Biogas fermentation technology for utilization of heavy metal contaminated soil restoration plant material
A technology for polluted soil and remediation of plants, applied in the field of environmental pollution control, can solve problems such as feasibility and improvement effect, no research reports, secondary pollution, etc., to solve the problems of energy and fertilizer sources, and the effect of no pollution to the environment
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0014] Embodiment 1: the mensuration of basic physical and chemical property of fermented material
[0015] The freshly collected plant materials were washed and dried, and the total solids content (TS) and volatile solids content (VS) were measured by conventional biogas analysis methods. The plant material was dried at 80°C, and the aboveground part was crushed and passed through a 100-mesh sieve for the determination of organic carbon, total nitrogen and copper content. Organic carbon content was determined by potassium dichromate oxidation-external heating method; total nitrogen was determined by H 2 SO 4 -H 2 o 2 Digestion, distillation and nitrogen determination; copper content was determined by atomic absorption spectrometry. The results of the measurement are shown in Table 1:
[0016] Table 1 Basic physicochemical properties of anaerobic fermentation substrate
[0017]
Embodiment 2
[0018] Embodiment 2 The influence of plant material copper concentration on anaerobic fermentation
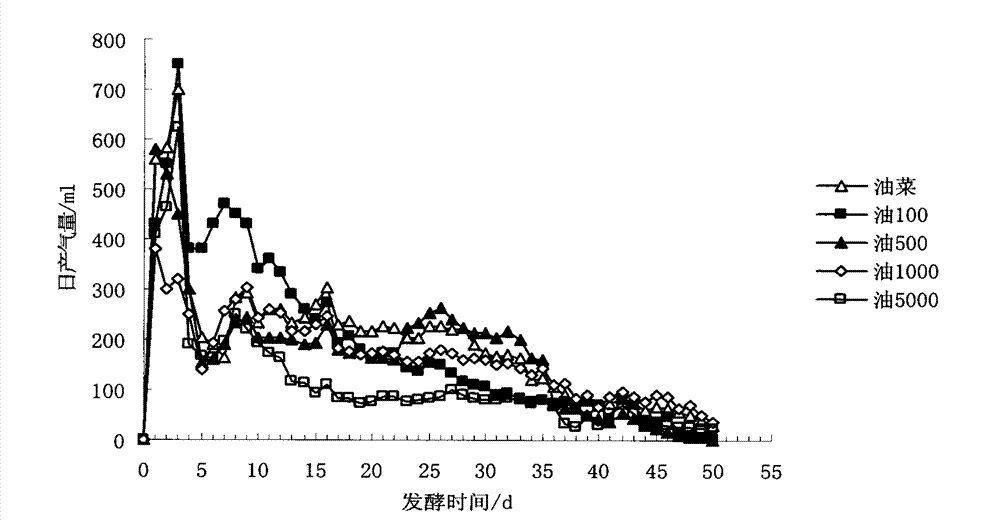
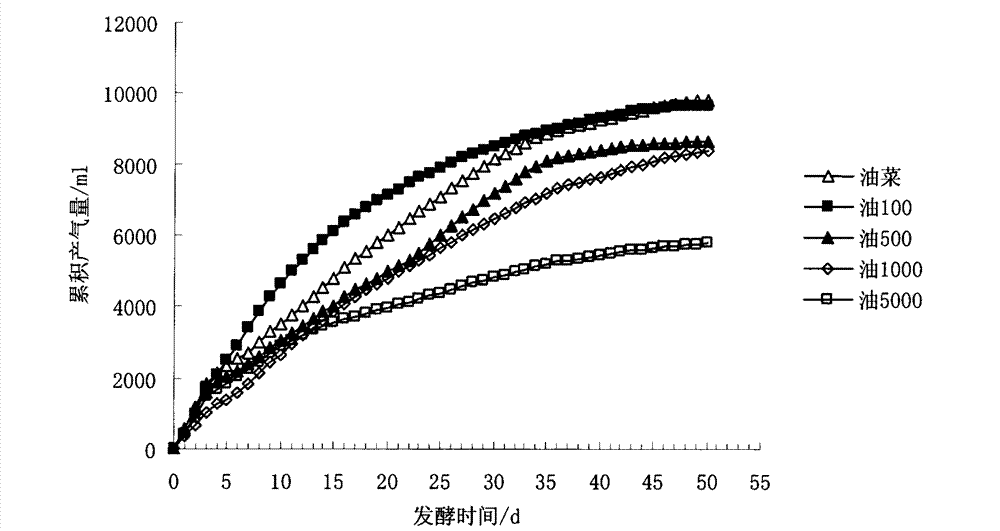
