Daptomycin high-producing strain and preparation method thereof
A technology of daptomycin and streptomyces roseospora, which is applied in the field of high-yield daptomycin strains and its preparation, can solve the problems of complex synthesis process, high production cost, and low product yield, and achieve good application prospects, culture The effect of convenient and efficient production
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
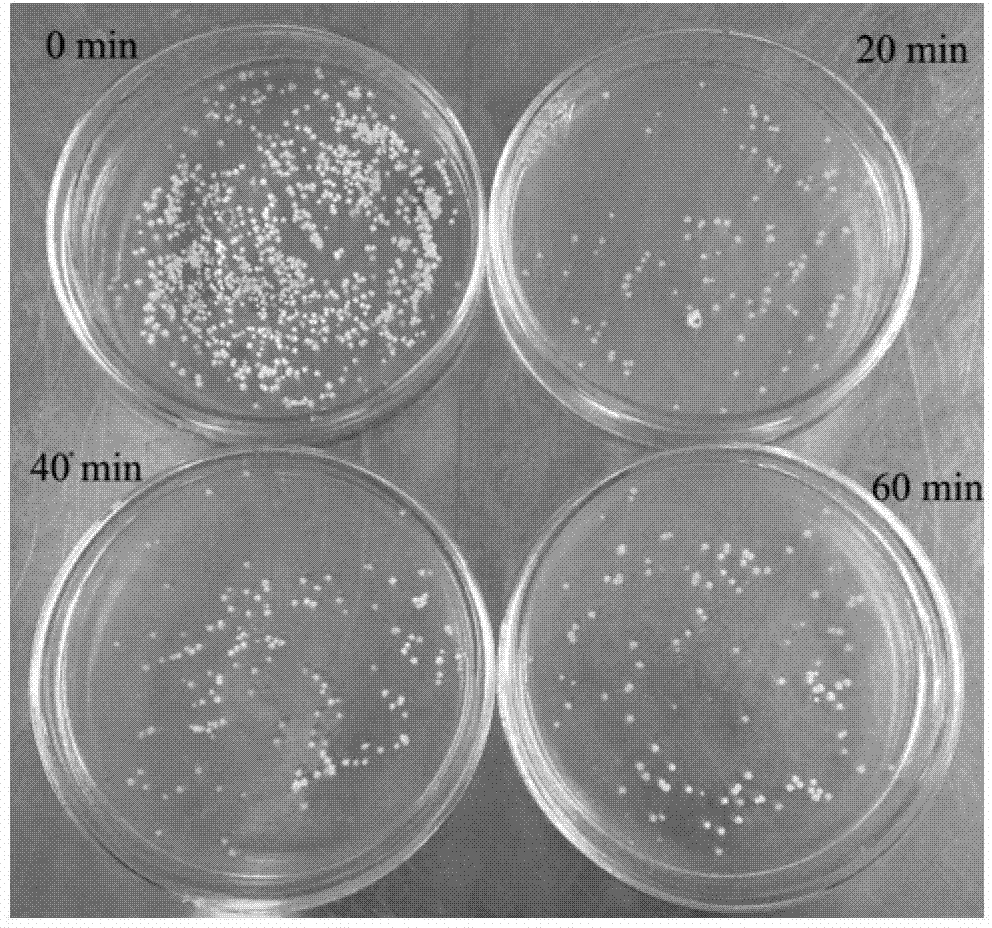
[0026] Example 1 Compound mutagenesis of Streptomyces roseosporus
[0027] 1. EMS mutagenesis
[0028] With Streptomyces roseosporus (Streptomyces roseosporus) NRRL 11379 as the starting strain, NRRL American Agricultural Research Service Culture Collection (Agricultural Research Service Culture Collection). Spores cultured on a slope for 14 days, washed with sterile physiological saline and added to an Erlenmeyer flask containing glass beads, treated at 30°C, shaking at 250 rpm for 2 hours, filtered with sterile gauze to obtain a spore suspension (1×10 6 / Ml). Add 1ml of spore suspension, 9ml of phosphate buffer and 0.1ml of ethyl methanesulfonate (EMS) solution into a 50ml Erlenmeyer flask to make the final concentration of EMS reach 1%, shake at a constant temperature of 30℃, and treat for a certain time (20-60min) ). Then take 0.5ml of the treatment solution, add 0.5ml of 5% sodium thiosulfate solution to wash twice to stop the reaction, and dilute to 2.5×10 3 After spores / ml...
Embodiment 2
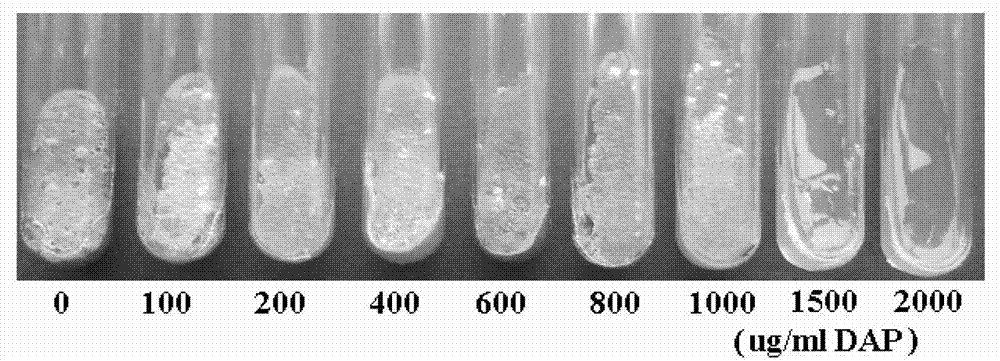
[0052] Example 2 Separation and purification of DAP
[0053] Collect the strain Streptomyces roseosporus SCU, fermented 270ml of bacteria liquid for 6-7d in the above example, at 4000rpm, centrifuged for 20min, and collect 250ml of supernatant. Extract twice with n-butanol, 100 ml each time, adjust the pH of the solution to 3.5-4.5, preferably 3.5 with 1 mol / L HCl, and rinse the n-butanol with 30 ml of double-distilled water to maintain the pH at 3.5-4.5, preferably 3.5. Add 100ml of double distilled water to adjust the pH to 6.5-7.3, preferably 7.3, add 1.0g of CaCl2 to the water phase and extract twice with n-butanol, each with 80ml. Collect the n-butanol extract, mix it with an equal volume of double distilled water, adjust the pH 3.5 with 1mol / L HCl, rinse once with 15 ml double distilled water, keep the pH 3.5 to remove Ca 2+ . Remove the water phase, mix the alcohol phase with 50ml of double distilled water, adjust the pH to 7.0 with 1mol / L NaOH, and A-21978C exists in the...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com