Soft contact limit mechanism for isolation layers
A technology of limit mechanism and shock-isolation layer, which is applied in the direction of shockproof and building components, can solve the problems of high contact stiffness, small rubber layer stiffness, impact of upper structure, etc., and achieve good limit effect, low cost and convenient construction Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
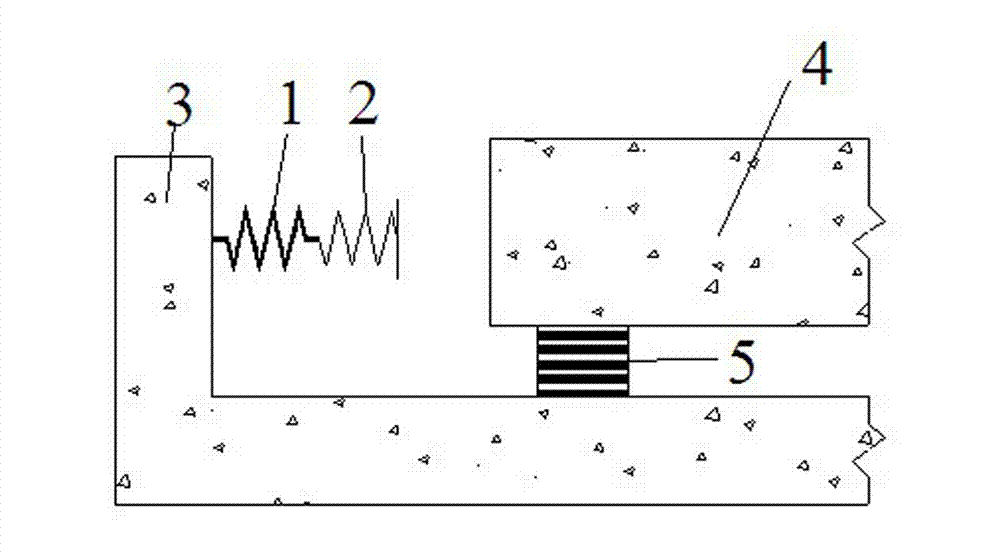
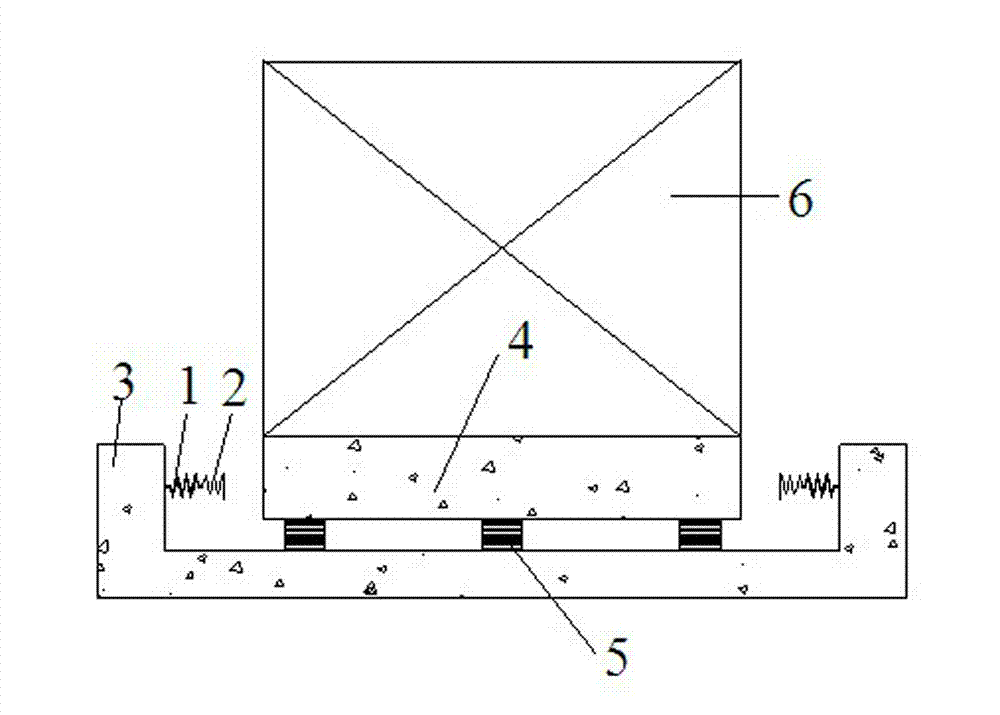
[0020] Such as Figure 1-2 As shown, a shock-isolation layer soft contact limit mechanism of the present invention includes a limiter 1, a buffer 2 and a reaction force support 3, both the limiter 1 and the buffer 2 are elastic devices, and the limiter 1 The stiffness is greater than the stiffness of the buffer 2; wherein, one end of the limiter 1 is fixed on the reaction support 3, the other end of the limiter 1 is fixedly connected to one end of the buffer 2, and the other end of the buffer 2 is connected to the spacer There is a reserved distance between the floors 4 on the upper part of the seismic floor; the reaction support 3 is connected to the lower part of the seismic