Constant time control method, control circuit and switching regulator using same
A constant time, control method technology, applied in the direction of control/regulation system, regulation of electrical variables, instruments, etc., can solve problems such as slow transient response, complex compensation design, etc., to reduce the difference, good compensation, and reduce fluctuations Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
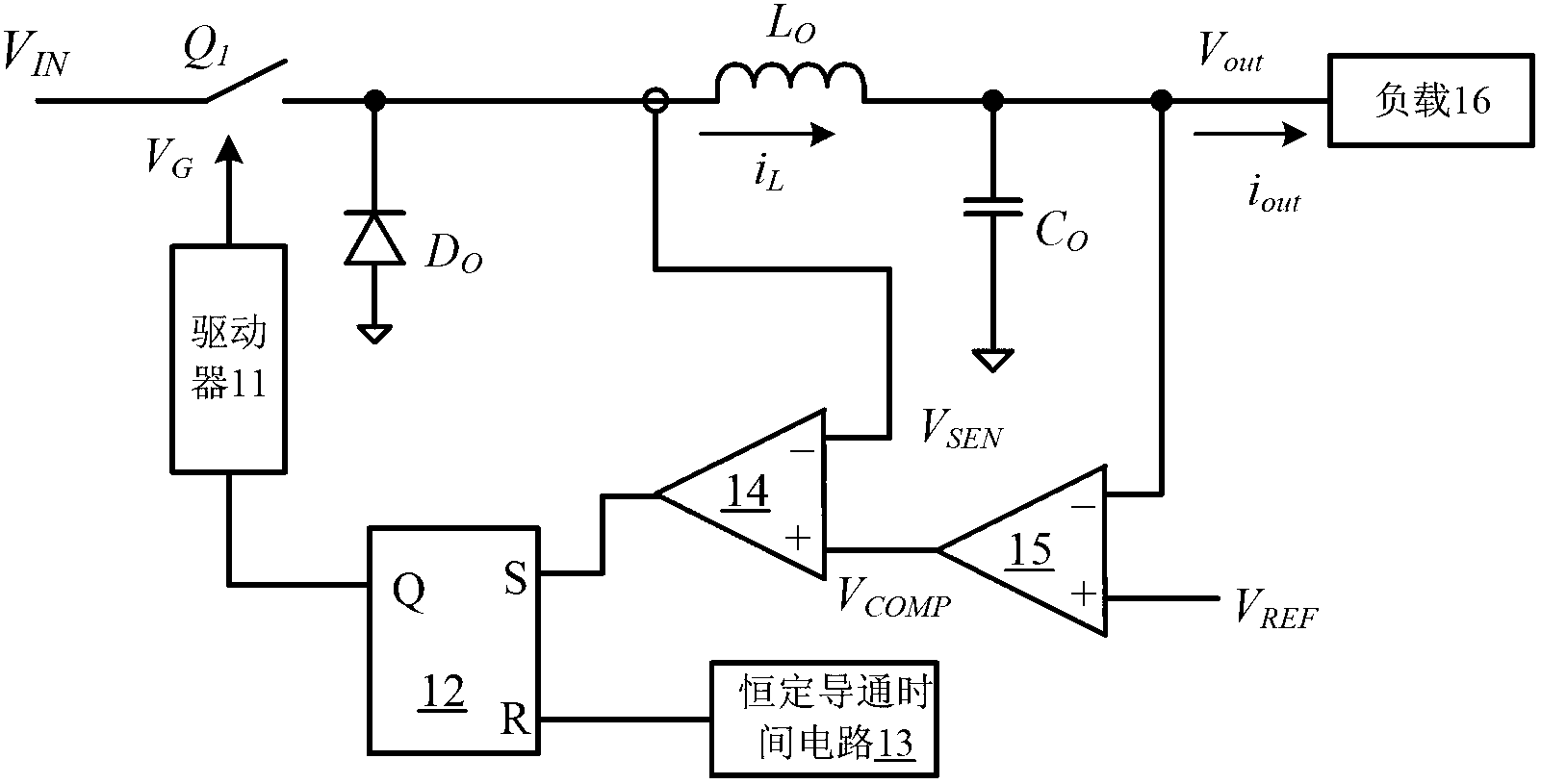
[0093] Referring to FIG. 2A, there is shown a schematic block diagram of a constant-time control circuit that can be used to control a switching regulator according to a first embodiment of the present invention.
[0094] For the convenience of description, in this embodiment, the working principle of the constant-time control circuit 200 is described by taking a step-down switching regulator as an example. Here, the main power switching device Q 1 , Diode D 0 , inductance L 0 and output capacitor C 0 A power stage circuit that forms a step-down topology, and its input terminal receives the input voltage V IN , the output terminal is connected to a load 16 .