[0019] According to relevant literature reports, heavy metals have an inhibitory effect on anaerobic fermentation. Therefore, the present invention evaluates the influence of different copper concentrations on anaerobic fermentation, and the evaluation content includes daily gas production and cumulative gas production. Add different concentrations of CuSO to plant samples 4 ·5H 2 O, so that the copper content of the plant material is 27.6, 100, 500, 1000, 5000 mg·kg -1 , (Table 2) and use urea as the nitrogen source to adjust the C / N ratio to 25:1, and add water to adjust the TS content of each fermentation tank to 12%. Put 35g of air-dried restorative plant material into a 700mL fermenter with an effective volume of 500mL, and then conduct a fermentation test. The fermentation period is 50 days, and the culture is carried out in a 37°C water bath. The gas production is mea...
Embodiment 3
[0027] The anaerobic fermentation effect comparison of different repair plant materials of embodiment 3
[0028] Put 35g each of the air-dried repairing plant materials rape, evening primrose, and Herba Cinnamon into the fermenter, and the specific test scheme is shown in Table 3. Then the fermentation test was carried out, the fermentation period was 50 days, and the culture was carried out in a water bath at 37°C. The gas production was measured by the drainage collection method and measured regularly every day.
[0029] Table 3 Test plan
[0030]
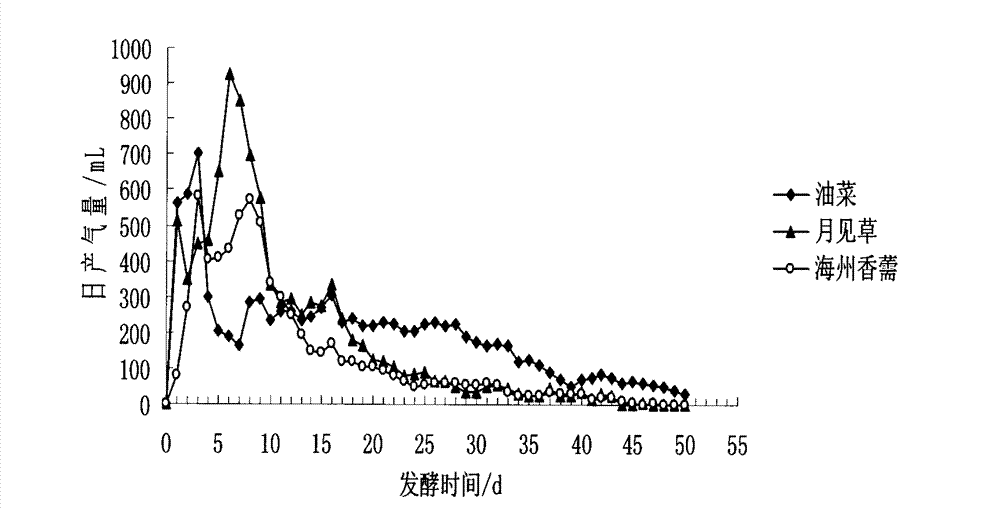
[0031] Such as image 3 As shown, comparing different plant materials, the order of the daily gas production peaks is A. haizhou (2d), rapeseed (3d), and evening primrose (6d). Among them, evening primrose (925mL) had the highest peak daily gas production, followed by rapeseed (700mL) and Haizhou fennel (580mL). It can be seen that the three kinds of restoration plants can carry out anaerobic fermentation.
[0032] Depend...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com