isolation floor. Wherein, the limiter 1 adopts a spring, and its rigidity is relatively large; the buffer 2 also adopts a spring, and its rigidity is relatively small. The shock-isolation layer adopts a rubber bearing 5 for shock isolation, and the rubber bearing 5 is provided with an upper floor 4 of t...
Embodiment 2
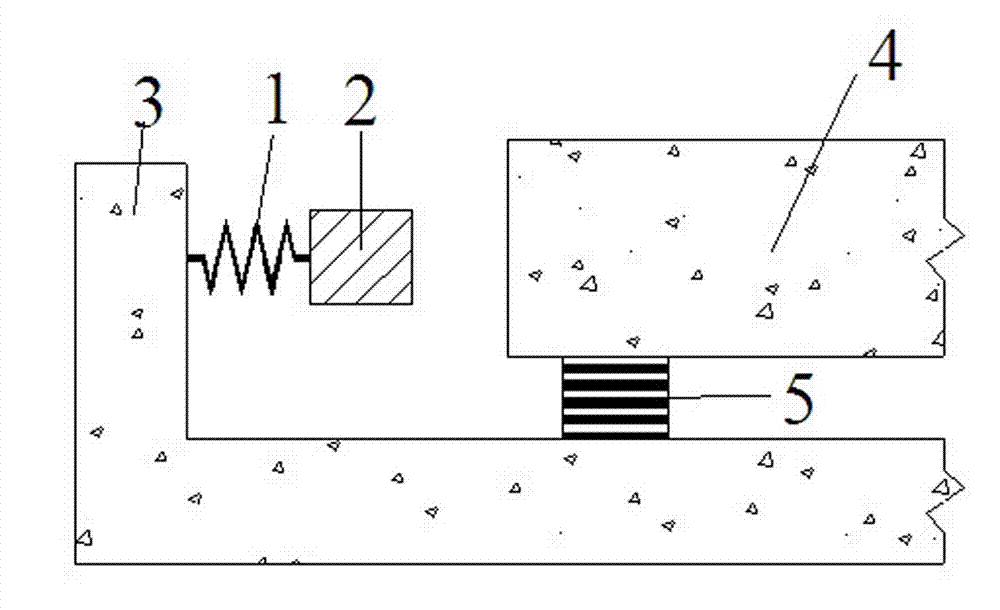
[0023] Such as image 3 As shown, in the shock-isolation layer soft contact limit mechanism of the present invention, the limiter 1 adopts a spring, and the buffer 2 adopts a rubber block. Other structures and principles are the same as those in Embodiment 1, and will not be described in detail here.
Embodiment 3
[0025] Such as Figure 4 As shown, in the shock-isolation layer soft contact limit mechanism of the present invention, the limiter 1 is made of U-shaped steel plate, and the buffer 2 is made of rubber block.
[0026] Wherein, the rubber bearing 5 in the base isolation structure of the rubber bearing of the above embodiment can also be replaced by a base sliding bearing, and used for position limitation in the base sliding base isolation structure.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com