[0095] connected in series at the output voltage V out The voltage dividing resistor network composed of resistor R1 and resistor R2 between the equipotential is used as a voltage feedback circuit to receive the output voltage V at the output terminal out , so that a voltage feedback signal V representing the outpu...
Embodiment 2
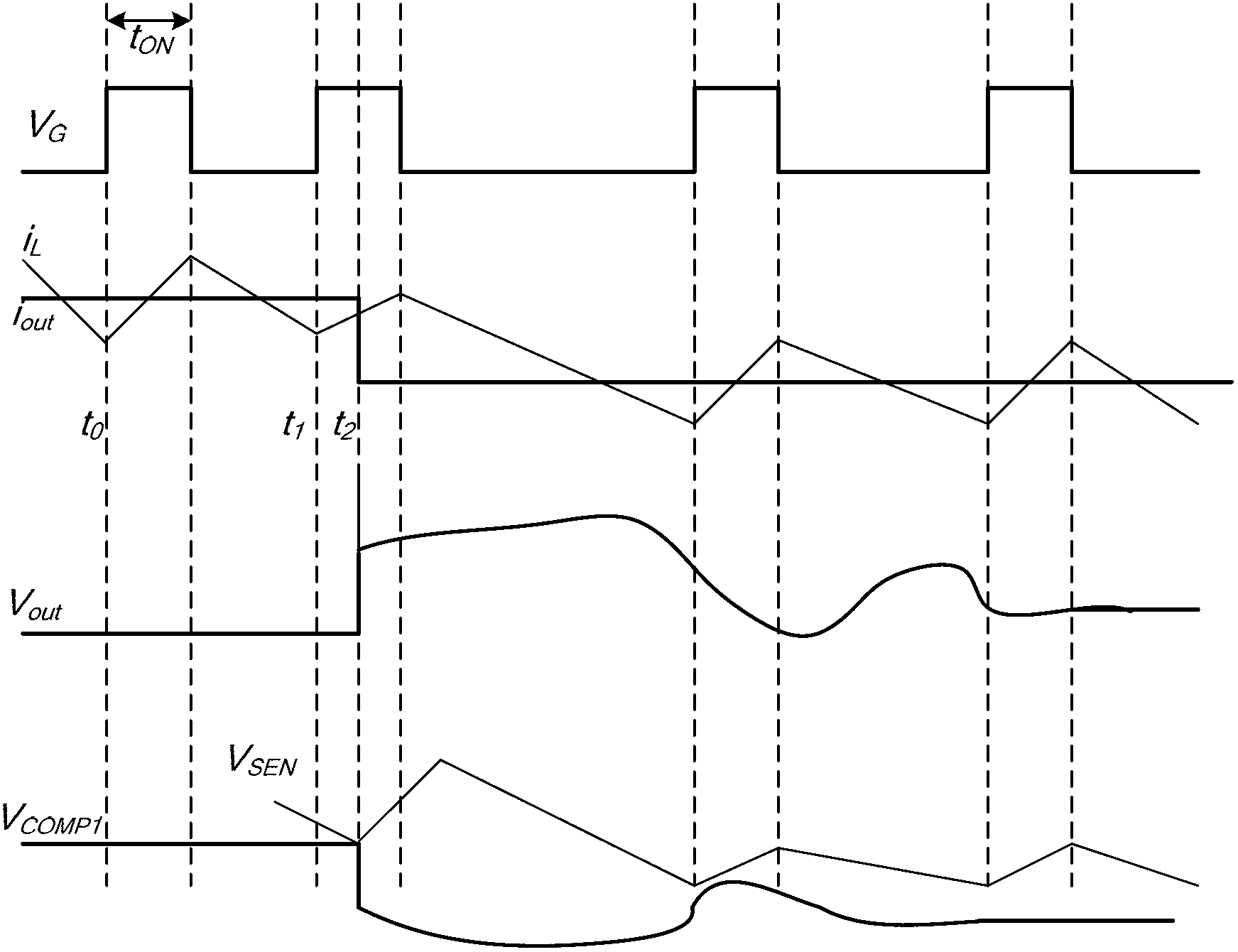
[0118] exist Figure 2A In the embodiment of the constant time control circuit shown, when the output current jumps from low to high, due to the limitation of the minimum off-time mini_off, the inductor current cannot continue to increase, which affects the transient state of the system to a certain extent Responsive performance. If the minimum off time can be shielded during the transient response, the transient response can be further accelerated. The following will combine Figure 4 The shown specific embodiment of the constant time control circuit according to the second embodiment of the present invention specifies its specific implementation.
[0119] exist Figure 2A On the basis of the illustrated embodiment, the constant time control circuit 400 adds a shielding circuit 404 to shield the minimum off time during the transient response, further reducing the transient response time and improving the transient response performance.
