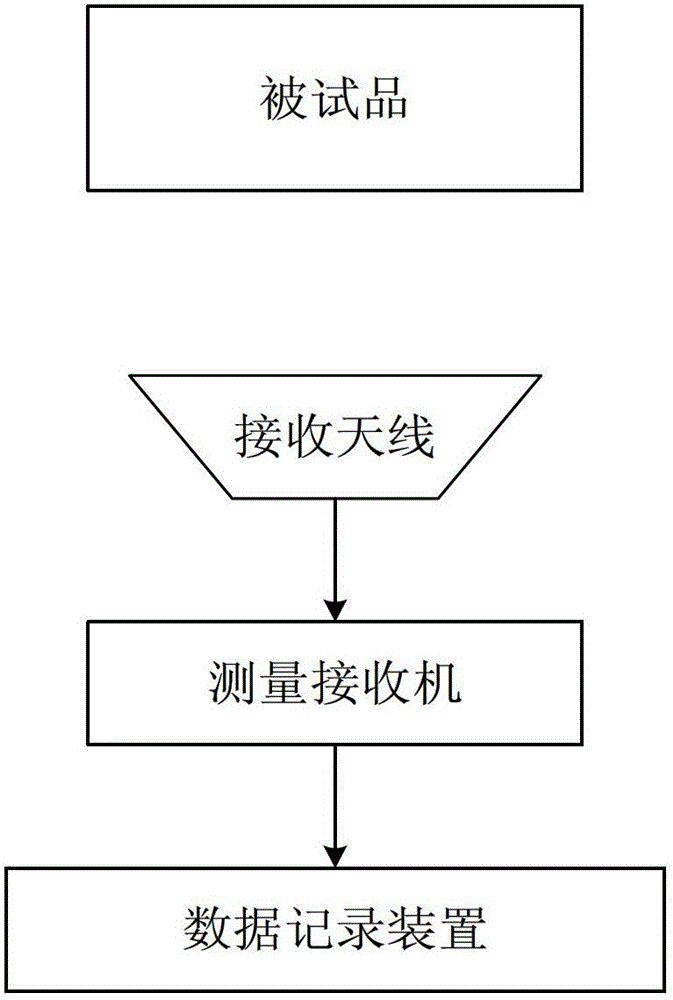
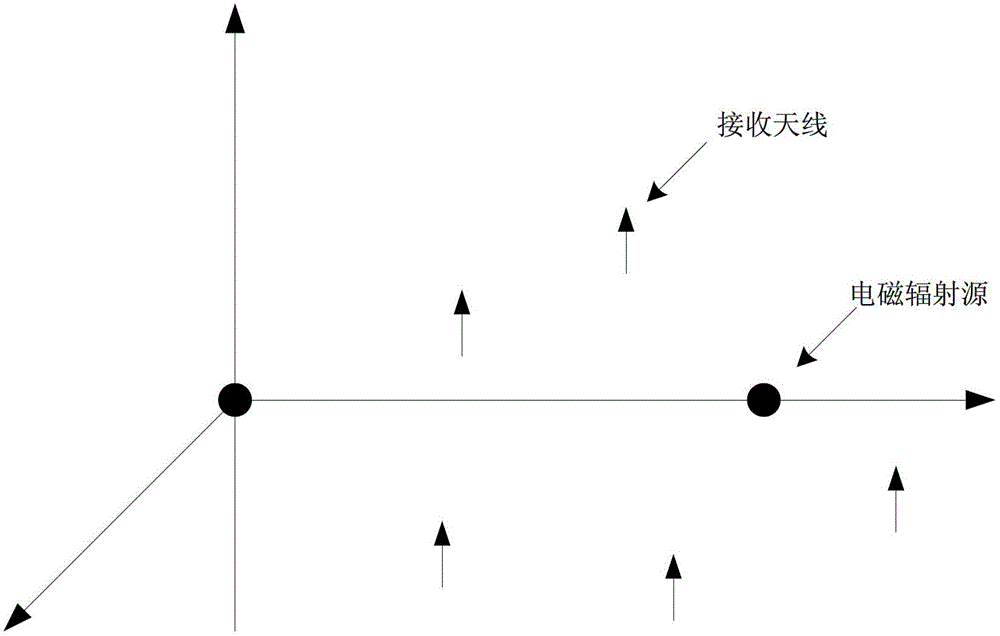
Method for improving radiating electromagnetic interference mixed signal blind source separation on basis of signal difference
A mixed-signal and electromagnetic interference technology, applied in the measurement of electricity, measuring electrical variables, measuring devices, etc., can solve the problem of low electromagnetic interference test accuracy, limited effect of blind source separation of electromagnetic interference mixed signals, and inability to collect electromagnetic interference mixed signals Time information and other issues to achieve the effect of improving separation speed and separation accuracy
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
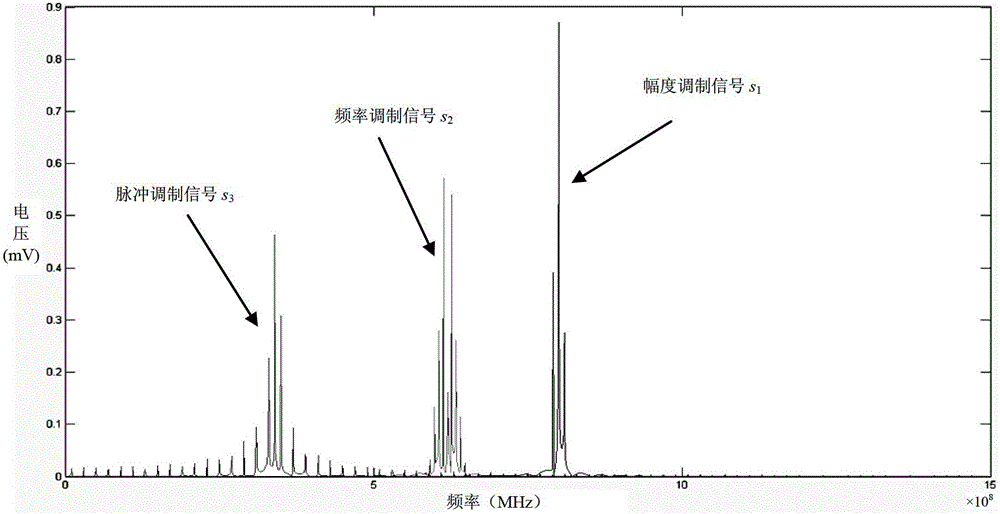
[0042] The method of the present invention is tested and verified with three radiated electromagnetic interference sources. Three sources of radiated EMI, one is an amplitude modulated signal s 1 , one is the frequency modulated signal s 2 , one is the pulse modulation signal s 3 . Among them, the amplitude modulation signal s 1 The fundamental carrier frequency is f 1 =800MHz, modulation frequency is f mod1 =9MHz, modulation depth is 80%; frequency modulation signal s 2 The fundamental carrier frequency is f 2 =620MHz, the modulation frequency is f mod2 =7MHz; pulse modulation signal s 3 The fundamental carrier frequency is f 3 =340MHz, the modulation frequency is f mod3 = 10MHz. The waveforms of the three signals are as follows figure 2 As shown, the mathematical expression is:
[0043] the s 1 =[1+0.8sin(2πf mod1 t)] sin(2πf 1 t)
[0044] f 1 =800MHz, f mod1 =9MHz;
[0045] the s 2 =cos[2πf 2 t+2cos(2πf mod2 t)]
[0046] f 2 =620MHz,f mod2 =7MHz; ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com