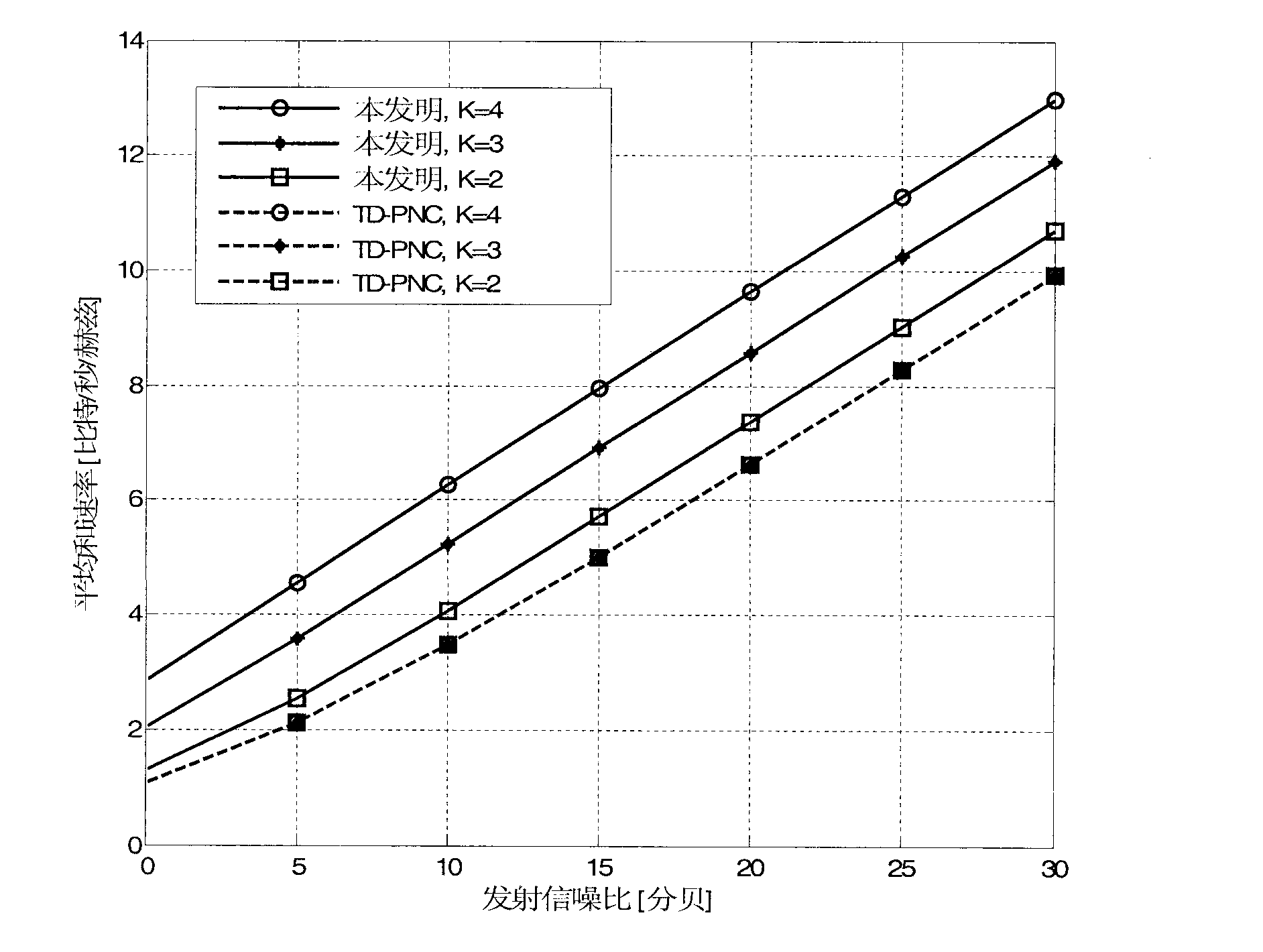
[0017] refer to figure 1 , figure 1 It is the application scenario of the example of the present invention. Such as figure 1 As shown, the considered multi-group multi-user two-way relay network consists of 2K single-antenna users and a relay node equipped with two antennas, and each user only communicates with partners belonging to the same group. u ki Indicates the i-th user of the k-th group, where k=1, 2, . . . , K, i=1, 2. Indicates user U ki The channel matrix to the relay node, each element of which is independent and identically distributed, and obeys distributed. According to the...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com