[0120] Specifically, the shielding...
Embodiment 3
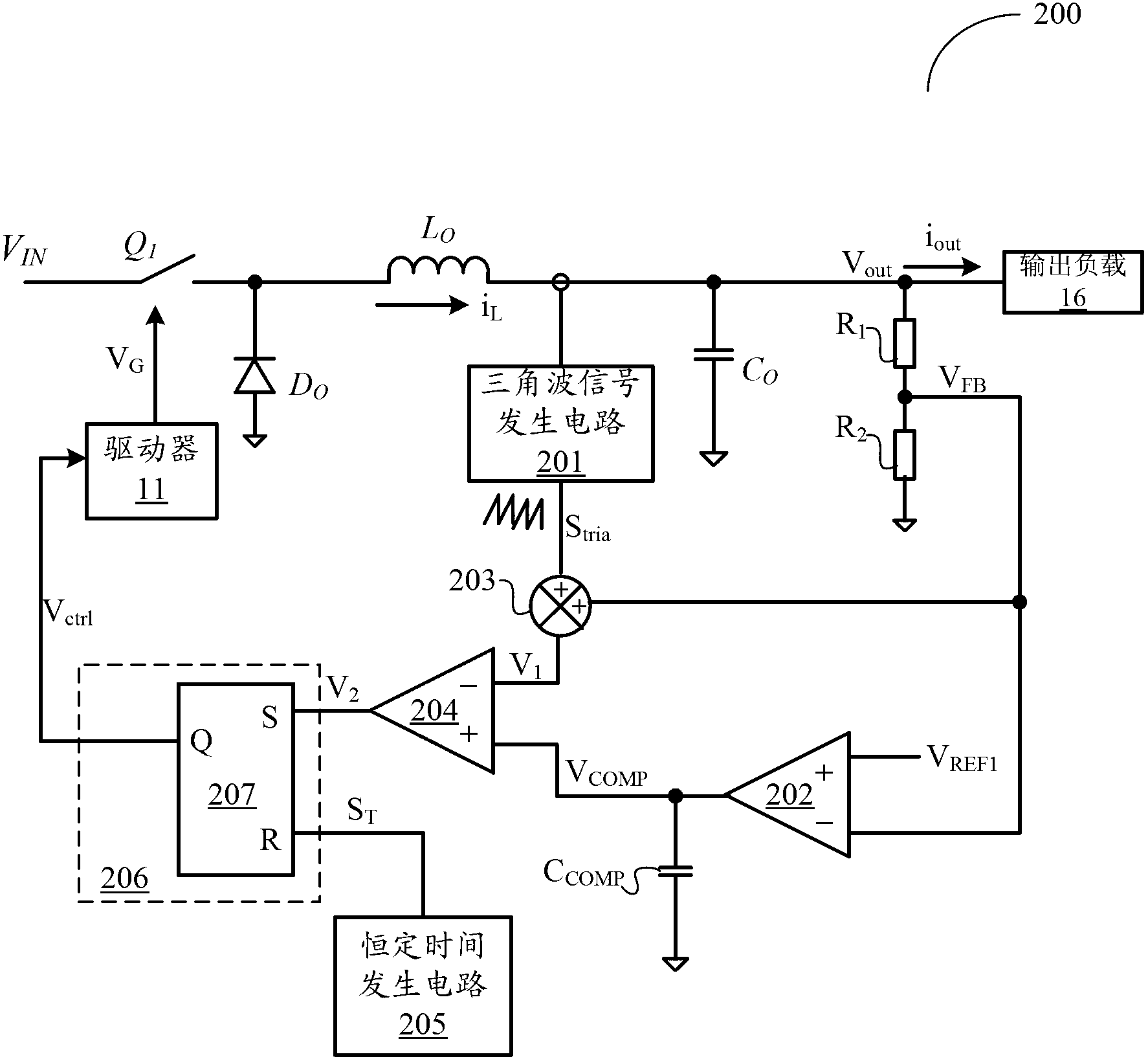
[0122] refer to Figure 5 , is a schematic block diagram of a constant-time control circuit according to a third embodiment of the present invention. In this embodiment, when the output current jumps, the constant time control circuit 500 directly prolongs the conduction time of the power switching device to complete the transient response as quickly as possible.
[0123] Specifically, in Figure 2A On the basis of the illustrated embodiment, the constant time control circuit 500 is added with a time extension circuit 505 . Specifically, the time extension circuit 505 includes a transient judging circuit 501 , an inverter 502 , an AND gate 503 and an OR gate 504 .
[0124] Transient judgment circuit 501 according to the voltage feedback signal V FB and the first reference voltage V REF1 The size relationship of the judgment of the occurrence of transient changes. It can be realized by different implementation methods, such as comparator and so on. When the output current...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com